3rd April 2024
- Published
03 April 2024 -
 Download PDF
Download PDF
Sweeping Powers of Directorate of Enforcement (ED)
Context
The Supreme Court endorsed the sweeping powers of the Directorate of Enforcement (ED), saying the Central agency could call “anybody for any information” even as it castigated Tamil Nadu District Collectors for failing to appear in person in response to a summons issued to them by the anti-money laundering body.
1: Dimension- Power and Function of ED:
- Search and Seizure- ED carries out search (property) and seizure (money/documents) under Section 16 and Section 17 of the PMLA.
- In case of Arrest-If the person is arrested, the ED gets 60 days to file the prosecution complaint (charge sheet) as the punishment under PMLA doesn't go beyond seven years.
- In property attachment- If no one is arrested and only the property is attached, then the prosecution complaint along with attachment order is to be submitted before the adjudicating authoritywithin 60 days.
2: Dimension- Power of ED for ‘interrogation’ and ‘Custody’:
- Under Prevention of Money Laundering Act, 2002 (PMLA):Following the recommendations of the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) India enacted PMLA.
- The ED has been entrusted with the responsibility of executing the provisions of PMLA by conducting investigation to trace the assets derived from proceeds of crime, to provisionally attach the property and to ensure prosecution of the offenders and confiscation of the property by the Special court.
- The ED carries out search (property) and seizure (money/documents)after it has decided that the money has been laundered, under Section 16 (power of survey) and Section 17 (search and seizure) of the PMLA.
- On the basis of that, the authorities decide if arrest is needed as per Section 19 (power of arrest).
- Under Section 50 of the PMLA, the ED can also directly carry out search and seizure without calling the person for questioning.
- It is not necessary to summon the person first and then start with the search and seizure.
- If the person is arrested, the ED gets 60 days to file the prosecution complaint (chargesheet) as the punishment under PMLA doesn't go beyond seven years.
- If no one is arrested and only the property is attached, then the prosecution complaint along with attachment order is to be submitted before the adjudicating authority within 60 days.
3: Dimension- Effectiveness of ED
- As of March 31, 2022, the ED's conviction rate was less than 0.5 per cent, with only 23 convictions in 5,422 PMLA cases. In comparison, the national conviction rate in India for offences of the Indian Penal Code was 57 per cent in 2021.
- Petitions challenging PMLA provisions, particularly related to arrests and property attachments, have been presented in the Supreme Court.
|
Fact Box Important Judgments:
Enforcement Directorate (ED):
|
|
Mains Practice Question Q: Despite being a central agency, the Enforcement Directorate possesses jurisdiction across India, posing intricate legal inquiries. Comment (250 words) |
|
UPSC PYQ (Related) Q: The jurisdiction of the Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI) regarding lodging an FIR and conducting probe within a particular state is being questioned by various States. However, the power of States to withhold consent to the CBI is not absolute. Explain with special reference to the federal character of India. (UPSC 2021) |
India risks ‘squandering’ demographic dividend: World Bank
Context
The World Bank's South Asia regional update, "Jobs for Resilience," highlights concerns regarding the region's utilization of its demographic dividend, particularly focusing on India's employment growth.
1: Dimension- Observations on Employment Trends
- Slow Job Creation: The South Asia region, including India, is not effectively leveraging its demographic dividend, as job creation lags behind the growth in the working-age population.
- Unemployment Rate: India, in particular, has witnessed employment growth significantly below the average growth in its working-age population from 2000 to 2023, leading to a decline in the employment ratio.
- The youth unemployment rate was 45.4 per cent in 2023, according to the Centre for Monitoring Indian Economy, a think-tank.
- Female employment ratios in many south Asian countries, including India, are among the lowest in the world, at less than 40 per cent.
2: Dimension- Untapped benefits from the demographic dividend
- Economic growth:Better economic growth is brought about by increased economic activities due to a higher working-age population and lower dependent population thereby increasing labor force along with rising in women workforce.
- Policy Framing: Effective policy making by strictly implementing schemes and programs for the benefit of the people.
- Rise in employment: A higher employment-seeking population will lead to the rapid increase of industrialization and urbanization.
- Increased workforce:The working-age population rising to 65% will increase the workforce.
- Swelling labour force:India’s labour force is swelling as its baby boomers reach working age. It would boost India’s growth.
- Effective diversion of resources: India’s population has the potential to divert resources from spending on irrelevant things to investing in physical and human infrastructure.
- Rise in women’s workforce:There is a rise in women’s workforce activity that naturally accompanies a decline in fertility.
- Easy accumulation: The fourth is that working ages also happen to be the prime years for savings, which is key to the accumulation of capital and technological innovation.
3: Dimension- Economic Growth and Employment
- Despite challenges in employment, India's economy is expected to exhibit robust growth of 7.5% in FY23/24, contributing to the overall strong performance of the South Asian region.
- However, the region could achieve even higher output growth if the employment rate matched that of other Emerging Market and Developing Economies (EMDEs).
4: Dimension- Approach to seize Demographic Advantage:
- Upgrading Education Standards: Irrespective of rural or urban settings, the public school system must incorporate skilling, training, and vocational education in line with market demand.
- Fulfilling Health-Related Requirements: Increasing government spending on health, education, and other social sectors will be crucial to realizing the potential dividend from India’s young demography.
- Inter-Sectoral Collaborations:Moving forward towards safeguarding the futures of adolescents, it is imperative to put in place mechanisms for better inter-sectoral collaboration.
- Bridging Gender Gaps in Workforce: New skills and opportunities for women and girls befitting their participation in a 3 trillion-dollar economy are urgently needed. This can be done by:
- Legally compulsory gender budgeting to analyze gender-disaggregated data and its impact on policies
- Increasing childcare benefits
- Boosting tax incentives for part-time work
- Federal Approach for Diverse States: Inter-ministerial coordination for strategic planning, investment, monitoring, and course correction should be an important feature of this governance arrangement.
|
Fact Box: India’s demographic dividend
|
|
UPSC PYQ Q: While we found India’s demographic dividend Q2: While we flaunt India’s demographic dividend, we ignore dropping rates of employability. What are we missing doing so? Where will the jobs that India desperately needs come from? Explain. (UPSC 2014) |
India’s new Indian EV policy
Context
India’s new EV policy, announced recently, allows imports from any country, including China.
1: Dimension- The new Indian EV policy
- Investment: The updated policy mandates automakers to invest a minimum of USD 500 million in India within three years, establishing local EV manufacturing facilities with 25% domestically sourced components.
- Reduced duty: Eligible carmakers can import up to 8,000 EVs annually with a 15% reduced import duty for vehicles priced at USD 35,000 and above. This aligns with the Indian government’s “Atmanirbhar Bharat” initiative, fostering self-reliance and technological advancement.
- Domestic Value Addition (DVA): The policy lays emphasis on Domestic Value Addition (DVA), aiming for a minimum of 50% DVA within five years.
- This reduces reliance on imports, stimulates job growth and promotes technological innovation in the Indian EV sector, supporting indigenous manufacturing.
- Accountability: Additionally, the policy ensures accountability by requiring companies to back investment pledges with bank guarantees.
- Non-compliance with DVA and investment criteria will lead to enforcement of guarantees, enhancing transparency and accountability.
2: Dimension- Implications of the strategy:
- Attracting global manufacturers: The Indian government aims to create policies that attract all EV manufacturers globally to establish operations in India, leveraging the country’s expanding economy.
- Ripple effect for economy: The goal is not just to attract these big players but to leverage their presence and create a ripple effect, fostering a network of smaller, specialized domestic suppliers for a robust and self-sustaining industrial ecosystem.
- Interest of domestic manufacturers: Domestic players such as Tata Motors and Mahindra & Mahindra had expressed concerns about increased competition from globally popular EVs, especially China.
|
Data Box: India’s EV Market
|
Heatwaves Conditions across India
Context
Anthropogenic climate change is turning ambient heat into an inevitable environmental hazard. India is poised to encounter an increased number of heat-wave days than usual from April to June and this expansion of the realm of extreme heat is potentially the gravest consequence of climate change for India.
1: Dimension: Impact of Heat Waves over different sectors
- Health impact:
- Heat Stress: Exposure to severe or continuous heat leads to heat stress. Illnesses range from superficial/mild and manageable (e.g. prickly heat, heat-related swelling, heat cramps, heat exhaustion) to a medical emergency (i.e. heat stroke).
- Heat stroke is the most severe of heat-related illnesses. It presents with impaired brain function (i.e. stroke) due to uncontrolled body heating. It is a time-critical condition that often turns fatal if there is a delay or failure in reducing body temperature by rapid, active cooling. Besides neurological impairment, high core body temperature (at least 40 degrees C), or hot, dry skin are other heat stroke symptoms. Someone in perfect health and participating in what seem to be normal activities may die from heat stroke within an hour.
- Environmental impact: Heatwaves also have compound and cascading environmental impacts like concurrent drought, glacial lake outbursts causing flash floods, urban/wildfires, and increased air pollution from ground-level ozone and dust storms.
- Economic Impact:
- Impact on crops: There are concerns about the potential adverse effects on wheat, rapeseed, and chickpea production. India, being the world’s second-largest wheat producer, could face significant repercussions.
- Power demand: There are possibility of surpassing power demand over supply during the summer season.
|
Fact Box Heat Wave
Favourable conditions of heat wave formation
|
|
Practice Question Q: Heatwave is the gravest consequence of climate change for India. Discuss the impact of heatwave as a disaster. (250 words) |
|
UPSC PYQ Q: Discuss the consequences of climate change on the food security in tropical countries. (UPSC 2023) |
'Kallakkadal' strikes coastal Kerala
Context
High sea waves which are also known as swell waves, have flooded numerous houses in the Kerala's coastal areas. This flooding caused by the swell waves is called swell surge or Kallakkadal in Malayalam.
What is Kallakkadal?
- Kallakkadal is a geographical phenomenon which causes flooding through high waves in the south-west coast of India, predominantly during the pre-monsoon season which is from April to May.
- The term Kallakadal was officially approved by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO).
- Kallakkadal is caused by swell waves which emerge due to ocean swell which is mostly caused by storms such as hurricanes or gale winds.
- During these fierce winds, a massive energy transfer takes place from the air into water.
- This then leads to formation of extremely high waves that can roll up to thousands of kilometres.
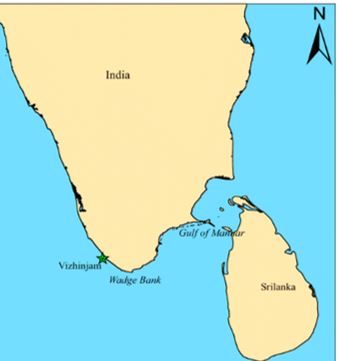
Wadge Bank
Context
New Delhi recognized the barren and uninhabited island of Katchatheevu as Sri Lankan territory in 1974 and Colombo later recognized the resource-rich, deep-sea fishing grounds of Wadge Bank as Indian Territory in 1976.
About
About Wadge Bank
- Wadge Bank is a 10,000 square kilometre submarine plateau, of the sea south of Kanyakumari that is rich in biodiversity and considered India’s richest fishery resource.
- Wadge Bank, located near Cape Comorin, is home to more than 60 species of ornamental fish and other oceanic animals.
- Wadge Bank measures approximately 3,000 square km, and is about 189 km from
- Wadge Bank came to India as part of the second of the two accords signed with Sri Lanka in the 1970s
Devika
Context
In a significant development, Mufeed VH, an Indian developer, has introduced Devika, an open-source AI software engineer, challenging the position of Devin, hailed as the world's first fully autonomous AI software engineer.
About
About Devika
- Devika is an Agentic AI Software Engineer who can understand high-level human instructions, break them down into steps, research relevant information, and write code to achieve the given objective.
- Devika aims to be a competitive open-source alternative to Devin by Cognition AI.
|
About Devin
|
Exchange Traded Currency Derivative
Context
A notification from the RBI on hedging of foreign currency risk caused a stir among market as it restricted the use of exchange traded currency derivative.
What is ETD?
- An Exchange Traded Derivative is a standardised financial contract that is traded on stock exchanges in a regulated manner.
- They are subject to the rules drafted by market regulators such as the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI).
|
Fact Box: Derivatives
|
Megadroughts
Context
A new modelling has revealed startling details about Australia as the continent heads for unprecedented drought conditions (megadroughts) that could last over two decades.
What are Megadroughts?
- Megadroughts are persistent, multi-year drought events that stand out as especially extreme in terms of severity, duration, or spatial extent when compared to other droughts of the last two thousand years
- Megadroughts have occurred on every continent outside of Antarctica, often causing major disturbances to ecosystems (e.g., forests in the Southwest U.) and societies (e.g., the Maya in Central America, the Ming Dynasty in northern China).
Meghalaya’s network of ancient caves
Context
Meghalaya’s network of ancient caves is facing environmental threats.
Important Caves in Meghalaya
- Meghalaya is called the Abode of the Clouds or Scotland of the East.
- Meghalaya has the highest number of caves in India, there are more 1,700 registered caves including:
- Krem Puri, the world’s longest sandstone cave.
- Krem Um Ladaw, which has the deepest shaft of any cave in the world.
- Neolissochilus Pnar, discovered recently, is the world’s largest cave fish.
- Liat Prah limestone cave, the longest cave
- Mawmluh Cave, locally known as Krem Mawmluh, is located in the Cherrapunji-Mawsynram area, known as the world’s wettest region.
- It is part of the region’s extensive network of limestone and rare sandstone caves, which are vital components of the eco-sensitive Hindu Kush Himalaya (HKH) region.
- Mawmluh Cave is identifiedas a geological heritage site by the International Union of Geological Sciences, a council that works closely with
- Favourable conditions: The state has all the ideal conditions for such formations to thrive: High-grade limestone, rainfall, and elevation, complete with a hot and humid climate.
|
Fact Box: Meghalayan Age
|
TERMS OF THE DAY
|
S.No. |
Term |
About |
|
1. |
AI chatbot |
An AI chatbot is an online program that can simulate human-like customer interactions on mobile apps and websites through the use of NLP and Machine Learning. |
|
2. |
Body Temperature
|
It is a measure of how well human body can make and get rid of heat. Normal human body temperature stays within a narrow range of 36.3-37.3 degrees C. It maintains thermal balance through radiation (40%), evaporation (30%), convection (27%), and conduction (3%). |
|
3. |
Domestic Value Added |
Domestic value added in gross exports is an estimation of value added, by an economy, in producing goods and services for export, simply defined as the difference between gross output at basic prices and intermediate consumption at purchasers' prices. |
|
4. |
Hindu Kush Himalayas (HKH) |
The Hindu Kush Himalayas (HKH) are the freshwater towers of South Asia and parts of Southeast Asia. Water originating from their snow, glaciers and rainfall feed the ten largest river systems in Asia. They stretch over 3500 kilometres and across eight countries – Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, China, India, Nepal, Myanmar and Pakistan |
|
5. |
Emerging Market and Developing Economies (EMDEs) |
An emerging market economy is one in which the country is becoming a developed nation and is determined to improve many socio-economic factors. |
Editorial
People are losing control over phones
Context:
The increasing dominance of mobile apps and app stores in the digital ecosystem has raised concerns about user privacy, security, and control over personal data.
Evolution of Internet Access:
- Early Internet Design: The Internet was initially designed to operate in a distributed manner, empowering individual machines to connect and interact without centralized control.
- Increased accessibility: Services such as emails, websites, and chats flourished, facilitating information sharing and e-commerce, driven by the accessibility and standardization of protocols and languages.
- App Space: However, the rise of mobile devices prompted a shift towards native mobile apps, leading to the introduction of app stores and a shift in control dynamics.
Challenges and Antitrust Cases:
- Scrutiny: App stores, acting as gatekeepers, have faced scrutiny and legal challenges for imposing high app taxes and allegedly abusing their dominant positions.
- Privacy concerns: Cases against tech giants like Google and Apple highlight concerns over control, revenue sharing, and user privacy within the app ecosystem.
- Reconsideration: The ongoing battle between businesses, app stores, and regulatory bodies underscores the need for users to reconsider the reliance on apps and advocate for alternatives such as web browsers for accessing internet services.
Editorial
Poll campaigns in India must reflect climate issues
Context:
The recently released State of the Global Climate report by the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) highlights 2023 as the hottest year in recorded history, raising concerns over the alarming rise in global temperatures and its adverse impacts.
Temperature Records and Environmental Impacts:
- Worrisome findings: The WMO report confirms 2023 as the warmest year on record, accompanied by numerous records being broken in areas like ocean temperatures, glacier retreat, and diminishing Antarctic ice cover.
- Rising sea levels and increased frequency of extreme weather events like heat waves, torrential rains, and tropical cyclones further underscore the severity of climate change's impacts.
- Impact on socio-economic activities: These events disrupt various socio-economic activities, including agriculture, posing significant challenges to global development.
Election Season as an Opportunity:
- Discussion: Amidst election season in many democracies, including India, the WMO report serves as a timely catalyst to initiate discussions on climate change across the political spectrum.
- Public awareness: Political parties have the opportunity to commit to enhancing public awareness on climate change and outlining concrete steps to mitigate global warming.
- Integral element: Addressing climate change becomes integral to India's pursuit of global leadership and economic prosperity, and political parties should incorporate climate action plans into their election agendas.
Editorial
A reform window: On the GST trajectory
Context:
Recent financial data reveals robust growth in revenue collections for the financial year 2023-24, with significant increases in both net direct tax collections and Goods and Services Tax (GST) revenues.
Strong Revenue Performance:
- Direct Tax and GST Collections: Net direct tax collections surged by 19.9% by mid-March, reaching 97% of the revised Budget targets for the financial year.
- GST revenues stood at a robust Rs20.18 lakh crore, with gross GST revenues in March crossing Rs1.78 lakh crore, marking the second highest tally since the rollout of GST six and a half years ago.
- Average monthly collections in 2023-24 have grown by 11.6% to over Rs1.68 lakh crore, setting a new revenue normalcy for the coming fiscal year.
Factors Driving Revenue Growth:
- Tax evasion: Increased collections may partly result from tax demands raised for past years and intensified efforts to curb tax evasion, particularly through measures targeting fake invoices and fraudulent input tax credits.
- Growth in net GST revenues and rising gross collections from domestic transactions indicate heightened economic activity in the last quarter of 2023-24.
- Reform: The strong revenue trajectory offers the government an opportunity to focus on essential reforms to the tax system, including rationalizing multiple GST rates, expanding its scope to include excluded items like electricity and petroleum products, and reducing high levies on key products such as cement and insurance.

 5 Questions
5 Questions 5 Minutes
5 Minutes




