20th April 2024
- Published
20 April 2024 -
 Download PDF
Download PDF
SC assails poll-time prohibitory orders
Context
The Supreme Court questioned the basis of Executive Magistrates issuing blanket orders prohibiting yatras to uphold democratic and electoral values, dharnas and public meetings during the entire duration of the Lok Sabha election, till the declaration of poll results.
1: Dimension - Legality and Basis of Orders
- Judicial Scrutiny: The recent remarks by the Supreme Court indicate a growing judicial scrutiny of the legality and necessity of blanket prohibitory orders issued during election periods. This scrutiny highlights the need for a clear legal basis and justification for such orders, emphasizing the principle of proportionality.
- Executive Discretion vs. Democratic Rights: The debate revolves around the balance between executive discretion and democratic rights. While authorities argue for the need to maintain law and order during elections, critics raise concerns about the infringement of fundamental rights, including the right to assembly and expression.
- Constitutional Validity: Advocates argue that prohibitory orders issued solely on the grounds of elections lack constitutional validity. They emphasize that elections, while significant, do not constitute an emergent situation justifying the imposition of sweeping restrictions on public activities.
2: Dimension - Impact on Democratic Rights
- Hindrance to Political Participation: Blanket prohibitory orders significantly hinder political participation by restricting public gatherings, protests, and awareness campaigns. This impediment undermines the democratic process by limiting citizens' ability to engage in political discourse and activism.
- Suppression of Civil Society: The prolonged duration of these orders suppresses civil society initiatives aimed at promoting voter awareness and monitoring election processes. Such suppression undermines the role of civil society in ensuring free and fair elections and fosters a culture of restricted civic engagement.
- Effect on Freedom of Expression: The fear of reprisal due to prohibitory orders creates a chilling effect on freedom of expression. Citizens, fearing legal repercussions, refrain from voicing their opinions or organizing peaceful demonstrations, thereby stifling dissent and diversity of political discourse.
3: Dimension - Lack of Response to Applications
- Administrative Inefficiency: The lack of response from authorities to applications seeking permission for public gatherings reflects administrative inefficiency. Many applications remain pending indefinitely, depriving citizens of their right to assemble and express their views.
- Violation of Due Process: The failure to respond to applications violates due process and procedural fairness. Citizens are left in a state of uncertainty, unable to plan or organize events effectively, which undermines the principle of rule of law.
- Obstruction of Democratic Engagement: The non-responsive approach of authorities obstructs democratic engagement by creating barriers to civic participation. This obstruction undermines the vibrancy of democracy and erodes trust in the electoral process.
|
Section 144
Powers under the Provision:
|
Mains Practice Question
Q. "Blanket prohibitory orders during election periods undermine democratic values and citizens' rights. Analyze
Forests a national asset and major contributor to financial wealth: SC
Context
The Supreme Court has asserted in a judgment that forests in India are a national asset and a major contributor to the nation’s financial wealth. Forests are not just a collection of trees; they are a vital asset for the nation's economy and environment.
1: Dimension- Importance of Forests
- Biodiversity Conservation: Forests harbor a rich diversity of plant and animal species, playing a crucial role in preserving biodiversity. They provide habitats for various flora and fauna, contributing to the ecological balance.
- Carbon Sequestration: Forests act as carbon sinks, absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and mitigating climate change. India's forests sequester approximately 24,000 million metric tonnes of carbon dioxide, helping to regulate the global climate.
- Soil and Water Conservation: Trees and vegetation in forests prevent soil erosion, regulate water cycles, and maintain groundwater levels. Forests act as natural water filters, purifying water and ensuring its availability for human consumption and agriculture.
2: Dimension- Economic Value of Forests
- Carbon Trading: Forests contribute to a nation's financial wealth by earning revenue through carbon trading. Countries with excess forest cover can sell carbon credits, incentivizing forest conservation and sustainable management practices.
- Timber and Non-timber Forest Products: Forests provide valuable timber resources and non-timber forest products (NTFPs) such as medicinal plants, fruits, and resins. These products contribute to local economies and provide livelihoods to forest-dependent communities.
- Tourism and Recreation: Forests attract tourists and nature enthusiasts, generating revenue through ecotourism activities such as wildlife safaris, trekking, and camping. Sustainable tourism practices can promote conservation efforts and support local communities.
3: Dimension- Threats to Forests and Conservation Measures
- Forest Conservation Laws: Strong legal frameworks and enforcement mechanisms are essential to protect forests from illegal logging, encroachment, and unsustainable land use practices. The Forest (Conservation) Amendment Act (FCAA) 2023 should be reviewed to ensure it upholds the principles of forest conservation.
- Community Participation: Involving local communities and indigenous groups in forest management and conservation efforts can help in sustainable resource utilization and conflict resolution. Community-based forest management initiatives empower local stakeholders and promote stewardship of forest resources.
- Monitoring and Enforcement: Regular monitoring, surveillance, and strict enforcement of forest laws are crucial for preventing deforestation, forest degradation, and wildlife poaching. Technology, such as satellite imagery and remote sensing, can aid in monitoring forest cover changes and illegal activities.
Conditions not ripe for easing restrictive monetary stance
Context
The recent meeting of the Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) highlighted the need to maintain a restrictive monetary stance due to persistent risks to price stability, as outlined by RBI Deputy Governor Michael Debabrata Patra.
Key Highlights of the Meeting
- Inflation Concerns: Recent inflation data, especially in food prices, indicates ongoing risks. Food inflation, which remained at 8.52% in March, shows resilience, particularly in cereals and meat.
- Price Momentum: Experts pointed out a build-up of price momentum with rising temperatures as summer approaches, indicating potential challenges until May 2024.
- Headline Inflation: Despite some disinflation in core areas and fuel, headline inflation might remain on the higher side until favorable base effects kick in during the second quarter of 2024-25.
1: Dimension - Reasons for Maintaining Restrictive Stance
- Persistent Inflation Risks: The steady core disinflation and fuel price de-escalation do not ensure a quick alignment of headline inflation with the target. Until significant base effects are seen, maintaining a restrictive stance is crucial.
- Uncertainty in Inflation Trajectory: Experts stressed the importance of maintaining downward pressure on inflation until clearer signs of a durable decline in inflation are evident and uncertainties in the near term are resolved.
2: Dimension - Impact of Loose Monetary Policy
- Inflationary Pressure: Loose monetary policy could fuel inflationary pressures, particularly with the vulnerability of the inflation trajectory to frequent supply-side shocks, especially in food inflation due to adverse weather conditions.
- Price Stability Concerns: RBI Governor emphasized the need to remain focused on ensuring durable price stability, highlighting the risks associated with supply-side shocks spilling over into core inflation.
3: Dimension - Required Measures
- Balancing Growth and Inflation: Any relaxation in the monetary stance should be contingent on a durable decline in inflation and a more balanced risk outlook, ensuring that it doesn't compromise the objective of maintaining price stability.
- Enhanced Confidence: Experts mentioned that a stronger revival in private consumption and corporate sales growth requires greater confidence in a sustained decline in inflation.
Mains Practice Question
Q: “Inflation remains a persistent challenge despite various measures”. Discuss the factors contributing to this and suggest strategies for effective inflation management.
|
Key-terms in the monetary policy review |
|
|
Repo rate |
|
|
Standing Deposit Facility (SDF) Rate |
|
|
Marginal Standing Facility (MSF) Rate |
|
|
Fine Tuning Operations |
|
|
Monetary policy stance |
There are various stances:
|
|
CPI Inflation |
|
Railways: On track for major overhaul but with speed limits
Context
The Indian Railways, as the country's largest national transport network, has long been a focal point for policymakers aiming to enhance its efficiency and modernize its infrastructure.
1: Dimension- Challenges in Enhancing Efficiency
- Human Resource Complexity: The Indian Railways is a significant employer, making it challenging for governments to implement changes swiftly due to the complexities associated with managing a large workforce. Dealing with human resource issues, such as training and deployment, poses a substantial challenge to railway modernization efforts.
- Safety Concerns: Despite advancements, safety remains a concern, especially regarding the implementation of systems like the Kavach anti-collision system and combating driver fatigue. Safety measures are crucial for preventing accidents and ensuring passenger and employee well-being.
- Infrastructure Complexities: The complexity of railway infrastructure poses hindrances to the seamless implementation of safety measures and technological upgrades. Upgrading existing infrastructure while ensuring minimal disruption to services is a daunting task.
2: Dimension- Progress and Achievements
- Vande Bharat Trains: The Vande Bharat trains, symbolizing a generational shift in Indian railways, offer high-speed point-to-point services with amenities akin to airlines, showcasing India's manufacturing capabilities. This initiative reflects the government's commitment to enhancing passenger experience and reducing travel time.
- Expansion of High-Speed Train Corridors: Efforts are underway to construct more high-speed train corridors, including the Mumbai-Ahmedabad bullet train project, aimed at enhancing connectivity and reducing travel time. These initiatives are crucial for meeting the growing demands of passengers and freight transport.
- Capital Outlays and Infrastructure Development: The Modi government's emphasis on capital outlay, including the highest-ever investments in railways, has led to significant advancements in track laying, electrification, maintenance, and infrastructure development. These investments are vital for modernizing railway infrastructure and improving operational efficiency.
3: Dimension- Future Strategies and Challenges
- Focus on Electrification: With a target of zero carbon emissions by 2030, railway electrification projects have been expedited, leading to a substantial increase in electrified route kilometers and a significant reduction in carbon footprint. However, challenges such as funding and technical hurdles need to be addressed to achieve the ambitious electrification goals.
- Modernization Initiatives: The station modernization program, including the Amrit Bharat station scheme, aims to revamp over 1,300 stations, enhancing passenger experience and infrastructure. While these initiatives are commendable, ensuring timely completion and quality execution remains a challenge.
- Freight and Passenger Service Balancing: While freight services remain a significant revenue source, efforts are needed to balance freight and passenger services efficiently, ensuring optimal utilization of railway infrastructure. This requires strategic planning and investment in infrastructure to accommodate both passenger and freight traffic effectively.
Mains Practice Question
Q: "Indian Railways stands at the crossroads of modernization, balancing speed with safety." Discuss.
EV charging: Alliance formed to promote payment and charging interoperability
Context
As electric vehicles (EVs) gain traction globally, the need for a robust charging infrastructure becomes increasingly evident. To address the challenges of payment and charging interoperability, twenty energy companies have come together to form an alliance aimed at creating an open energy network similar to the United Payments Interface (UPI). This initiative, named the Unified Energy Interface (UEI), seeks to facilitate seamless transactions within EV charging networks.
1: Dimension- Key Challenges
- Payment Settlement Mechanism: A significant challenge in scaling up peer-to-peer (P2P) energy trading projects is the lack of a reliable payment settlement mechanism between the involved parties. Presently, utilities manage payments for P2P trades, which can be cumbersome and inefficient.
- Adoption Hurdles: Despite the potential benefits of P2P trading, adoption is hindered by complexities in payment systems. Streamlining payment processes is essential for encouraging widespread adoption of green energy initiatives.
- Infrastructure Costs: Establishing interoperable charging networks incurs infrastructure costs. The alliance aims to address this challenge by equally distributing the minimal infrastructure costs among its members.
2: Dimension- Seamless Interface
- Beckn Protocol: The UEI network is built on the Beckn protocol, an open-source protocol developed in India. Similar to protocols like ONDC and UHI, Beckn facilitates open networks, ensuring seamless transactions across various platforms.
- Government Support: The Department of Science and Technology has endorsed the UEI network, signaling governmental support for its implementation. This support is crucial for fostering innovation and standardization in the energy sector.
- Growth Prospects: The UEI network has already facilitated significant energy transactions and is poised for exponential growth with the expected inclusion of prominent B2C apps. This growth is essential for expanding the reach and efficiency of EV charging infrastructure.
3: Dimension- Charging Infrastructure
- Operational EV Charging Stations: India has seen a steady increase in the number of operational public EV charging stations, with Maharashtra leading the tally. States like Delhi, Karnataka, Kerala, and Uttar Pradesh also have substantial numbers of charging stations.
- Collective Effort: Large networks such as Kazam, Pulse Energy, ChargeZone, and Trinity collectively operate thousands of EV charging stations across the country. The alliance aims to foster collaboration among various stakeholders to ensure the seamless integration of charging infrastructure.
- Global Development Focus: The UEI alliance is committed to fostering global development and compliance with unified standards for energy transactions. This focus on standardization and scalability is essential for facilitating the widespread adoption of EVs and green energy solutions worldwide.
Mains Practice Question
Q: "The Unified Energy Interface (UEI) alliance marks a significant step towards enhancing the efficiency and accessibility of EV charging infrastructure." Discuss.
Mobility, carbon tax cloud talks on India-UK trade deal
Context
Negotiations between India and the UK for a free trade agreement (FTA) are facing hurdles, particularly concerning issues like carbon tax, mobility rights, and duty-free access for goods. Despite being at an advanced stage, unresolved issues are delaying the signing of the agreement.
1: Dimension- Indian Requests and UK Stand
- Carbon Tax Proposal: India has proposed various options regarding the carbon tax, ranging from a longer transition period to complete exemption. However, the UK is unlikely to accept India's request for exemption from the proposed Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism, citing the need to reduce emissions and support domestic industries.
- Mobility Rights: India is advocating for mobility rights for its skilled professionals, demanding more visas and the right to mobility as part of the agreement. These provisions are crucial for ensuring the movement of skilled labor between the two countries.
- Duty-Free Access: India seeks duty-free access for certain goods in the UK market, aiming to boost exports and enhance economic cooperation. However, negotiations on this front have yet to yield concrete results.
2: Dimension- Progress and Challenges
- Advanced Stage Talks: Despite being described as being at an advanced stage, talks have been prolonged due to unresolved issues. The negotiations, although progressing, are encountering difficulties in finding common ground on critical matters.
- Controversial Carbon Tax: The UK's reluctance to exempt India from the carbon tax is causing contention, as India argues its status as a developing country should merit exemption. However, the UK views such an exemption as controversial and counterproductive to its emissions reduction goals.
- Delays and Deadlines: The FTA negotiations have surpassed their initial deadline by over a year, mainly due to issues like professional visas, goods duties, and migration concerns. These delays are impeding the finalization of the agreement despite efforts from both sides to expedite the process.
3: Dimension- Recent Developments
- Bilateral Talks: Both India and the UK have been engaged in bilateral talks, with a four-member team from India discussing key issues in London. Virtual discussions have also been held to address FTA-related matters.
- Growth in Trade: Despite the challenges, trade between India and the UK has been growing steadily, reaching $20.36 billion in fiscal year 2023. This demonstrates the significance of a potential FTA in further enhancing bilateral trade relations.
- Push for Conclusion: Prime Minister Narendra Modi and his British counterpart Rishi Sunak have emphasized the need for an early conclusion to the FTA, providing impetus to negotiators to resolve outstanding issues and finalize the agreement.
|
India-UK Trade
|
|
Examples of non-tariff barriers:
|
Mains Practice Question
Q: "The challenges in the India-UK FTA negotiations highlight the complexities involved in balancing economic interests and environmental concerns." Discuss.
Vasuki Indicus
Context
Researchers have reported the discovery of fossils of one of the largest snakes that ever existed and likely lived 47 million years ago during Middle Eocene period. The fossils were found in Kutch, Gujarat, and the reptile, named Vasuki Indicus.
About
- It is a giant predator snake estimated to be as large as the longest snake ever discovered.
- The fossilised remains, measuring 10-15 metres long, were found in Gujarat’s Panandhro Lignite Mine in Kutch.
- Madtsoiidae are Gondwanan terrestrial snakes that lived between the Upper Cretaceous (100.5 million to 66 million years ago) and the Late Pleistocene (0.126 million years ago to 0.012 million years ago).
- The giant madtsoiid snake identified in the new study is one of the largest snakes ever reported.
Govind Guru
Context
Govind Guru was the leader of “one of the most efficient movements against British rule in India”.
About
- Govind Guru Banjara, (1858–1931) was a social and religious reformer in the early 1900s in the tribal border areas of present-day Rajasthan and Gujarat states in India.
- He is seen as having popularized the Bhagat movement, which was first started in the 18th century.
- His teachings, Vashishth’s work asserts, was based on an appreciation of rationality, a tendency to shun superstition, and monotheism, among other principles.
- Govind Guru preached a religion that involved praying at Dhunis (firepits).
- Followers of this religion wore a rudraksh around their neck and carried iron tongs. Special worship took place on Sundays.
Brahmos
Context
India delivers first batch of BrahMos supersonic missiles to Philippines
About
- The BrahMos supersonic cruise missile has a two-stage solid propellant booster engine as its first stage which takes it to supersonic speed.
- The second stage is the liquid ramjet engine which takes it closer to Mach 3 (3 times the speed of sound) speed in the cruise phase.
- The BrahMos missile is universal for multiple platforms and can be launched from air, land, and sea platforms.
- The missile works on the 'Fire and Forget principle', meaning it doesn't require further guidance after launch, and it maintains a high supersonic throughout the flight.
|
Brahmos NG
|
FSSAI
Context
The Consumer Affairs Ministry asked the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) to initiate “appropriate action” against the Nestle group for allegedly selling baby products with high sugar content in India.
About
- Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) is an autonomous statutory body established under the Food Safety and Standards Act, 2006 (FSS Act).
- Ministry of Health & Family Welfare, Government of India is the administrative Ministry of FSSAI.
- The FSSAI consists of a chairperson and 22 members.
- The FSSAI is in charge of establishing food standards so that consumers, traders, manufacturers, and investors only have to deal with one organization.
- Statutory powers granted to FSSAI
- Framing of Regulations to lay down food safety standards
- Laying down guidelines for accreditation of laboratories for food testing
- Providing scientific advice and technical support to the Central Government
- Contributing to the development of international technical standards in food
- Collecting and collating data regarding food consumption, contamination, emerging risks, etc.
- Disseminating information and promoting awareness about food safety and nutrition in India.
Shompen
Context
For the frst time, members of the Shompen, one of the Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs) took part in the election process by casting their votes in the Andaman and Nicobar Lok Sabha constituency.
About
- The Shompen are an indigenous group of people who live on Great Nicobar Island in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
- They are hunter-gatherers who hunt wild game, forage for fruits and forest foods, and farm yams, roots, vegetables, and tobacco.
- The Shompen are one of the most populated tribes in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, with around 200–300 people living mainly on Great Nicobar Island.
- They were first contacted in the 1840s and are designated as a Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Group (PVTG).
- They have nuclear families comprising husband, wife, and their unmarried children.
- The family is controlled by the eldest male member, who controls all activities of the women and kids.
- Monogamy is the general rule, although polygamy is allowed too.
|
Tribes of Andaman and Nicobar Islands
|
Location |
|
Strait Islands |
|
|
Little Nicobar |
|
|
Middle and South Andaman |
|
|
Great Nicobar |
|
|
Great Nicobar |
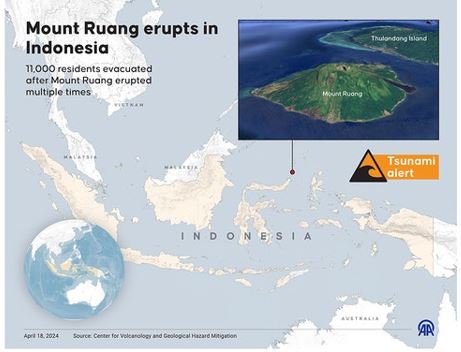
Mount Ruang volcano
Context
Indonesia's Mount Ruang volcano erupted five times in a row, prompting the closure of a nearby airport and a tsunami alert.
About
- Ruang is situated in the Sangihe Islands arc, North Sulawesi, Indonesia.
- It comprises an island that is 4 by 5 kilometers wide, with a summit containing a partial lava dome reaching an altitude of 725 meters (2,379 ft).
- From its summit, peaks such as Klabat, Siau, and Ternate can be observed in the south, north, and east, respectively.
- The top of the mountain is partially filled with a lava dome formed as a result of activity in 1904.
|
Types of Volcanoes:
|
Greater Adjutant(Leptoptilos dubius)
Context
Greater adjutant is facing threats due to garbage mountains of Guwahati and habitat destruction.
About
- It is a member of the stork family, Ciconiidae. Its genus includes the lesser adjutant of Asia and the marabou stork of Africa.
- There are only three known breeding grounds – one in Cambodia and two in India (Assam and Bihar).
- IUCN Status: Endangered
Unique CA Number
Context
A unique numbering system for chartered accountants rolled out five years ago is beginning to offer new insights into their services in high demand, and economic activity at the state level.
About
- In 2019, the Institute of Chartered Accountants of India (ICAI) introduced a unique document identification number (UDIN) for CAs, aimed to prevent crooks issuing fake certificates.
- The new system is proving to be a gauge of economic activities across the country, down to district level.
- UDIN can be generated for the documents / certificates available on the UDIN portal by selecting a document from the list and providing other details like date of signing the document, detail of financial figures and document description.
- UDIN generation does not require any document upload.
TERM OF THE DAY
|
S.No. |
Term |
About |
|
1. |
Carbon Tax |
Carbon taxes are designed to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by increasing prices of the fossil fuels that emit them when burned. This both decreases demand for goods and services that produce high emissions and incentivizes making them less carbon-intensive. |
|
2. |
Disinflation |
Disinflation is a decrease in the rate of inflation. It's when prices are still rising, but at a slower rate than before. The inflation rate is still positive, but at a lower level. |
|
3. |
Ecofeminist |
Ecofeminism is a political movement and intellectual critique that combines feminism and environmentalism. Ecofeminist thinkers use gender analysis to examine the relationships between humans and the natural world. |
|
4. |
Faustian Bargain |
A Faustian bargain is a deal where someone gives up something of great moral or spiritual importance in exchange for a worldly or material benefit. The term comes from the medieval legend of Faust, who traded his soul to the devil in exchange for knowledge and power. |
|
5. |
Flash mobs |
A flash mob is a group of people who suddenly assemble in a public space, perform for a short time, and then quickly disperse.. |
|
6. |
gerrymandering |
Gerrymandering is the practice of dividing or arranging an area into political units to give one political party an unfair advantage over its rivals. It can also refer to diluting the voting power of members of ethnic or linguistic minority groups. |
|
7. |
Glycemic Index |
The glycemic index (GI) is a scale that measures how much specific foods increase blood sugar levels. Foods are ranked on a scale of 0–100, with lower GI numbers indicating less effect on blood sugar levels |
|
8. |
Grooming |
Grooming is when someone builds a relationship, trust and emotional connection with a child or young person so they can manipulate, exploit and abuse them. Children and young people who are groomed can be sexually abused, exploited or trafficked. |
|
9. |
National Cadet Corps (NCC ) |
The National Cadet Corps (NCC) is the youth wing of the Indian Armed Forces with its headquarters in New Delhi, India. It is open to school and college students on voluntary basis as a Tri-Services Organisation, comprising the Army, the Navy and the Air Force. Cadets are given basic military training in small arms and drill. Officers and cadets have no liability for active military service once they complete their course. |
|
10. |
Ranching |
Ranching is the practice of raising herds of animals on large tracts of land. Ranchers commonly raise grazing animals such as cattle and sheep. Some ranchers also raise elk, bison, ostriches, emus, and alpacas. |
|
11. |
Restrictive monetary Policy |
Restrictive monetary policy refers to the monetary policy of slowing the money supply's growth to decelerate the economy. Usually, its objective is to reduce inflation. It is also referred to as contractionary or tight monetary policy. |
Editorial
Israel, a two-state solution, some recent perceptions
Context:
Amidst the ongoing conflict between Hamas and Israel, understanding the complexities of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict and the various viewpoints surrounding it is crucial for assessing the current situation and prospects for peace.
Top of Form
Origin and questions:
- Historical Context: The idea of a Jewish national home and its development since recorded history remain debated.
- Challenges to Established Myths: Historian Ilan Pappé challenged myths surrounding the origin and identity of contemporary Israel, highlighting issues such as the empty land myth and the displacement of Palestinians.
- Recent Political Assertions: Bilateral and multilateral efforts to seek a solution have faced challenges, with recent assertions by Israel's Likud Party supporting West Bank annexation.
Balance of forces:
- Impact of Historical Events: Former negotiator Prof. Itamar Rabinovich assessed the impact of the 1967 war on Israel-Arab relations, emphasizing the lack of a political settlement.
- Complexities of Peace Processes: Further regional turmoil, including the Intifada, led to the Madrid Conference of 1991, aiming for peace but facing complexities.
- Current Dynamics: Recent assessments indicate growing American support for Israel, but also a distancing of younger Jewish populations from Israel.
The players:
- Palestinian Aspirations: Palestinians seek recognition as a state with international rights, as outlined in the Palestinian Non-Paper of June 12, 2002.
- Israeli Stance: Israel aims to retain control over vital security areas while allowing Palestinian self-government.
- American Influence: The United States supports a two-state solution, emphasizing demilitarization and regional normalization.
- Arab States' Perspectives: Arab states seek a revitalized Palestinian state and may consider American suggestions of an Arab Mandate.
Editorial
Scientists and a wish list for the incoming government
Context:
Amidst the ongoing general election in which 970 million Indians are exercising their franchise, scientists express their expectations and concerns regarding the incoming government. Supporting science and scientists is essential in India’s quest to become a major economic powerhouse.
Increase Spending:
- Increase in Research Expenditure: Scientists urge for a substantial rise in the nation’s gross domestic expenditure on research and development, currently below 0.7% of GDP. They propose an increase by at least 50% year-over-year, aiming for nearly 4% of GDP at the end of the government's term.
- Private Sector Participation: Private players, contributing less than 40% of the current spending, need to increase their investment. One suggested avenue is through contributions to the Anusandhan National Research Foundation (ANRF), with a target of ?36,000 crore over five years.
- Mechanisms for Funding: Detailed plans and mechanisms, including escrow accounts, are required to ensure the implementation of increased funding. The skilled scientific workforce needs to be expanded to utilize funds effectively.
Focus on Merit:
- Transparent Hiring Practices: Scientists emphasize the need for transparent, merit-based hiring processes in educational and research institutions. The selection criteria should strictly follow global standards, and appointment processes should take no longer than six months.
- Global Norms in Hiring: The hiring process should align with established global norms to ensure the selection of the most suitable candidates free from external influences.
- Efficient Grant Management: A robust grant management system with minimal red tape is essential. Timely disbursal of grants and fellowships, autonomy in spending for researchers, and streamlined fund allocation are crucial for effective research.
Ensure Freedom:
- Academic Freedom: Scientists stress the importance of academic freedom, allowing them to speak and write based on evidence without interference. Full autonomy for scientists to form companies, hire staff, and spend research funds is necessary.
- Support for Innovation: An ecosystem supporting innovation and entrepreneurship is vital for scientific progress. The government should provide flexibility in administrative processes, hiring, and spending to foster innovation.
- Accountability and Quality: While ensuring freedom, scientists must be held accountable for the quality of their work. Accountability should be based on the quality of research, products, and knowledge dissemination.
Editorial
How rural co-operatives can be strengthened
Context:
The Indian agricultural sector, particularly small and marginal farming, requires robust support systems to facilitate various activities like accessing quality inputs, receiving timely crop advisories, and securing fair prices for produce. Co-operatives play a crucial role in providing this support and act as a link between private and public sector initiatives.
Importance of Co-operatives in Agriculture:
- Anchor for Agricultural Activities: Co-operatives serve as a crucial anchor in supporting small and marginal farmers by providing quality inputs, timely advisory services, and ensuring fair prices for their produce.They facilitate activities such as arranging seeds, fertilizers, and manure, thus contributing to the overall agricultural productivity.
Ministry of Co-operation Initiatives:
- The Ministry of Co-operation, formed in July 2021, initiated several path-breaking measures to strengthen co-operatives:
- Formulation of model bye-laws for Primary Agricultural Credit Societies (PACS) to undertake multi-purpose activities.
- Development of a National Co-operative Policy.
- Launching schemes for computerization of functional PACS, creation of a National Cooperative Database, and promoting multi-State co-operative societies for various agricultural activities.
- Inclusion of State Co-operative Banks (StCBs) and District Central Co-operative Banks (DCCBs) as member lending institutions with CGTMSE.
Ways to Strengthen Rural Co-operatives:
1. Governance and Culture Improvement:
- Handholding Approach: State Cooperative Banks (StCBs) should mentor affiliated District Central Co-operative Banks (DCCBs), which in turn should mentor primary societies.
- Fair Elections: Establishing dedicated State Co-operative Election Commissions for fair and transparent elections is necessary.
- Leadership Development: Enhancing governance and leadership skills of elected board members should be systematically undertaken to ensure effective decision-making.
2. Technological Upgradation and Business Diversification:
- Financing Agri Value Chain: Rural credit co-operatives should lead in financing activities across the agricultural value chain, integrating production, processing, storage, transport, and marketing.
- Leveraging Technology: StCBs and DCCBs should offer digital services like internet/mobile banking, Unified Payment Interface (UPI), and others to attract customers and improve services.
3. Human Resource Development and Capacity Building:
- Recruitment and Training: Transparent recruitment policies and capacity building measures should be adopted to ensure quality manpower.
- Members' Education: Emphasis on educating members about co-operative principles, management, rights, and duties is essential.
- Encouraging Innovation: Promoting start-ups in the co-operative sector can bring fresh ideas and innovation, fostering growth and sustainability.
Policy Goals and Targets:
- Increase in Agricultural Credit Share: The aim should be to increase the share of rural co-operative banks in agricultural credit from 11% to 20% by 2030 and to 40% by FY 2047.





 5 Questions
5 Questions 5 Minutes
5 Minutes




