What share of global CO2 emissions come from aviation?
Context
Aviation, despite constituting only a fraction of global carbon emissions, has a disproportionate impact on climate change. Understanding the dynamics of aviation emissions is crucial in devising strategies to mitigate its environmental impact.
1: Dimension - Historical Trends
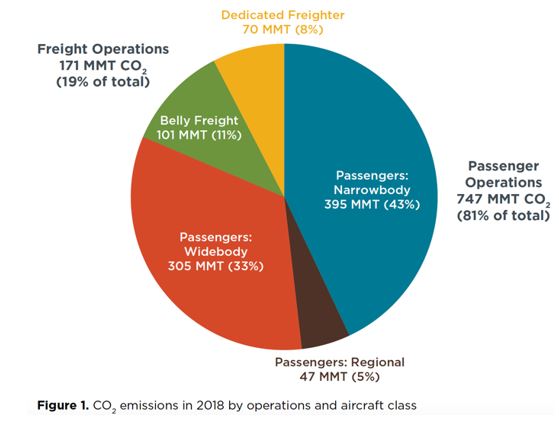
- Surge in Aviation Demand: Between 1990 and 2019, global aviation demand, encompassing both passenger and freight travel, experienced a fourfold increase. This surge reflects evolving travel patterns and economic growth, driving higher air travel volumes.
- Enhanced Energy Efficiency: Over the same period, aviation witnessed significant improvements in energy efficiency, with flying becoming more than twice as energy-efficient. Advancements in technology, aircraft design, and improved load factors contributed to this enhancement.
- Influence of Technological Advancements: The aviation sector's evolution, marked by innovations in aircraft design and propulsion systems, has played a pivotal role in improving energy efficiency. Larger aircraft with higher passenger capacity and streamlined operations have contributed to reduced emissions per passenger-kilometer.
2: Dimension - Carbon Intensity
- Persistence of Carbon-Intensive Fuels: Despite advancements in aviation technology, the sector continues to rely predominantly on carbon-intensive jet fuels. The limited integration of cleaner alternatives like biofuels underscores challenges in reducing carbon intensity.
- Need for Sustainable Fuel Solutions: Addressing aviation's carbon intensity necessitates a concerted effort to explore and implement sustainable fuel solutions. Biofuels and synthetic fuels show promise but require scaling up to make a substantial impact on emissions reduction.
- Regulatory Frameworks for Emission Reduction: Effective regulation and policy frameworks are crucial in incentivizing the adoption of cleaner fuels and technologies. Government initiatives, coupled with industry collaboration, can accelerate the transition towards low-carbon aviation.
3: Dimension - Impact on CO2 Emissions
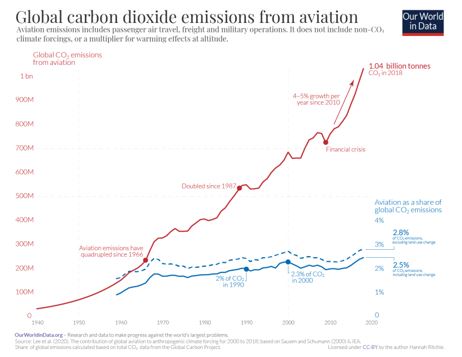
- Doubling of Emissions: Despite improvements in energy efficiency, the exponential growth in aviation demand has resulted in a doubling of CO2 emissions since 1990. This underscores the challenge of reconciling economic growth with environmental sustainability.
- Global Emission Trends: In 2019 alone, global aviation emitted approximately 1 billion tonnes of CO2, marking a significant contribution to overall emissions. The sector's emissions trajectory reflects broader trends in transportation and energy consumption.
- Urgency of Mitigation Strategies: Mitigating aviation emissions requires urgent action, encompassing technological innovation, policy intervention, and industry collaboration. Efforts to decarbonize aviation must align with global climate goals to limit temperature rise and mitigate environmental degradation.
UPSC Mains Practice Question
Q. Discuss the historical trends, carbon intensity, and impact on CO2 emissions of the aviation sector, highlighting the urgency of mitigation strategies to address its environmental impact.
India to get above-normal monsoon rainfall: IMD
Context
While several States reel under heatwaves, the India Meteorological Department (IMD) has forecast a bountiful monsoon for the year.
Key-highlights of the Forecast
- Above-Normal Rainfall: The IMD predicts that the rainfall in June-September will be 6% more than the annual average of 87 cm during these months.
- Impact of El Nino: Last year, El Nino affected India’s monsoon negatively by denting it by 6%. However, this year, the El Nino is expected to fade by June, progressing to La Nina, which usually results in surplus rainfall by the second half of the monsoon.
- Forecasting Methods: The IMD utilizes statistical associations and a dynamical approach to forecast the monsoon. Both methods indicate a similar outlook for the monsoon this year.
- Updated Forecast: The IMD is expected to update its monsoon forecast in May, just ahead of the monsoon onset in June, providing more information on spatial distribution.
- Factors Favoring Rainfall: Positive Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD) and below-normal snow cover in the northern hemisphere and Eurasia are factors favoring plentiful rain in India.
1: Dimension - Factors Influencing Monsoon Forecast
- El Nino Impact: Last year, El Nino dampened India’s monsoon by 6%. However, this year, while El Nino has not fully faded, it is expected to transition to La Nina by June. La Nina typically brings surplus rainfall in the latter half of the monsoon season.
- Positive Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD): A positive IOD, characterized by cooler than normal temperatures in the eastern Indian Ocean, is favorable for bringing rainfall to southern India. Although currently neutral, it is anticipated to turn positive by August, enhancing monsoon rainfall.
2: Dimension - Dynamical Approach
- Simulating Weather Patterns: The dynamical approach involves simulating weather patterns across the globe and using powerful computers to extrapolate this weather into future time periods.
- Computational Modeling: Sophisticated computational models are employed to simulate atmospheric conditions and predict weather phenomena, enhancing the accuracy of monsoon forecasts.
- Integration of Data Sources: Data from various sources, including satellite observations, ground-based weather stations, and ocean buoys, are integrated into dynamical models to improve forecasting capabilities.
3: Dimension - Implications for Agriculture and Economy
- Importance of June and July: June and July are critical months for agriculture, especially for the kharif crop, as a significant portion is planted during this period. Above-normal rainfall during these months can boost agricultural productivity and contribute to economic growth.
- Spatial Distribution: IMD plans to provide updated forecasts in May, just before the onset of the monsoon season in June. These forecasts will offer insights into the spatial distribution of rainfall across different regions, aiding agricultural planning and water management.
- Potential for 'Excess' Rainfall: The models suggest a 30% chance of rainfall exceeding 10%, categorized as 'excess' by IMD standards. Such abundant rainfall could have both positive and negative impacts, affecting agriculture, infrastructure, and flood management.
- Crop Planning: Farmers rely on monsoon forecasts to plan their cropping patterns, irrigation schedules, and input procurement, ensuring optimal utilization of resources and maximizing yields.
- Risk Mitigation Strategies: Access to accurate monsoon forecasts enables policymakers and agricultural stakeholders to implement risk mitigation strategies, such as crop insurance schemes and water management initiatives, to mitigate the impact of weather variability on agricultural livelihoods.
|
Measurement of Normal to average rainfall:
|
|
El Nino Southern Oscillation (ENSO):
|
|
Monsoon Trough:
|
Mains Practice Questions
Q. "Effective agricultural planning hinges on accurate monsoon forecasts." Discuss the significance of monsoon forecasts for Indian agriculture, elucidating the implications for farmers and food security.
EC pegs pre-poll seizure at ?4,650 cr.
Context
The Election Commission (EC) announced significant seizures of inducements, including drugs and cash, ahead of the elections, reflecting its commitment to ensuring electoral integrity.
Key-highlights of the Seizures
- Record-Breaking Seizures: The EC reported seizures amounting to ?4,650 crore, surpassing the figure recovered during the previous Lok Sabha election in 2019.
- Composition of Seized Items: The seized amount includes drugs worth ?2,069 crore, cash exceeding ?395 crore, and liquor valued at more than ?489 crore, highlighting the diverse nature of inducements.
- Daily Seizure Rate: Since March 1, the EC has been seizing goods worth ?100 crore every day, indicating proactive enforcement measures.
- Emphasis on Drug Seizures: Approximately 75% of the total seizures in January and February comprised drugs, underscoring the EC's focus on combating the nexus between drugs and electoral malpractices.
1: Dimension - Enforcement Efforts
- Comprehensive Planning: The EC attributed the successful seizures to comprehensive planning, collaborative efforts among agencies, proactive citizen participation, and optimal utilization of technology.
- Scaled-Up Collaboration: Enhanced collaboration among law enforcement agencies, electoral authorities, and citizens facilitated efficient seizure operations, ensuring a robust response to electoral malpractices.
- Unified Deterrence Action: Unified deterrence actions, backed by stringent enforcement measures, served as a deterrent against electoral misconduct, promoting a level playing field for all political stakeholders.
2: Dimension - Electoral Integrity
- Threat of Black Money: The EC cautioned against the use of black money and excessive political financing, emphasizing its potential to skew the electoral process in favor of resourceful parties or candidates.
- Ensuring Level Playing Field: The seizures underscored the EC's resolve to conduct elections free from inducements and malpractices, aiming to maintain a level playing field and uphold the integrity of the electoral process.
- Standard Procedures: Standard procedures, such as the checking of helicopters carrying political leaders, were implemented to prevent inducements and ensure adherence to electoral guidelines, promoting transparency and fairness.
3: Dimension - Mitigating Electoral Malpractices
- Inducement-Free Polls: The seizures were integral to the EC's efforts to conduct inducement-free polls, mitigating the influence of illegal inducements on electoral outcomes and preserving the sanctity of the electoral process.
- Level-Playing Field Assurance: By actively curbing inducements and electoral malpractices, the EC reaffirmed its commitment to maintaining a level-playing field, fostering electoral competition based on merit and policy agendas.
- Standardized Checks: Standardized checks, including helicopter searches, were conducted to uphold electoral integrity, ensuring adherence to electoral guidelines and deterring attempts to influence voters through inducements.
Mains Practice Question
Q. Analyze the role of comprehensive planning and collaborative efforts among law enforcement agencies in curbing electoral malpractices. How can enhanced cooperation further strengthen the electoral process?
How India’s beaches can unlock a nuclear-powered future
Context
As the nation seeks to balance energy security with environmental concerns, the exploration of thorium as a fuel source gains significance. The Indigenous Prototype Fast Breeder Nuclear Reactor exemplifies India's efforts to harness thorium for a cleaner, more sustainable future.
1: Dimension- Thorium's Role in Energy Security
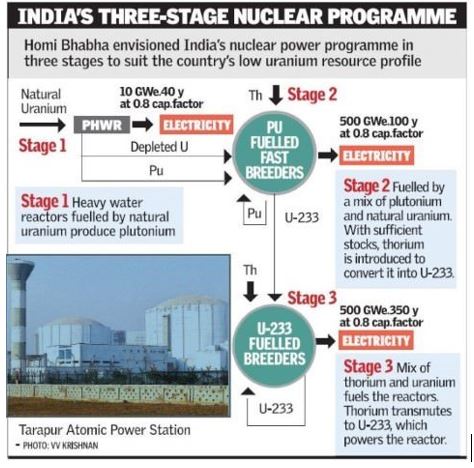
- Thorium is hailed as a practically inexhaustible energy source that emits no greenhouse gases, making it a sustainable alternative.
- India's extensive thorium deposits present an opportunity to reduce dependence on the uncertain uranium supply chain.
- The three-stage nuclear power programme aims to utilize thorium as a primary fuel, ensuring long-term energy security.
2: Dimension- Global Competition and Cooperation
- China's advancements in molten salt thorium nuclear reactor technology highlight the global race in thorium-based systems.
- Despite past hesitations, renewed collaboration between India and the US signals potential advancements in nuclear energy technology.
- Negotiations with other countries like France, Canada, and Russia showcase India's efforts to diversify its nuclear partnerships.
3: Dimension- Challenges and Opportunities
- Commercial utilization of thorium hinges on the availability of Uranium-233 or Plutonium resources, posing a technological challenge.
- India's efforts in thorium research and development aim to overcome technical barriers and accelerate progress towards commercial viability.
- Thorium-based systems offer immense potential in decarbonizing India's energy sector and achieving sustainable development goals.
4: Dimension- International Engagement and Diplomacy
- India's participation in international forums like the IAEA positions it as a key player in thorium-based systems.
- Leveraging its research and non-proliferation credentials, India can advocate for accelerated development of thorium-based technologies on the global stage.
Centre reveals forest records after 28 years; seven states miss deadline
Context
Earlier this year, the Supreme Court issued an interim directive to the Centre to refer to its understanding of ‘forest’ as “broad and all-encompassing” in order to classify India’s forests as per the order given in the T N Godavarman judgment of December 1996.
1: Dimension-Legal and Regulatory Framework
- Court Mandate: The Supreme Court directed a broad interpretation of ‘forest’ in line with the T N Godavarman judgment, necessitating an amendment to the Forest (Conservation) Act, 1980.
- Amendment: The Act was amended to Van Sanrakshan Evam Adhiniyam, 2023 by the Centre to bring clarity to the definition of ‘forest’ as per the Godavarman judgment.
- Enforcement Mechanisms: Strengthening enforcement mechanisms is essential to ensure adherence to the amended regulations and prevent forest degradation.
2: Dimension-Data Transparency and Completeness
- Uniform Reporting Standards: Standardized guidelines are imperative to promote transparency and uniformity in reporting forest records across states.
- Public Access to Information: Making forest records easily accessible to the public fosters accountability and enhances public participation in conservation efforts.
- Accuracy and Precision: Geo-referencing and clear demarcation of forest areas are necessary to facilitate accurate monitoring and management of forest resources.
3: Dimension-Impact on Environmental Conservation
- Ecological Ramifications: Inadequate identification and protection of forest areas can lead to irreversible ecological damage and loss of biodiversity.
- Community Welfare: Effective forest conservation measures are essential for ensuring the well-being of local communities dependent on forest resources for their livelihoods.
- Global Implications: India's forest conservation efforts have significant implications for global climate change mitigation and sustainable development goals.
4: Dimension- Required measures
- Standardization of Data
- Centralized Guidelines: Establishing centralized guidelines for data collection and reporting ensures consistency and reliability in forest records.
- Capacity Building: Providing training and resources to state agencies improves their capacity to collect, analyze, and report forest data accurately.
- Integration of Technology: Leveraging technology such as GIS mapping enhances the accuracy and efficiency of forest monitoring and management efforts.
- Enhanced Monitoring and Enforcement
- Surveillance Systems: Implementing robust surveillance systems helps in detecting and preventing illegal activities such as encroachments and deforestation.
- Collaborative Enforcement: Collaboration between law enforcement agencies, forest departments, and local communities strengthens enforcement efforts and promotes accountability.
- Swift Action: Prompt action against violators of forest conservation laws deters future infringements and protects vulnerable forest ecosystems.
- Public Awareness and Participation
- Stakeholder Engagement: Engaging stakeholders, including local communities, NGOs, and academia, fosters a sense of ownership and collective responsibility towards forest conservation.
- Educational Initiatives: Promoting environmental education and awareness programs enhances public understanding of the importance of forests and encourages sustainable practices.
- Community Empowerment: Empowering local communities with rights and responsibilities over forest resources promotes sustainable forest management practices and strengthens conservation efforts.
|
Classification of Forest by FSI:
|
Mains Practice Question
Q: Assess the implications of the Supreme Court's directive to reinterpret the definition of 'forest' in India and the challenges faced in implementing the amended regulations.
Arctic Council
Context
India’s maiden winter expedition at the Arctic have put the focus back on cooperation with Arctic circle countries and related governance architecture.
About Arctic Council
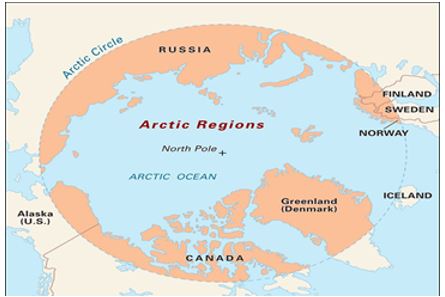
- The Arctic Council is the leading intergovernmental forum promoting cooperation, coordination and interaction among the Arctic States, Arctic Indigenous Peoples and other Arctic inhabitants on common Arctic issues, in particular on issues of sustainable development and environmental protection in the Arctic. It was formally established in 1996.
- All Arctic Council decisions and statements require consensus of the eight Arctic States.
- The Arctic Council is a high-level intergovernmental body set up in 1996 by the Ottawa declaration to promote cooperation, coordination and interaction among the Arctic States together with the indigenous communities and other Arctic inhabitants.
- Arctic Councilis an intergovernmental forum that addresses issues faced by the Arctic governments and the indigenous people of the Arctic.
- At present, eight countries exercise sovereignty over the lands within the Arctic Circle.
- Members of Arctic Council are- Canada, Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway, Russia, Sweden and United States.
- Headquarters of Arctic Circle is located at Tromso, Norway.
- Permanent participants:
- Aleut International Association (AIA),
- Arctic Athabaskan Council (AAC)
- Gwich'in Council International (GCI)
- Inuit Circumpolar Council (ICC)
- Russian Association of Indigenous Peoples of the North (RAIPN)
- Saami Council
- India has observer status since 2013.
|
Status of India’s presence in Arctic as of now?
|
WholeSale Price Inflation
Context
India’s wholesale price in- ?ation quickened to a three-month high of 0.53% in March, from 0.2% in February, with the food index rising 4.65%.
About WPI
- A wholesale price index (WPI) measures change in the overall price of goods before they are sold at retail.
- This includes the prices charged by manufacturers and, often outside the U.S., wholesalers.
- Usually expressed in terms of the percentage change from the prior month or a year earlier, the WPI is an inflation indicator.
- Wholesale price indexes are reported monthly to track the overall rate of change in producer and wholesale prices.
- The index is set at 100 for its base period, and calculated based on subsequent price changes for the aggregate output of goods.
How does it indicate Inflation? (WPI vs. CPI)
- A wholesale price index (WPI) is a measure of inflation based on the prices of goods before they reach consumers.
- It includes price rise in food, fuel and all other commodities. The inflation rate expressed in Wholesale Price Index (WPI) usually denotes the ‘headline inflation’.
- Though Consumer Price Index (CPI) values are often higher, WPI values traditionally make headlines.
- WPI tracks inflation at the producer level and CPI captures changes in prices levels at the consumer level. WPI does not capture changes in the prices of services, which CPI does.
- The WPI is dominated by the prices of manufactured goods while the CPI is dominated by the prices of food articles.
- As such, broadly speaking, if food prices go up sharply, it will bump up the retail inflation rate far more than it would spike the wholesale inflation rate. The reverse will happen when prices of manufactured products (such as TVs and cars) rise sharply.
|
Parrot Fish (Family: Scaridae)
Context
Parrotfish are colorful, tropical creatures that spend about 90% of their day eating algae off coral reefs. However it’s eating habit are proving to be a challenge for coral rejuvenation
About Parrot Fish
- Parrotfish are named for their dentition, which is distinct from other fish, including other labrids.
- Their numerous teeth are arranged in a tightly packed mosaic on the external surface of their jaw bones, forming a parrot-like beak with which they rasp algae from coral and other rocky substrates.
- The parrotfishes’ digestive system, which includes more teeth inside their throats breaks down coral bits into the white sands that make South Pacific beaches famous.
- IUCN Status: Can face localized extinction
Tiger Hill
Context
Iconic Tiger Hill near Darjeeling under ‘development’ threat, NGT pulls up government departments as it has been severely deteriorated due to unplanned activities.
About
- Tiger Hill is famous for watching sunrises on the background of Mt Kanchenjunga.
- It is part of the Senchal wildlife sanctuary, one of the oldest wildlife sanctuaries in the country that was established in 1915, holding two lakes that act as the main sources of drinking water to the town of Darjeeling.
- The hill is 2,590 meters high, 13 kilometers from Darjeeling.
LCA Mark 1A
Context
Defence ministry to procure 97 LCA Mark 1As from HAL in biggest-ever indigenous military equipment order.
About LCA
- Light Combat Aircraft Mk-1A variant is an indigenously designed, developed and manufactured state-of-the-art modern 4+ generation fighter aircraft.
- Tejas LCA Mk-1A will be superior over previous variants of LCA Tejas, in terms of avionics, performance, and weapons capabilities.
- This aircraft is equipped with critical operational capabilities of Active Electronically Scanned Array (AESA) Radar, Beyond Visual Range (BVR) Missile, Electronic Warfare (EW) Suite and Air to Air Refuelling (AAR).
- LCA Tejas Mk-1A will be flexible enough for hardware and software integration that would be required to fire different types of Beyond Visual Range (BVR), which are available in the inventory of the Indian Air Force (IAF).
- It is the first “Buy (Indian-Indigenously Designed, Developed and Manufactured)” category procurement of combat aircrafts with an indigenous content of 50% which will progressively reach 60% by the end of the programme.
TERM OF THE DAY
|
S.No. |
Term |
About |
|
1. |
Bioerosion |
Bioerosion describes the breakdown of hard ocean substrates – and less often terrestrial substrates – by living organisms. Marine bioerosion can be caused by mollusks, polychaete worms, phoronids, sponges, crustaceans, echinoids, and fish |
|
2. |
Waqf Board |
Waqf is a permanent dedication of movable or immovable properties for religious, pious or charitable purposes as recognized by Muslim Law. The Waqf Institutions deal with the religious, social and economic life of Muslims. |
|
3. |
Follow on Public Offer (FPO) |
A follow-on offering (FPO) is an issuance of stock after a company's initial public offering (IPO). |
|
4. |
Bleisure |
Bleisure is a travel trend that combines business and leisure travel, often by adding vacation days or activities to trips after meetings. |
|
5. |
Parkinson’s disease |
Parkinson's disease (PD) is a chronic brain disorder that affects the central nervous system's motor and non-motor systems. Symptoms include: Slow movement, Tremors, Involuntary movement, Rigidity, Trouble walking, Imbalance, Cognitive impairment, Mental health disorders, Dementia, Sleep disorders, and Pain |
|
6. |
Police State |
A police state describes a state whose government institutions exercise an extreme level of control over civil society and liberties. |
|
7. |
Climate litigation |
Climate litigation is a global movement that involves lawsuits against governments, fossil fuel firms, and airlines. The lawsuits are used to set precedents for climate action and shape climate policy. |
Editorial
India’s Arctic imperative
Context
India's heightened Arctic interest stems from environmental shifts, economic opportunities, and geopolitical dynamics. As Arctic ice melts, India eyes trade routes, balancing economic gains with environmental and strategic concerns amid global power competition. Crafting a nuanced Arctic policy becomes imperative for India.
Growing Interest in the Arctic:
- Environmental Concerns Driving Engagement:India's recent winter expedition to the Arctic highlighted its growing interest in the region, marked by a shift in policy due to alarming scientific data on Arctic warming.
- Economic Considerations: India sees potential benefits in utilizing Arctic Sea routes to reduce shipping costs and time, especially through the Northern Sea Route.
- Geopolitical Implications: Concerns over China's increasing presence in the Arctic and Russia's strategic decisions have led India to reassess its Arctic engagement in the context of geopolitical tensions.
India's Historical Engagement and Internal Debate:
- Historical Context: India has a longstanding engagement with the Arctic dating back to the signing of the Svalbard Treaty in 1920 and establishing research bases in subsequent years.
- Internal Debate: India's academic and policy communities are divided over the economic and environmental implications of increased Arctic engagement, particularly concerning resource exploitation.
- Need for Balanced Policy: The debate underscores the necessity for India to develop a balanced policy framework that addresses both economic interests and environmental concerns in the Arctic.
Potential for Collaboration and Sustainable Engagement:
- Partnership with Norway: India seeks to collaborate with Arctic countries like Norway to focus on green energy, clean industries, and sustainable resource development.
- Transformational Collaboration: Collaboration with Norway could enhance India's participation in Arctic Council working groups and facilitate responsible resource development.
- Sustainable Policy Design: India aims to design a sustainable Arctic policy that accommodates scientific research, environmental protection, and economic opportunities, with Norway's expertise playing a crucial role
Editorial
New data law, a barrier to journalistic free speech
Context
The Digital Personal Data Protection (DPDP) Act, 2023, introduced in India, raises concerns about its impact on journalistic free speech, particularly regarding the use of personal data for journalistic activities.
Implications for Journalistic Free Speech:
- Removal of Exemption: Unlike previous drafts, the final DPDP Act does not exempt journalistic activities from privacy obligations, requiring journalists to obtain consent before using personal data for stories involving public figures like politicians.
- Constraints on Investigative Reporting: Journalists relying on private data for investigative reporting may face hurdles in accessing and using such information, impacting their ability to hold public figures accountable.
- Government Authority and Confidentiality: The Act grants the government the power to request information from data processors, potentially compromising the confidentiality of journalistic sources and research materials.
Need for Transparent Consultation:
- Lack of Transparency: The absence of public disclosure regarding the removal of exemptions for journalistic activities from subsequent drafts of the DPDP Act highlights the need for a more transparent consultation process.
- Limited Public Engagement: While the government conducted town halls and consultations on the drafts, crucial issues like journalistic exemptions were not adequately discussed, hindering meaningful public engagement.
- Call for Clarity: There is a demand for the government to clarify the reasons behind the removal of exemptions and to engage in open debate and deliberation to address concerns regarding the impact of the DPDP Act on journalistic free speech.
Ensuring Journalistic Free Speech:
- Government Intervention: The government has the authority to provide exemptions under the DPDP Act, which could be utilized to safeguard journalistic entities from undue obligations, ensuring the Act does not curtail journalistic free speech.
- Incorporating Exemptions: While exemptions for journalistic activities should ideally be included in the core text of the law, immediate action through rules under the Act can mitigate the negative impact on journalistic free speech.
- Empowering Journalistic Entities: Exempting journalistic entities, including citizen journalists, from privacy obligations under the DPDP Act would uphold the principles of free speech and press freedom in India.
Editorial
‘Ghuskemarenge’ is a warning to our neighbours. Hot pursuit is recognized in law
Context
Defence Minister Rajnath Singh's recent statement regarding India's right to conduct hot pursuit operations across borders has sparked controversy and raised questions about its legal and ethical implications in the context of international law.
Understanding Hot Pursuit:
- Legal Framework: Hot pursuit, a concept deeply entrenched in international law, allows states to pursue aggressors across borders in response to ongoing attacks or imminent threats, based on principles of self-defense and protection of national interests.
- Military Strategy: Hot pursuit serves as a critical tool in military operations, enabling the neutralization of threats and safeguarding of national security interests by pursuing aggressors into foreign territory.
- Ethical Considerations: While hot pursuit is legally justified under certain conditions, it raises ethical concerns regarding proportionality, respect for territorial sovereignty, and the potential impact on civilians caught in the crossfire.
Criteria for Hot Pursuit:
- Immediacy: Pursuit must be initiated promptly in response to an ongoing attack or imminent threat, rather than based on past events or speculative threats.
- Proportionality: The response must be proportionate to the threat posed, avoiding excessive use of force or collateral damage that may violate international humanitarian law.
- Territorial Sovereignty: Pursuing forces must respect the sovereignty of the territory entered, refraining from unnecessary interference with the territorial integrity of the state.
- Notification: Ideally, the pursuing force should notify relevant authorities in the territory being entered, seeking cooperation; however, in urgent situations, such notification may not always be feasible.
- Termination: Hot pursuit must cease once the immediate threat is neutralized or once the pursuing force reaches a point of safety, to avoid accusations of unlawful aggression or violations of international law.
India's Policy and Examples:
- Context of Statements: Defence Minister Rajnath Singh's assertion of India's right to conduct hot pursuit operations across borders must be understood within the framework of self-defense and protection of national security interests.
- Historical Precedents: India's past actions, such as surgical strikes in response to cross-border terrorism incidents, align with the concept of hot pursuit, aiming to neutralize threats and protect national interests while minimizing escalation.
- Importance of Proportionality: India's responses to cross-border incidents emphasize the importance of proportionality in military operations, ensuring that actions are justified, measured, and respectful of international norms and human rights.
Ethical and Legal Considerations:
- Balancing National Security and International Norms: India's pursuit of hot pursuit operations must balance the imperative of national security with adherence to international legal and ethical standards, avoiding actions that may escalate conflicts or violate sovereignty.
- Transparency and Accountability: The government must ensure transparency and accountability in the planning and conduct of hot pursuit operations, adhering to legal frameworks and respecting human rights.
- Diplomatic Implications: India's assertion of its right to conduct hot pursuit operations may have diplomatic repercussions, necessitating careful consideration of international perceptions and engagement with neighboring countries to prevent escalation and promote regional stability.

 5 Questions
5 Questions 5 Minutes
5 Minutes




