Green Investments and Sustainability
Context
As the world aims to bring the Greenhouse gas emissionsto sustainable levels by 2050 to prevent irreversible damage to the environment, the Companies have to work for Environment, Social and Governance (ESG) factors for making its impacts more sustainable in all aspects.
About
What are ESG Goals?
- Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) goals are a set of standards for a company’s operationsthat force companies to follow better governance, ethical practices, environment-friendly measures and social responsibility. These includes:
|
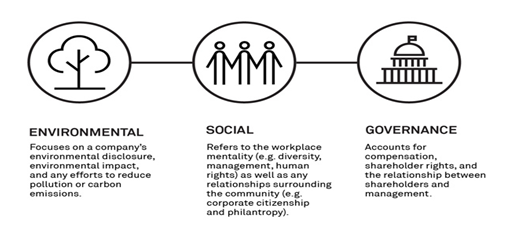
Environmental |
Social |
Governance |
|
Environmental is all about an enterprise focus and action leadership around energy usage, waste management, and natural resources conservation. |
Social deals with an enterprise relationship and reputation with its employees, customers, stakeholders, institutions and the larger community. |
Governance is all about how an enterprise manages with the proper management structure, executive compensation and ensuring stakeholder rights, especially employees, shareholders and customers. |
- It focuses on non-financial factorsas a metric for guiding investment decisions wherein increased financial returns is no longer the sole objective of investors.
- Ever since the introduction of the United Nations Principles for Responsible Investing (UNPRI)in 2006, the ESG framework has been recognised as an inextricable link of modern day businesses.
|
Europe has been a pioneer in ESG norms with some countries initiating ESG investment mandates. |
India and ESG norms:
- ESG as a concept is not new to India.
- SEBI requires top 1,000 listed companies to issue Business Responsibility and Sustainability Report that includes ESG concepts in its disclosures.
- India also has a green bond market, proceeds of which are used to fund renewable energy projects.
What Initiatives have been taken to Ensure ESG Compliance?
- National Voluntary Guidelines: One of the initial milestones towards identifying ESG disclosure requirements for companies was the release of the National Voluntary Guidelines on Social, Environmental and Economic Responsibilities of Business (NVGs) in 2011 by the Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA).
- Business Responsibility Reports: In 2012, the SEBI formulated the Business Responsibility Reports (BRR) which mandated top 100 listed entities (which was extended to top 500 listed entities in 2015) by market capitalization to file BRR as part of their annual report.
- Business Responsibility and Sustainability Report: In 2021, SEBI replaced the existing BRR reporting requirement with a more comprehensive integrated mechanism, the Business Responsibility and Sustainability Report (BRSR).
- It will be mandatorily applicable to the top 1,000 listed entities (by market capitalization) from FY 2022-23 onwards.
- The BRSR seeks disclosures from listed entities on their performance against the nine principles of the ‘National Guidelines on Responsible Business Conduct’ (NGBRCs).
Persistent Challenges:
- Lack of standardisation of reporting requirements across borders pose difficulties in harmonising ESG principles, frameworks and considerations.
- Lack of transparency, consistency, and materiality of ESG standards pose roadblocks in the seamless implementation of ESG reporting framework ahead.
- Requirement of high capital costs and/or lack of expertise in implementing ESG measures.





