4th April 2024
- Published
04 April 2024 -
 Download PDF
Download PDF
Disaster Relief Funds & Delay
Context
The Tamil Nadu government has moved the Supreme Court against the Centre for allegedly not releasing relief funds for damages caused by the recent floods and cyclone Maichung. The inaction on the part of the Centre is ex-facie illegal, arbitrary and violative of fundamental rights guaranteed to its citizens under Article 14 and Article 21 of the Indian Constitution.
1: Dimension-Centre's Constitutional Responsibilities in Disaster Times
- The constitutional framework governing Centre-State relations in disaster management is not explicitly outlined in the Seventh Schedule of the Constitution.
- Disaster management does not fall under any of the three lists – Union, State, or Concurrent.
- Since disaster management is not mentioned in any of the lists, it falls under the residuary powers of the Union government as per Article 248 of the Constitution.
- The Disaster Management Act, 2005 was enacted by the Union government by tracing its legislative competence to the Concurrent List entry on “Social security and social insurance; employment and unemployment.”
- The primary responsibility for disaster management rests with the states.
- The Centre plays a supportive role by providing financial assistance, technical expertise, and coordination between multiple states during disasters, as mandated by the Act
- NDMA: The Act established the National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA) as the apex body for disaster management in India, with the Prime Minister as its chairperson.
- SDMA: At the state level, the Act mandated the creation of State Disaster Management Authorities (SDMAs), headed by the Chief Ministers.
2: Dimension- Issues arising out of debate
- Central vs. State Responsibilities in DM: The case highlights the debate regarding the division of responsibilities between the Central and State governments in managing natural disasters.
- Financial Assistance and Relief Funds: It raises questions about the adequacy and timeliness of financial assistance provided to states affected by natural calamities. This issue reflects on the effectiveness of disaster management policies and procedures in the country.
- Principles of distributive justice: The allegation of differential treatment and class discrimination in the release of funds underscores the importance of equity and fairness in resource allocation during times of crisis.
- Constitutional and Legal Remedies: Tamil Nadu’s decision to approach SC highlights the role of constitutional and legal mechanisms in resolving disputes between the Centre and the states.
- Impact on development and public welfare: Delayed relief efforts hamper state's development and affect public welfare.
|
Fact Box: Constitutional Articles involved in the dispute
|
State’s Borrowing Limits and Challenges
Context
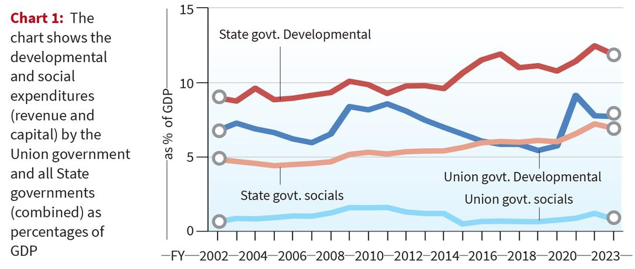
Kerala recently approached the Supreme Court regarding the permissible borrowing limits for State governments. It challenges the Centre’s stance, which restricts the State's borrowing capacity to 3% of its income or Gross State Domestic Product (GSDP). Kerala argues that such limitations infringe upon its ability to meet essential financial obligations and violate the principle of federalism.
1: Dimension- Concerns highlighted by Kerala’s plea
- Federal Fiscal Relations: The dispute between Kerala and the Union government underscores the complexities of fiscal federalism in India.
- State Expenditure Priorities: The significant disparity between Union and State government spending, particularly in social sectors like health and education, raises questions about allocation priorities and the respective roles of different tiers of government in addressing societal needs.
2: Dimension- Complex Resource Sharing System in India:
In resource sharing, there are majorly four kinds of flows:
- Statutorily Defined Share for States: Defined set of tax revenues garnered by the Centre is shared with States as per recommendations of Finance Commissions. Principles governing the share devolved and distributed to individual States.
- Statutorily Mandated Grants: Includes revenue deficit grant to identified States to cover revenue account gap post-devolution. Grants-in-aid to States have decreased from Rs.1,95,000 crore in 2015-16 to Rs.1,65,000 crore in 2023-24.
- Discretionary Spending: Previously mediated by the Planning Commission, now solely at the discretion of the Centre. Involves Centre’s share of expenditure in Centrally sponsored schemes implemented in States, with States meeting a specified proportion of projected expenditure.
- Central Sector Schemes: Implemented by Centre in individual States' jurisdictions, with all expenditure met by Central government.
3: Dimension- Significance/Need of State’s spending:
Kerala's plea prompts broader discussions on the role of government spending in fostering economic growth.
- Economic growth: Spending by the states has helped to alleviate the livelihood crisis in India, caused due to the slow growth of rural incomes and employment.
- Positive transformation: State’s spending positively transform a region’s economy and society.
- Social growth: A sizeable chunk of the government expenditure on social services is in the revenue account, paid as salaries and for covering day-to-day expenses. In states, teachers, nurses, and other government employees are key drivers of social achievements.
|
Fact Box: The Spending Structure
|
PRATUSH - India's Moon based Telescope
Context
Astronomers are looking forward to opening a new window on the universe by posting high-resolution telescopes on the moon, and in orbit around it. One such proposal, PRATUSH, hails from India.
1: Dimension-Challenges for Earth-based Telescopes:
- Earth-based telescopes, optical telescopes (which collect visible light at longer wavelengths) and radio telescopes (which collect radio waves with the shortest wavelengths), face hurdles due to the atmosphere's interference.
- Optical telescopes struggle with pollution, while radio telescopes contend with electromagnetic interference from various sources, including communication signals.
- It also does not help that the earth’s ionosphere blocks radio waves coming from outer space.
2: Dimension-Benefits of placing telescope on Moon
- Scientists are considering placing optical and radio telescopes on the far side of the moon, which always faces away from the earth.
- Clear visibility: The pristine, airless desolation of the moon provides optical telescopes crystal-clear seeing conditions throughout the long lunar night.
- Protection: Radio telescopes on the lunar far side will also be protected by the moon (its diameter is 3,476 km) — that blots out radio transmissions from the earth and electrically charged plasma winds blowing from the Sun.
- It promises the most radio-quiet location in the solar system.
|
Fact Box: About PRATUSH
|
US-UK Partnership on AI
Context
The United States and Britain announced a new partnership on the science of artificial intelligence safety, amid growing concerns about upcoming next-generation versions.
What is the partnership on AI safety, testing?
- Objective: to jointly develop advanced AI model testing.
- This is the first agreement of its kind anywhere in the world.
- Under the formal partnership, Britain and the United States plan to perform at least one joint testing exercise on a publicly accessible model and are considering exploring personnel exchanges between the institutes. Both are working to develop similar partnerships with other countries to promote AI safety.
- Both countries will share vital information about the capabilities and risks associated with AI models and systems, according to the agreement, which has taken effect immediately.
- They will also share fundamental technical research on AI safety and security with each other, and work on aligning their approach towards safely deploying AI systems.
Need of the Initiative
- The move comes as the world is figuring out a way to set guardrails around the fast proliferation of AI systems.
- Although these systems offer opportunities, they pose a significant threat to a number of societal set-ups, from misinformation to election integrity.
AI Regulation around the world
- As the private industry innovates rapidly, lawmakers around the world are grappling with setting legislative guardrails around AI to curb some of its downsides.
- India: The IT Ministry issued an advisory to generative AI companies deploying “untested” systems in India to seek the government’s permission before doing so.
- However, after the government’s move was criticised by people from across the world, the government scrapped the advisory and issued a new one which had dropped the mention of seeking government approval.
- EU: Last year, the EU reached a deal with member states on its AI Act which includes safeguards on the use of AI within the EU, including clear guardrails on its adoption by law enforcement agencies.
Glacial Lake outburst
Context
The Uttarakhand government has decided to evaluate the risk posed by five potentially hazardous glacial lakes in the region. These lakes are prone to Glacial Lake Outburst Floods (GLOFs), the kind of events that have resulted in several disasters in the Himalayan states in recent years.
What is Glacial Lake outburst?
- When the boundary around unstable glacial lake breaks, and huge amounts of water rush down the side of the mountains, which could cause flooding in the downstream areas.
- This is called glacial lake outburst floods or GLOF.
- Factors causing GLOF:
- GLOF can be triggered by several reasons, including earthquakes, extremely heavy rains and ice avalanches.
- These lakes are also often found in steep, mountainous regions, which means landslides or ice avalanches can sometimes fall directly into the lakes and displace the water, causing it to over-top the natural dam and flood downstream.
- Features of GLOF:
- They involve sudden (and sometimes cyclic) releases of water.
- They tend to be rapid events, lasting hours to days.
- They result in large downstream river discharges (which often increase by an order of magnitude).
Onion Exports
Context
India has allowed onion exports to a few countries on priority in response to diplomatic requests, but it will continue to ban overseas shipments amid projections of lower output for two years in a row.
Onion Production in India
- Rabi or winter-harvested onion is critical for country’s availability as it contributes 72-75% of India’s annual production.
- It is also crucial for ensuring year-round availability as it has a better shelf life compared to kharif or summer onion, and therefore can be stored for supplies till November-December.
- India is the world’s largest exporter of onion.
- Projection of lower output: India is expected to harvest 19.3 million tonnes of rabi or winter-grown onions during 2023-24, which is about 18% lower than the production of 23.6 million tonnes in the previous season.
|
Fact Box
|
|
UPSC PYQ: (Changing pattern) |
|
|
Q: Consider the following crops: (UPSC 2013)
Which of these are Kharif crops? (c) 1,2 and 3 (d) 2, 3 and 4 |
Consider the following statements: (UPSC 2021) 1. Moringa (drumstick tree) is a leguminous evergreen tree. 2. Tamarind tree is endemic to South Asia. 3. In India, most of the tamarind is collected as minor forest produce. 4. India exports tamarind and seeds of moringa. 5. Seeds of moringa and tamarind can be used in the production of biofuels. Which of the statements given above are correct? a) 1, 2, 4 and 5 b) 3, 4 and 5 c) 1, 3 and 4 d) 1, 2, 3 and 5 Solution: (c) |
India’s First Commercial Crude Oil Strategic Storage
Context
India, the world's third biggest oil consumer and importer, plans to build its first commercial crude oil strategic storage as part of efforts to shore up stockpiles as insurance against any supply disruption.
About
- India, which meets over 85 per cent of its oil needs through imports, will use the strategic reserves in any emergency situation like supply disruption or war.
- This approach mirrors the models adopted by countries like Japan and South Korea, allowing private lessees, predominantly oil majors, to engage in crude oil trading.
- The expansion of oil storage capacity also aligns with India’s aspiration to become a member of the International Energy Agency (IEA), necessitating members to maintain a minimum of 90 days of oil consumption.
|
Fact Box: International Energy Agency (IEA)
|
TERMS OF THE DAY
|
S.No. |
Term |
About |
|
1. |
Federalism |
Federalism is a system of government in which the power is divided between a central authority and various constituent units of the country. |
|
2. |
Gross State Domestic Product (GSDP) |
Gross State Domestic Product (GSDP) or State Income is a measure in monetary terms, the sum total volume of all finished goods and services produced during a given period of time, usually a year, within the geographical boundaries of the State, accounted without duplication. |
|
3. |
Ionosphere |
Ionosphere is part of Earth's upper atmosphere, between 80 and about 600 km where Extreme UltraViolet (EUV) and x-ray solar radiation ionizes the atoms and molecules thus creating a layer of electrons. It is important because it reflects and modifies radio waves used for communication and navigation. |
|
4. |
Radio waves |
Radio waves are a type of electromagnetic radiation. The best-known use of radio waves is for communication. Radio waves are used for wireless transmission of sound messages, or information, for communication, as well as for maritime and aircraft navigation. |
|
5. |
Strategic petroleum reserves (SPRs) |
Strategic petroleum reserves (SPRs) are stockpiles of crude oil maintained by countries for release in the event of a supply disruption. |
Editorial
West against the rest
Context:
NATO celebrates its 75th anniversary, but controversy surrounds its legacy and actions.
NATO's History of Aggression
- Formation objective: NATO, established to defend member states, has a history of offensive military actions.
- Doubts about NATO’s pursuit of peace: It has been involved in over 200 military conflicts worldwide, often leading to destruction and human suffering.
- Examples: Examples include the bombing of Yugoslavia, invasion of Iraq, and intervention in Syria, raising questions about its pursuit of peace.
Escalating Tensions and Provocative Actions
- Concerning expansion: Despite assurances, NATO has expanded its reach, particularly towards Russia, heightening tensions.
- Provocative actions: The alliance's aggressive stance and military build-up in Eastern Europe and beyond have been viewed as provocative.
- Geopolitical tensions: NATO's strategic concept identifies Russia as a significant threat, further exacerbating geopolitical tensions.
Calls for Constructive Dialogue and Cooperation
- Dialogue to address security concerns: Russia advocates for constructive dialogue and mutual respect to address security concerns.
- Cooperation: It emphasizes the importance of cooperation over confrontation in maintaining global stability.
- Reconsideration: There is urgent need for NATO to reconsider its approach and prioritize cooperation to foster a sustainable system of European and global security.
Editorial
Turning the spotlight on the urban poor
Context:
The India Employment Report (IER) 2024, released by the Institute for Human Development and International Labour Organization, sheds light on the disparity in employment and income between rural and urban areas amidst a 5.4% average real economic growth from 2015-16 to 2022-23.
Findings and Trends:
- Trend Analysis: The IER 2024 reveals a divergent trend between rural and urban areas, with a relatively higher unemployment rate observed in urban areas, contrasting with higher average monthly earnings for self-employed, regular employed, and casual labor in urban regions.
- Migration Patterns: Despite overall migration increasing, there's been a decline in male migration for economic mobility, particularly towards urban areas. Instead, rural poor households tend to migrate to slums, highlighting the need to analyze income and employment trends among slum dwellers.
- Survey Results: A survey conducted in Kolkata's slums between 2012 and 2022-23 showcased stable major occupations like unskilled labor, alongside notable shifts such as a rise in petty businesses and construction work. Income trends depict varied fluctuations across different employment categories, suggesting evolving economic dynamics in urban slums.
Implications and Recommendations:
- Need for Gainful Employment: The decline in income across certain sectors underscores the necessity for viable employment options, particularly for medium to large shop owners who have witnessed a decrease in real income.
- Gender Composition and Casual Work: While casual labor has seen a rise due to increasing wages, it lacks adequate work conditions and social security. The decline in inequality alongside falling income signals deeper poverty among the urban poor, necessitating enhanced public support for accessible employment and basic necessities.
- Policy Focus: Focusing on rural non-farm sectors and providing support for gainful employment and affordable essentials in urban areas becomes imperative to address the challenges of economic mobility and quality of work for the urban poor highlighted in the IER 2024.
Editorial
Systems science for a better future
Context:
The Pew Research Center's survey in 2023 on citizens' preferences for authoritarian rulers versus multi-party democracy reveals concerning trends across various countries, including significant support for dictatorial leadership in both the Global South and the West.
Survey Findings:
- Preference for Authoritarianism: The survey highlights substantial support for authoritarian rulers in countries like India, Indonesia, South Africa, and Brazil in the Global South, with a significant percentage of citizens favoring dictators over multi-party democracy. Surprisingly, even in Western democracies like the United Kingdom and the United States, a notable proportion of respondents expressed preference for authoritarian leadership.
- Economic Discontent: Citizens' waning trust in their governments' economic policies is evident, with growing income inequality and the concentration of wealth among the very rich. Large corporations and financial institutions wield considerable influence, shaping government policies to favor their interests, which exacerbates economic disparities and environmental exploitation.
- Environmental Concerns: The survey underscores the looming environmental crisis, exacerbated by rapid global economic growth and population expansion. Scientists warn of the unsustainable use of fossil energy and the depletion of vital resources like water, particularly in countries like India, which faces severe water scarcity despite its significant population share.
Challenges and Recommendations:
- Fragmented Sciences: The fragmentation of sciences into narrow silos impedes holistic understanding of complex systems, including social, economic, and environmental dynamics. A lack of interdisciplinary collaboration hinders comprehensive solutions to multifaceted challenges, such as the interplay between democracy, capitalism, and environmental sustainability.
- Economic Ideologies: The rise of free market fundamentalism has entrenched economic ideologies that prioritize capital interests over human welfare and environmental conservation. Narrow economic perspectives fail to address systemic inequalities and environmental degradation, perpetuating unsustainable growth models.
- Need for Holistic Approaches: Addressing contemporary global challenges requires a paradigm shift towards holistic, systems-based approaches that integrate diverse perspectives and promote cooperation over competition. Embracing a science of self-adaptive systems and fostering organizations driven by cooperation rather than competition can facilitate sustainable solutions to complex societal and environmental issues.

 5 Questions
5 Questions 5 Minutes
5 Minutes




