Anthropology Optional by Dr. Sudhir
- Category
Optional - Test Date
28-01-2022 07:00 AM - Evaluated
Yes

To participate in answer writing program, Register yourself for the test. Copies will be evaluated only for the registered students. Registration will be closed after the scheduled date.
48 Hrs. Answer Writing, Copy Evaluation and Marks Improvement Cycle
- Step 1 (Answer Writing): Questions will be uploaded on the portal on the scheduled date at 7:00 AM. You have to write your answers on an A4 size sheet leaving margins on both sides based on the UPSC pattern. Mention your name on the 1st page and page number on each page. After writing the answer, Click pictures of each page of the answer sheet and upload them altogether (in JPG/JPEG/PNG format) in the comment section of the same question. Answers should be uploaded before 7:00 PM on the same day.
- Step 2 In Next 48 Hrs (Copy Evaluation & Discussion): After evaluation, the first 50 copies will be uploaded on the same comment box and will be sent to you. In the evening 8:00 PM marks improvement sessions for the test with respective faculty in a group will be conducted online. So that students can get a wider perspective of the topics. Here you can discuss your evaluated copies also with the faculty.
Instruction:
- Attempt One question out of the given two.
- The test carries 15 marks.
- Write Your answer in 150 words.
- Any page left blank in the answer-book must be crossed out clearly.
- After Writing the Essay upload your copy in JPEG format in the comment box.
- Evaluated Copy will be re-uploaded on the same thread after 2 days of uploading the copy.
- Discussion of the question and one to one answer improvement session of evaluated copies will be conducted through Google Meet with concerned faculty. You will be informed via mail or SMS for the discussion.
Question #1. Explain the structural analysis of kinship as proposed by Levi’s Strauss.
(Examiner will pay special attention to the candidate's grasp of his/her material, its relevance to the subject chosen, and to his/ her ability to think constructively and to present his/her ideas concisely, logically and effectively).
Model Answer
Question #1. Explain the structural analysis of kinship as proposed by Levi’s Strauss.
Claude Lévi-Strauss was a French anthropologist and ethnologist whose work was key in the development of the theories of structuralism and structural anthropology.
Structuralism is a theory, a methodology that works to uncover the structures that underlie all the things that humans do, think, perceive, and feel.
Structuralists believe that the human mind is patterned in binary.
Nature : Culture
Animal : Human
Me : Others
Incest : Incest taboo
The transition of nature (animal) to Culture (human) involve exchange and cooperation, which led to formation of first social category- Kinship.
Structuralism and Kinship:
Levi Strauss applied a structural approach to explain Kinship (Kinship is a universally existent social institution found in varying forms in different societies).
Kinship, according to Strauss kinship is surface manifestation of human mind, which is patterned in binary.
Based on this idea of Structuralism, Levi Strauss developed Alliance theory to explain Kinship, which was a reaction against the descent theories developed by British Anthropologists-Brown, Fortes etc.
Alliance theory:
The aforementioned alliance theory is referred to as the structural analysis of kinship or the generalized theory of exchange. It is more of an idealistic approach which is in contrast with the objective approach of descent theorists.
Reaction Against: Descent Theorists
Influenced by: Linguistics, Mercel Mauss, Philosophical Idealism
Premise:
- For analysis of kinship, Strauss found answers in the deep unconscious mental structures patterned on binary oppositions of wevs others.
- As per Strauss, the thought of survival is innate to humans for which they seek cooperation. Alliances formed by marriages is one of the means to secure cooperation.
Explanation of the theory:
- Profoundly influenced by the work of Marcel Mauss on the central role of reciprocal gift giving in “primitive” societies, Lévi-Strauss held that the transition from the animal world of “nature” to the human one of “culture” was accomplished through the medium of exchange: it was in the act of giving that the category of the self in opposition to another, or of one’s own group to another group, was actually constituted. Thus, the first social categories originated not in the realm of ideas but through the exchange of gifts.
- Strauss defined society as a total system of solitary Kinship groups linked to one another by marriage.
- His theory of Kinship subsumed the blood ties and gave more importance to marriage alliances.
- He also held that affinal relations framed the most basic and irreducible unit of kinship—what he called the “atom of kinship.”
- Where descent theorists defined a set of parents and children as the core of kinship relations, Lévi-Strauss defined it as a husband and wife, their son, and the wife’s brother.
- Kinship is based on positive prescriptive marriage rules, which prescribe whom to marry and regulates regular exchange of women between groups.
- This reciprocal exchange of women give rise to the elementary structures of Kinship.
- He classified kinship systems in two types: Elementary form and Complex form.
- Elementary form is the characteristic of simple society, whereas complex form is the characteristic of modern society.
- Elementary form can be formed either due to direct exchange, which is symmetrical in nature, or indirect/ delayed exchange, which gives rise to asymmetrical structures.
Significance:
This theory gave a normative explanation of the social phenomena found in deep structural patterns, not observable easily.
Critique:
- By supporters of Descent theorists
- By Feminist Anthropologists
- By Followers of Strauss like Dumont and Needham.
|
Chromosomal Aberration or Chromosomal abnormalities occur when there is a defect in the number of chromosomes in a cell of an organism or in the arrangement of genetic material (Genes) on the chromosome. Chromosomal abnormalities give rise to specific physical symptoms, however, the severity of these depends on the type of aberration.
Basis of aberrations:
Normally, a human cell has 23 pairs of chromosomes, making 46 in total. Any abnormality in the structure of chromosomes or in the number of chromosomes leads to the chromosomal aberration.
Types:
There are two main types of chromosomal Aberration that can occur during meiosis and fertilization.
- Numerical Aberrations
- Structural aberrations
A- Numerical Aberrations
Numerical aberrations are generally caused by a failure in chromosome division during meiosis that results in gametic cells with an extra chromosome or a deficiency in the number of chromosomes. Variation in chromosome number involves
1) addition or loss of one or more chromosomes (Aneuploidy)
2) addition or loss of one or more haploid sets of chromosomes (Euploidy)
Examples:
- Monosomy: The loss of one chromosome produces a monosomic (2n-1) and the condition is known as monosomy. Its example is Turner syndrome (2n-1 = 45 chromosomes in humans)
- Trisomy: The gain of one extra chromosome produces trisomic (2n+1) and the condition is called trisomy. Example are
- Down syndrome (2n+1= 47 chromosomes in humans).
- Trisomy 18 (Edwards syndrome) have an additional copy of chromosome 18
- Trisomy 13 (Patau syndrome) have an additional copy of chromosome 13
- Trisomy 8 (Warkany syndrome 2) have an additional copy of chromosome 8
Structural aberrations
These occur due to a loss of genetic material, or a reorganization in the location of the genetic material.
They include deletions, duplications, inversions, ring formations, and translocations.
Unbalanced rearrangements include deletions, duplications, or insertions of a chromosomal segment.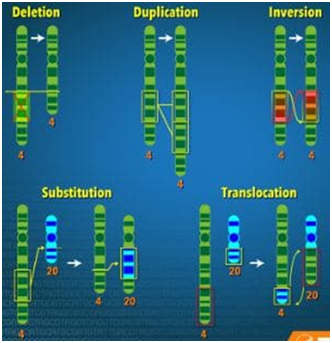
Example:
- Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 1A, which can be caused by duplication of the gene encoding peripheral myelin protein 22 (PMP22) on chromosome 17.
- Chromosomal translocations are typically seen in cases of leukemia, like, for instance, in acute myeloid leukemia.
- Robertsonian translocations between chromosomes 13 and 14 (when transmitted in unbalanced for may lead to Trisomy 13) lead to the trisomy 13 (Patau) syndrome.
Illustration on the impact on mind and body:
Trisomy 21 (Down’s syndrome) is termed mongoloid idiocy or mongolism
It is characterized by:
- Growth failure
- Small and arched palate.
- Short neck
- Big wrinkled tongue.
- Mental retardation.
- Dental Anomalies.
- Flat back of head.
- Congenital heart diseases
- Cognitive impairment.
- Intestinal blockage.
- Shortened life span.
- Umbilical Hernia.
- Hearing loss
- Abnormal pelvis.
- Spots in eyes
- Diminished muscle tone.
- Leukemia
- Broad flat face
- Thyroid problems
- Slanting eyes.
- Poor IQ.
- Short nose.
- Strabismus (crossed eyes)
Similarly, Cri-du-chat syndrome which is a structural chromosomal aberration is characterized by:
- distinctive, high-pitched, catlike cry in infancy with growth failure, microcephaly, facial abnormalities, and mental retardation throughout life.
- Some common clinical manifestations are:
- Cry that is high-pitched and sounds like a cat
- Downward slant to the eyes
- Low birth weight and slow growth
- Low-set or abnormally shaped ears
- Mental retardation (intellectual disability)
- Partial webbing or fusing of fingers or toes
- Slow or incomplete development of motor skills
- Small head (microcephaly)
- Small jaw (micrognathia)
- Wide-set eyes
General Diagnosis:
- Based on maternal age
- Clinical examination.
-
- Amniocentesis
- Chorionic villus sampling
- Umbilical cord
- Karyotyping
Although treatment is mostly not available in many cases of chromosomal aberrations, prevention is considered as the most viable way. It involves preventing late age pregnancies, abortion in severe cases of malformations.
Genetic counseling is an important aspect while going for:
- family planning to prevent transfer of faulty genes from parents to children
- Gene products like gene therapy
- Advise on abortions
- Recommendations on Cognitive behavioral therapy
Procedure of Answer Writing:
To participate in the answer writing program, Register yourself for the test. Copies will be evaluated only for the registered students. Registration will be closed after the scheduled date.
Answer Writing, Copy Evaluation, and Marks Improvement Cycle:
Step 1 (Theme, Details & Its Topics):
- Every round of Answer writing initiative will be around a theme related to the Subject/Topic.
- Please read the theme and its description, and try to cover the topics given within the theme before writing the answer along with the sources.
Step 2 (Answer Writing):
- Questions will be uploaded on the portal on the scheduled date at 7:00 AM.
- You have to write your answers on an A4 size sheet leaving margins on both sides based on the UPSC pattern.
- Mention your name, email id, location, and phone number on the 1st page in the top right corner and the page number on each page.
- After writing the answers, Click pictures of each page of your answer sheet, merge them all in a single PDF and upload them in the upload section of the same question.
- Kindly submit your written answers before 7:00 PM. Only the first 100 copies will be considered for evaluation. No request for late submission or evaluation will be entertained once the 100 mark is reached.
Note: Answer sheets without the proper guidelines given above will not be accepted for evaluation.
Step 3 (Copy Evaluation): Copies will be evaluated in the next 72 hours of the test date. After evaluation, copies will be uploaded into your account. During the copy evaluation period, doubt clearing and discussion about the theme or topic of the test with respective mentors of the test will be done in the telegram group.
Step 4 (Mentorship): Evaluated copies will be sent to you via mail and also uploaded into your account on the website. After that a mentorship session for the marks improvement with respective faculty will be conducted on the Google Meet, so that students can get a wider perspective of the topics. Here you can discuss your evaluated copies also with the faculty. Top 5 copies of every test will be shared in the telegram group for reference.
Note: Aspirants who have not written the test can also participate in the mentorship session.
For Updates and Mentorship of the session, you will be notified through SMS or Telegram Group.
Note: You have to write your answers on an A4 size sheet leaving margins on both sides based on UPSC pattern. Mention Your Name on 1st page and Page Number on each page. After writing the answer, Click pictures of each page of your answer sheet, merge them all in a single PDF and upload in the Your Answer Copy section of the same question.





