11th April 2024
- Published
11 April 2024 -
 Download PDF
Download PDF
Resurgence of Minilateral Groupings against China
Context
China’s assertive foreign policy has spurred the formation of several minilateral groupings in recent years. The resurgence of the Quad, comprising Australia, India, Japan, and the US, in 2017-2018 and the establishment of AUKUS—Australia, UK, and the US—in 2021 were largely driven by concerns over Beijing’s aggressive and coercive policies. Now, a novel trilateral partnership between the US, Japan, and the Philippines is currently in progress.
1: Dimension- Reasons for Resurgence of Minilateral Groupings:
- China's Assertive Foreign Policy: Beijing's aggressive and coercive policies, particularly in the South China Sea and beyond, have alarmed countries in the Indo-Pacific region and spurred them to form minilateral alliances as a response.
- Concerns over Regional Stability: China with its activity, has raised concerns among neighboring countries about regional stability and security.
- Need for Collective Security: Recognizing the limitations of bilateral engagements, countries have turned to minilateral groupings to strengthen collective security and deterrence against China's hegemonic ambitions.
2: Dimension- Implications of Minilateral Groupings:
- Enhanced Security Cooperation: Minilateral alliances like the Quad and the trilateral partnership between the US, Japan, and the Philippines facilitate enhanced security cooperation, intelligence sharing, and joint military exercises to counter China's influence.
- Balancing China's Power: By forming alliances, countries aim to balance China's growing power and influence in the region, preventing any single country from dominating the Indo-Pacific and ensuring a rules-based order.
- Geopolitical Realignment: The resurgence of minilateral groupings signifies a geopolitical realignment in the Indo-Pacific, with countries aligning themselves strategically to safeguard their interests.
- Diplomatic Pressure on China: It puts diplomatic pressure on China and signals a united front against its aggressive policies, thereby influencing Beijing's behavior and promoting stability in the region.
- Economic Cooperation: Such groupings also promote economic collaboration among member countries, fostering trade, investment, and development initiatives.
|
Fact Box About Minilaterals
Asia’s minilaterals Examples
|
India posts defence attaché to expand strategic presence
Context
For the first time, India will post defence attaches in several countries including Ethiopia, Mozambique, Ivory Coast, Philippines, Armenia and Poland in line with its broader policy initiative to expand strategic ties with key regions, a move that comes amid renewed geopolitical rivalries.
Key-highlights
- After a gap of several decades, India will also post a defence attaché in Ethiopia.
- A new military attaché is also being posted to Djibouti and will be only the second officer to hold the post.
- Djibouti serves as a major maritime gateway around the Red Seaand Gulf of Aden, and is considered as a prized location for military bases.
- New Delhi is also planning to rationalise the strength of its teams of military officials in its embassy in Moscow and high commission in London.
- Last year, the European Union (EU) posted a military attache to its mission in India for the first time.
- A total of 16 defence attaches from the Indian Army, the Navy and the Indian Air Force will shortly assume their new position.
1: Dimension- Objective of the move
- The decision to appoint defence attaches in African countries is in sync with New Delhi's priority to expand its strategic engagement with the African continent.
- In the last few years, India has been positioning itself as a leading voice, flagging concerns, challenges and aspirations of the Global South or the developing nations, especially the African continent.
- India-Africa: India's ties with the African continent have witnessed a major uptick amid China's persistent efforts to expand its influence in the African countries.
- The induction of the 55-nation African Union as a permanent member of the G20 was seen as major milestones of India's presidency of G20.
- India- Philippines: India is also looking at further expanding defence ties with the Philippines against the backdrop of growing global concerns over China's increasing military assertiveness in the South China Sea.
- The defence and strategic ties between India and the Philippines have been on an upswing in the last few years.
- In January 2022, India sealed a USD 375 million deal with the Philippines for supplying three batteries of the missile.
2: Dimension- Role of Defence attachés
- Defence attachés play a crucial role in several spheres.
- In friendly nations such as Russia and the US, they are closely involved in efforts to acquire new weapons systems and military hardware and also help shape military-to-military cooperation in areas such as joint exercises and training.
- In adversarial nations such as China and Pakistan, they are involved in gathering information and keeping a close eye on the latest developments in military and security issues.
|
Fact Box: Defence Attaché
|
India's Struggle with Agricultural Labor Dependency
Context
The recent report highlighting India's comparatively lower rate of transitioning its working-age population away from farm-related work compared to its neighboring countries has brought renewed attention to the longstanding issue of agricultural labor dependency in the country.
Key-highlights of the Report (the shift)
- Report by: World Bank’s April South Asia Development Update report.
- Time Period: 2000 to 2023
- Crux: India has managed to move a smaller share of its working-age population away from farm-related work than many of its neighbours.
- Bangladesh, Bhutan, Sri Lanka and Nepal managed to shift a bigger share of jobs to non-agricultural work than India.
- Only Pakistan and the Maldives show a lower shift among South Asian peers.
- The share of working-age Indians who are employed in agri-based jobs has come down over the years. This employment ratio for India was 63.9 per cent in 2000. It declined to 58.9 per cent by 2010; and further to 53.8 per cent in 2019.
- Since 2000, South Asian countries witnessed rising productivity but only marginally rising, or even declining, employment ratios.
- Employment ratios fell in Bhutan, India, Maldives, and Nepal, while in Bangladesh, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka.
- Men’s employment ratio in India declined by 9.6 percentage points. Most South Asian countries recorded a decline.
- Women’s employment ratio in India increased by 1.4 percentage points. It was the highest for Bangladesh at 11.6 percentage points. The increased participation of women could be driven by rising self-employment among them driven by economic distress.
1: Dimension- Why the findings are concerning?
- Growth challenges: The slower transition of India's working-age population from agriculture poses challenges for sustainable economic growth and inclusive development.
- Distress: Both self-employment and agriculture constitute fallback options for workers who have lost work and cannot afford to remain unemployed.
- Reduced earnings: More women serving the same market translated into increased competition and lower earnings.
- Poor quality of jobs: Indian agricultural labourers mostly moved to other low-paying and informal jobs such as petty retailing, small eateries, domestic help, sanitation, security staffing, and transport.
- Low-paid employment: The labour transfer is happening within the low-productivity informal economy. The jobs that are getting generated outside agriculture are mostly in low-paid services and construction.
2: Dimension- Required measures
- Investment: India aims to reduce agriculture's 'self-exploitation' through non-farm jobs. This requires addressing problems with job laws, promoting direct benefit transfer, improving infrastructure and human capital, and reforming social security and labor codes.
- Creating opportunities in non-agricultural sectors to uplift rural populations from the cycle of self-exploitation in agriculture.
- Skill development of this workforce that is moving away from farms into other sectors is essential.
- Gender disparities in employment trends underscore the need for targeted interventions to empower women in the workforce and unlock their potential contribution to India's economy.
|
Fact Box Workforce Distribution
Government Initiatives to Shift Farmers to Non-Agricultural Jobs
|
|
UPSC PYQ Q1: “Economic growth in the recent past has been led by increase in labour productivity.” Explain this statement. Suggest the growth pattern that will lead to creation of more jobs without compromising labour productivity. (UPSC 2022) Q2: Normally countries shift from agriculture to industry and then later to services, but India shifted directly from agriculture to services. What are the reasons for the huge growth of services vis-a-vis industry in the country? Can India become a developed country without a strong industrial base? (UPSC 2014) |
Unified standard of time for the moon
Context
NASA has been directed to establish a unified standard of time for the moon (Coordinated Lunar Time (LTC)) and other celestial bodies, the same way as Earth has.
What is a time standard?
- A time standard is a specification for measuring time intervals, defining the units of time (e.g., seconds, minutes, hours) and providing a reference for timekeeping.
- Time standards are not similar to time zones, as a time zone is a region of the Earth that has the same standard time.
- Need of time standard: The need for establishing a time standard for the Moon is paramount as several countries plan to send astronauts to the lunar surface in the latter half of the 2020s.
- The Moon requires a time standard due to factors such as differing gravitational forces and other celestial influences, which alter the time compared to Earth.
- Time on the Moon moves a tad quicker — 7 microseconds every day — compared to the Earth.
|
Working of Earth’s Time Standard
|
QS World University Rankings
Context
Quacquarelli Symonds (QS) World University Rankings by Subject has been released recently.
Key-highlights of the Rankings
- Indian Institute of Management (IIM) Ahmedabad has been ranked among the top 25 institutions globally for business and management studies.
- IIM-Bangalore and IIM-Calcutta have been ranked among the top 50.
- Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Guwahati has secured a global ranking of 51-70 in data science, and 51-100 in petroleum engineering.
- Jawaharlal Nehru University (JNU) in Delhi is the highest-ranked university in India. JNU is in the 20th position globally for development studies.
- Expanding research: India stands as one of the world’s most rapidly expanding research centres. From 2017 to 2022, its research output surged by an impressive 54 per cent.
- In terms of volume, India is now the world's fourth-largest producer of research, generating 1.3 million academic papers in this period, trailing only behind China's 4.5 million, the United States' 4.4 million, and slightly less than the United Kingdom's 1.4 million.
- Challenge for India: Providing high-quality tertiary education in the face of exploding demand. Though this challenge was recognised by 2020's NEP (National Education Policy), which set the ambitious target of a 50 per cent gross enrolment ratio by 2035.
|
Fact Box: QS World University Rankings
|
Higgs Boson
Context
Nobel prize-winning physicist Peter Higgs, who proposed the existence of the so-called "God particle" that helped explain how matter formed after the Big Bang, has died at age 94.
Higgs' theory
- The Higgs boson is the fundamental force-carrying particle of the Higgs field, which is responsible for granting other particles their mass. This field was first proposed by Peter Higgs in 1964?.
- The particle was finally discoveredon July 4, 2012, by researchers at the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) — the most powerful particle accelerator in the world.
- Higgs' theory related to how subatomic particles that are the building blocks of matter get their mass.
- The LHC confirmed the existence of the Higgs field and the mechanism that gives rise to mass.
- This theoretical understanding is a central part of the so-called Standard Model, which describes the physics of how the world is constructed.
- Higgs won the 2013 Nobel Prize in Physics for his work, alongside Francois Englert of Belgium, who independently came up with the same theory.
- Higgs' work helps solve one of the most fundamental riddles of the universe: how the Big Bang created something out of nothing 13.7 billion years ago.
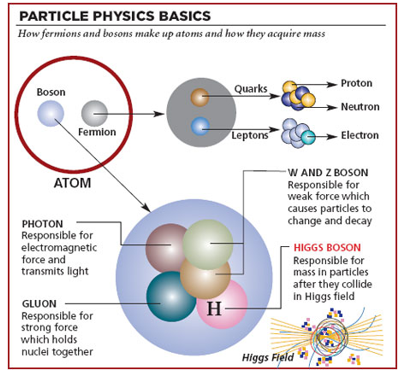
What is Higgs Boson?
- The Higgs boson has a mass of125 billion electron volts (130 times more massive than a proton).
- It is also chargeless with zero spin?-?a quantum mechanical equivalent to angular momentum. The Higgs Boson is the only elementary particle with no spin.
- The Higgs boson is popularly known as the "the God Particle".
- A boson is a "force carrier" particle that comes into play when particles interact with each other, with a boson exchanged during this interaction.
- For example, when two electrons interact they exchange a photon-the force-carrying particle of electromagnetic fields.
- Because quantum field theory describes the microscopic world and the quantum fields that fill the universewith wave mechanics, a boson can also be described as a wave in a field.
- So a photon is a particle and a wave that arises from an excited electromagnetic field and the Higgs boson is the particle or "quantized manifestation" that arises from the Higgs field when excited. That field generates mass via its interaction with other particles and the mechanism carried by the Higgs boson called the Brout-Englert-Higgs mechanism.
|
Fact Box: Large Hadron Collider (LHC)
|
Preservation of Baobabs
Context
In a groundbreaking conservation endeavour, the Global Society for the Preservation of Baobabs and Mangroves (GSPBM) has initiated a mission to rejuvenate the iconic baobab trees through seedling transplantation.
About
- Baobab tree (Adansonia digitata) is native to the African savannah where the climate is extremely dry and arid.
- Ecologically, baobabs are keystone species in Madagascar's unique landscapes.
- Their massive trunks and extensive root systems are vital for storing water in arid environments, providing a critical resource for both the trees and the surrounding ecosystem during drought periods.
- It is a succulent, which means that during the rainy season it absorbs and stores water.
- Baobab trees grow in 32 African countries. They can live for up to 5,000 years, reach up to 30 metres high and up to an enormous 50 metres in circumference.
- It has a fruit that is one of the most nutrient-dense foods in the world. Baobab is the only fruit in the world that dries naturally on its branch.
TERMS OF THE DAY
|
S.No. |
Term |
About |
|
1. |
Electromagnetic fields |
Electromagnetic fields are a combination of invisible electric and magnetic fields of force. They are generated by natural phenomena like the Earth’s magnetic field but also by human activities, mainly through the use of electricity. Example: Mobile phones, power lines and computer screens generates electromagnetic fields. |
|
2. |
Photon |
Photons are fundamental subatomic particles that carry the electromagnetic force — or, in simpler terms, they are light particles (and so much more). The photon is also the "quantum," or fundamental unit, of electromagnetic radiation. |
|
3. |
Subatomic particles |
Subatomic particles are the particles found inside an atom and are responsible for forming the structure of an atom. |
|
4. |
Seedling transplantation |
Seedling transplantation is the process of transferring young seedlings from a seedbed or nursery to their final growing location in a field or garden, typically done to ensure optimal spacing and growth conditions for the plants. |
Editorial
US-Japan-Philippines trilateral isn’t just about development
Context:
China's assertive foreign policy has led to the formation of several minilateral groupings in recent years, including the resurgence of the Quad and the establishment of AUKUS, driven by concerns over Beijing's aggressive actions.
US-Japan-Philippines Trilateral Partnership:
- Trilateral partnership: The US, Japan, and the Philippines are currently engaged in a trilateral partnership, with the inaugural Trilateral Leaders' Summit that aims to enhance cooperation and peace and security in the Indo-Pacific region and beyond.
- Addressing concerns: While China opposes the formation of exclusive groupings, citing concerns about regional peace and stability, the trilateral partnership seeks to address shared concerns regarding China's assertiveness and coercive policies.
- Convergence of interests: The significance of the US-Japan-Philippines trilateral lies in Japan's defense alliance with the US and the Philippines' status as a major non-NATO ally, reflecting a convergence of interests among the three countries in response to the China threat.
Philippines' Response and Strategic Shifts:
- Reduce reliance on ASEAN: Despite implicit discussions about China, the trilateral summit aims to enhance cooperation without targeting any specific country. However, Philippines' strategic shift towards extra-regional powers reflects its efforts to reduce reliance on fellow ASEAN members amid strained relations with China.
- Strong backing: The potential involvement of the US and Japan in any conflict between China and Philippines underscores the significance of the trilateral partnership, offering substantial backing for the Philippines against China's assertiveness in the South China Sea.
- Effectiveness of Minilateral Groupings: While minilateral groupings like the US-Japan-Philippines trilateral and the Quad aim to address security challenges posed by China, questions are being raised about their efficacy. Despite their proliferation, few have translated into concrete actions, casting doubt on their ability to effectively tackle complex security issues.
Editorial
The advent of a holistic approach to ‘one health’
Context:
The recent decision by the cabinet on the 'National One Health Mission' marks a significant step in addressing the interdependence between humans, animals, and the environment, especially in light of the emergence of pandemics like COVID-19.
Goals of the National One Health Mission:
- Integrated disease surveillance: The mission aims to develop strategies for integrated disease surveillance, joint outbreak response, coordinated research and development (R&D), and seamless information sharing to control routine and pandemic diseases affecting humans, animals, and the environment.
- Addressing diseases affecting not only humans but also livestock and wildlife (foot and mouth disease, lumpy skin disease), is important, which can impact productivity, trade, and conservation efforts.
- Pandemic preparedness is emphasized, highlighting the need for strong R&D to develop tools like vaccines, therapeutics, and diagnostics, with participation from all sectors.
Creation of a Network of Laboratories:
- National network: Under the mission, a national network of high-risk pathogen laboratories (Biosafety level 3 and 4) has been established to facilitate better disease outbreak response across human, animal, and environmental sectors.
- Resource optimization and collaboration: This initiative enables resource optimization and collaboration between different departments, enhancing the response to diseases like Nipah that involve multiple species.
- 'One Health' is recognized as a global topic, endorsed by organizations like the G-20 during India's presidency, emphasizing collaboration in areas like surveillance capacity building and setting up international networks of 'One Health' institutes.
Editorial
FEMA trouble
Context:
The Reserve Bank of India's (RBI) recent policy reiteration regarding participation criteria for exchange traded currency futures and options contracts has disrupted the functioning of this segment, leading to a significant decline in daily turnover and outstanding contracts.
Impact on Currency Futures and Options Segment:
- Impacted daily turnover: Since the RBI's circular, daily turnover in currency futures and options on the NSE has plummeted to less than one-tenth of the daily average, prompting domestic brokers and foreign portfolio investors to unwind existing contracts.
- Threatened liquidity: The absence of participation from proprietary traders and foreign portfolio investors, who constitute over 65% of the currency derivatives volume, threatens liquidity in the segment, potentially exacerbating volatility in rupee movement and affecting hedging options for market participants.
- Increased volatility: Foreign portfolio investors, unable to trade in currency contracts on domestic exchanges, may shift to the rupee NDF market in overseas financial hubs, potentially leading to increased volatility.
Regulatory Framework and Concerns:
- Exchange traded currency derivatives, governed by FEMA rules, allow small businesses and individuals to hedge their foreign exchange exposure with smaller contract sizes. They have witnessed substantial growth, with volumes increasing nearly six-fold between FY18 and FY24.
- A circular issued in June 2014 allowed trading in currency derivative contracts on exchanges without requiring documentary evidence, but the RBI's recent policy enforcement aims to curb speculation by ensuring adherence to hedging norms.
- Potential Solutions: Collaborative efforts between the RBI and the government to remove foreign currency traded derivatives from FEMA's purview could offer a solution to address regulatory concerns while ensuring a conducive environment for genuine hedging activities.

 5 Questions
5 Questions 5 Minutes
5 Minutes




