Bill to set up carbon markets passed in LS
Context
The Energy Conservation (Amendment) Bill, 2022 passed in Lok Sabha that will bring the establishment of carbon credit markets and also bring large residential buildings under the energy conservation regime.
Analysis
- The Bill seeks to amend the Energy Conservation Act, 2001.
- The Act promotes energy efficiency and conservation.
- It provides for the regulation of energy consumption by equipment, appliances, buildings, and industries.
|
Key features of the Energy Conservation (Amendment) Bill:
Obligation to use non-fossil sources of energy:
- The central government will decide the energy consumption standards.
- The government may require the designated consumers to meet a minimum share of energy consumption from non-fossil sources.
- Different consumption thresholds may be specified for different non-fossil sources and consumer categories.
- Designated consumers include:
- Industries such as mining, steel, cement, textile, chemicals, and petrochemicals.
- transport sector including Railways
- Commercial buildings
-
Penalties under the Act:
- Failure to meet the obligation for use of energy from non-fossil sources will be punishable with a penalty of up to Rs 10 lakh.
- It will also attract an additional penalty of up to twice the price of oil equivalent of energy consumed above the prescribed norm.
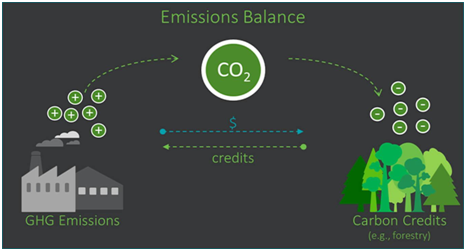
Carbon Trading:
- The Bill empowers the central government to specify a carbon credit trading scheme.
- Carbon credit implies a tradeable permit to produce a specified amount of carbon emissions.
- The central government or any authorised agency may issue carbon credit certificates to entities registered under and compliant with the scheme.
- The entities will be entitled to purchase or sell the certificate.
- Any other person may also purchase a carbon credit certificate on a voluntary basis.
Energy conservation code for buildings:
- The central government will decide on energy conservation code for buildings.
- The code prescribes energy consumption standards in terms of area.
- The Bill amends this to provide for an ‘energy conservation and sustainable building code’.
- This new code will provide norms for energy efficiency and conservation, use of renewable energy, and other requirements for green buildings.
Applicability to residential buildings:
- Under the Energy Conservation (Amendment) Act, the energy conservation code applies to commercial buildings:
- Erected after the notification of the code
- Having a minimum connected load of 100 kilowatts (kW) or contract load of 120 kilo-volt ampere (kVA).
- It will also apply to the office and residential buildings.
- The Bill also empowers the state governments to lower the load thresholds.
Standards for vehicles and vessels:
- The energy consumption standards may be specified for equipment and appliances which consume, generate, transmit, or supply energy.
- The Bill expands the scope to include vehicles (as defined under the Motor Vehicles Act, 1988), and vessels (includes ships and boats).
Penalties under the Act:
- The failure to comply with standards will be punishable with a penalty of up to Rs 10 lakh.
- Non-compliance in case of vessels will attract an additional penalty of up to twice the price of oil equivalent of energy consumed above the prescribed norm.
- Vehicle manufacturers in violation of fuel consumption norms will be liable to pay a penalty of up to Rs 50,000 per unit of vehicles sold.
Regulatory powers of SERCs:
- State Electricity Regulatory Commissions (SERCs) will adjudge penalties under the Energy Conservation (Amendment) Act.
- SERCs may also make regulations for discharging their functions.
|
Composition of the governing council of BEE:
|
Objective of the Energy Conservation (Amendment) Act:
- To reduce India’s power consumption via fossil fuels and minimize the nation’s carbon footprint.
- To develop India’s Carbon market and boost the adoption of clean technology.
- To meet its Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs), as mentioned in the Paris Climate Agreement, before its 2030 target date.
Measures to reduce India’s Carbon Footprints:
- Domestic Solar Manufacturing: In Budget 2022-23, the government allocated Rs 19,500 crores to facilitate domestic solar manufacturing in India.
- Biomass Co-firing: Use of 5-7 % biomass pellets for co-firing in thermal power plants.
- Blending of Fuel: To promote the blending of fuel, an additional differential excise duty of Rs 2/litre is to be levied on unblended fuel.
- Battery Swapping Policy: To achieve clean transport, a new battery swapping policy is to be formulated for electric vehicles
- Green Bonds: Issue Green Bonds - fixed-income financial methods to fund projects with positive environmental effects - to raise capital for green infrastructure. Such sovereign green bonds can be used in climate adaptation projects which lack private funding.
Conclusion
Energy conservation helps to reduce the carbon footprint in the universe. It will regulate the use of non-fossil sources, including biomass and ethanol, for energy and feedstock, along with the use of green hydrogen and green ammonia.





