17th April 2024
- Published
17 April 2024 -
 Download PDF
Download PDF
Online voting, an idea that holds promise
Context
The landscape of governance and civic engagement has been evolving rapidly with the advent of digital technologies. From banking to e-commerce, various sectors have embraced automation and digitization. The concept of online voting emerges as a natural progression in this digital era, promising convenience and efficiency in the electoral process.
1: Dimension- Nominations
- Transition to Online Filing: Candidate nominations should be shifted from physical to online filings before Election Commission (EC) officials, incorporating robust identity verification measures.
- Leveraging E-filing Platforms: Drawing from the success of e-filing platforms in income tax and corporate laws, the transition to online nominations should be streamlined and seamless.
- Ensuring Validation Checks: Appropriate identity and validation checks must be integrated into the online filing system to maintain the integrity of the nomination process.
2: Dimension- Polling Booths
- Redundancy of Traditional Infrastructure: With the adoption of online voting, the traditional infrastructure of polling booths, EVMs, and duty personnel will become obsolete, necessitating a redefinition of roles.
- Role Redefinition: Presiding officers and EC officials' roles may need to be redefined to align with virtual monitoring and supervision, reducing the reliance on physical infrastructure.
- Limited Need for Physical Booths: While a limited number of physical booths may still be necessary initially, the gradual shift towards online voting will significantly reduce the requirement for physical infrastructure.
3: Dimension- Voter list
- Streamlining Voter Registration: Linking Aadhaar with the voter ID facilitates seamless identification of voters, enhancing the efficiency of the registration process.
- Addressing Existing Voters: Proactive measures are required to ensure the linkage and confirmation of Aadhaar with existing voter IDs, ensuring inclusivity and accuracy in the voter list.
- Facilitating Global Voting: Integration with Aadhaar enables voters to cast their ballots from anywhere in the world on the polling day, enhancing accessibility and participation.
4: Dimension- Securing the Process
- Authentication Process: On polling day, voters should receive a web link via SMS to access the voting site on their registered mobile, initiating a two-step authentication process.
- Ensuring Integrity: Stringent measures must be implemented to prevent duplicate voting and safeguard voter data, maintaining the secrecy and integrity of the voting process.
- Addressing Data Privacy: System controls should ensure restricted access to voter data and segregation of databases to uphold data privacy and confidentiality.
Mains Practice Question
Q. “Online voting holds the potential to revolutionize the electoral process”. Discuss
‘Most micro entrepreneurs lack training; SC, ST aspirants face greater knowledge gap’
Context
Micro-entrepreneurship in India faces hurdles of inadequate training and knowledge gaps, exacerbating disparities among marginalized communities. A recent survey by Bhartiya Yuva Shakti Trust reveals concerning trends, necessitating urgent policy interventions to foster inclusive economic growth.
1: Dimension - Training Discrepancies
- Training Deficiency: The survey conducted by Bhartiya Yuva Shakti Trust (BYST) highlights a concerning reality: less than one-third of micro-entrepreneurs have received any form of training. This dearth of training extends to over half of the respondents who are unaware of the fundamental factors involved in commencing a business venture.
- Disparities in Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes (SC/ST): Particularly alarming is the sharp decline in training accessibility among micro-entrepreneurs from the SC/ST category. Only a dismal 17% and 28% of SC/ST entrepreneurs, respectively, reported receiving adequate training or mentorship.
2: Dimension - Knowledge Gap Challenges
- GST Awareness: The survey findings underscore a significant knowledge gap among micro-entrepreneurs regarding essential business components such as the Goods and Services Tax (GST). A mere 28% of all respondents and a paltry 20% of SC/ST entrepreneurs exhibit awareness of GST-related matters.
- Financial Literacy: The survey illuminates the pervasive lack of financial literacy among micro-entrepreneurs, particularly concerning tax management and governmental policies. Only 43% of all respondents and 37% of SC/ST entrepreneurs profess knowledge in managing and filing business taxes.
3: Dimension - Digital and Environmental Preparedness
- Digital Readiness: The survey evaluates the digital preparedness of micro-entrepreneurs, revealing notable gaps in digital presence, payments, and marketing strategies. While 43% of all entrepreneurs maintain a digital presence, only 21% of SC/ST entrepreneurs are active on social media platforms.
- Environmental Consciousness: Concerns regarding environmental sustainability are also highlighted, with a significant proportion of micro-entrepreneurs admitting inconsistent adherence to green processes and practices.
4: Dimension- Addressing the Disparities
- Policy Reevaluation: Policy reforms are needed to enhance entrepreneurship opportunities, particularly for underserved demographics. The necessity of updating existing policies to accommodate the diverse needs of micro-entrepreneurs, especially women.
- Financial Support and Education: Initiatives such as the Mudra Yojana and Stand-Up India Scheme are pivotal in fostering entrepreneurship. However, concerted efforts are required to ensure that financial support is complemented by comprehensive education and training programs tailored to the specific requirements of micro-entrepreneurs.
- Digital Literacy Promotion: Alongside traditional business training, emphasis should be placed on enhancing digital literacy among micro-entrepreneurs, thereby empowering them to leverage digital platforms for business growth and expansion.
Mains Practice Question
Q. "Access to training and knowledge remains a critical barrier to the inclusive growth of micro-entrepreneurship in India." Discuss.
IMF raises India’s GDP forecast to 6.8% for FY25
Context
With an anticipated surge in domestic demand, the IMF now estimates India's GDP growth to reach 6.8 percent, marking an upward revision of 30 basis points from its previous forecast. This adjustment reflects the enduring strength of domestic demand and the ascending trajectory of the working-age population within the country.
Key Highlights from IMF's World Economic Outlook (WEO)
Strengthened Growth Trajectory
FY24 Projections: India's GDP growth for FY24 is projected at 7.8 percent, showcasing a robust economic performance.
Continued Strength in Domestic Demand
Driving Factors: The sustained robustness in India's economic growth is attributed to the enduring vigor in domestic demand, coupled with the burgeoning working-age population.
1: Dimension- Comparative Analysis
- IMF vs. Other Projections: While the IMF's revised projection is optimistic, it remains slightly conservative compared to forecasts by other institutions. The Asian Development Bank (ADB) recently revised its projection for India's growth to 7%, citing robust public and private sector investment and improving consumer demand.
- RBI's Outlook: The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) echoes a positive sentiment, with Governor Shaktikanta Das highlighting bright prospects in agriculture and rural activity, projecting a growth rate of 7% for the Indian economy.
2: Dimension- Impact on Economic Sectors
- Rural Economy and Monsoon: Forecasts of an above-normal monsoon by the India Meteorological Department (IMD) bode well for rural demand, crucial for overall economic growth. Last year's below-normal monsoon dampened farm growth, underscoring the significance of favorable weather conditions for agricultural productivity.
- Manufacturing and Services: Despite agricultural challenges, robust growth in manufacturing and services sectors played a pivotal role in propelling the economy to over 7.5% growth in the previous year.
3: Dimension- Global Economic Context
- Global Economic Outlook: The global economy is anticipated to grow at a steady pace of 3.2% in 2024 and 2025, although below the historical average. This projection reflects factors such as restrictive monetary policies, withdrawal of fiscal support, and subdued productivity growth.
- Regional Variances: Advanced economies are expected to witness slight growth upticks, particularly in the euro area. Meanwhile, emerging market and developing economies are poised for stable growth, albeit with regional disparities.
Mains Practice Question
Q. “For developing economies like India, sustained economic growth depends not only on domestic factors but also on navigating through the complexities of the global economic environment." Discuss
Run-up to Ottawa: Arctic a ‘hemispheric sink’ for chemicals & plastics; 13 million people in region at risk, says report
Context
A report released ahead of negotiations for a Global Plastic Treaty in Ottawa, Canada, highlights the Arctic's alarming status as a repository for chemicals and plastics. The region's 13 million inhabitants face significant risks due to this environmental crisis.
Key-highlights of the Report
- Report Title: 'The Arctic’s Plastic Crisis: Toxic Threats to Health, Human Rights, and Indigenous Lands from the Petrochemical Industry'
- Launching Organizations: Alaska Community Action on Toxics (ACAT) and the International Pollutants Elimination Network (IPEN)
- Advocacy: Urgent need for a Just Transition framework to shift from an extractive to a regenerative economy in the Arctic and globally.
- Intergovernmental Negotiating Committee: Scheduled session in Ottawa, Canada, from April 23-29, 2024, preceding regional consultations on April 21.
1: Dimension- Interconnected Challenges
- Sources: The report identifies plastics, toxic chemicals, and climate change as interconnected challenges in the Arctic.
- Pollution Origins: Both local exploitation and global emissions contribute to Arctic pollution, with pollutants transported via atmospheric and oceanic currents.
- Climate Impact: Arctic warming occurs at a rate four times faster than the global average, exacerbating environmental degradation and threatening indigenous communities.
2: Dimension- Petrochemical Industry's Role
- Historical Exploitation: The Arctic has a long history of colonization and resource extraction, with multinational corporations often disregarding environmental consequences.
- Current Threats: Despite global shifts towards renewable energy, the fossil fuel industry aims to increase petrochemical production, intensifying environmental risks for Arctic communities.
- Indigenous Impact: Indigenous peoples face displacement, loss of traditional lands, and threats to cultural practices due to climate-induced changes and pollution.
3: Dimension- Recommendations for Action
- End Fossil Fuel Subsidies: Governments should halt subsidies to the fossil fuel and petrochemical industries and transition to renewable energy sources.
- Sustainable Practices: Emphasize clean, renewable energy and promote a toxics-free materials economy to mitigate further environmental damage.
- Indigenous Involvement: Support initiatives led by indigenous communities to restore traditional values and foster post-extractive futures.
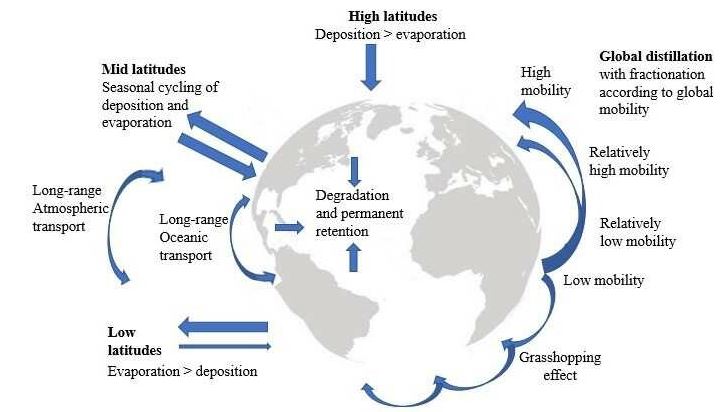
|
Grasshopper Effect
|
Mains Practice Question
Q: “The Arctic's plight underscores the urgent need for global environmental cooperation.” Discuss.
checkerboard wrasse (Halichoeres hortulanus)
Context
Three fish species that live in the Laccadive Sea, off the southwest corner of the Indian coast, are capable of using tools.
About
- It is a fish belonging to the wrasse family. It is native to the area including the Indian Ocean to central Pacific Ocean.
- The species feeds primarily on sand-dwelling gastropods, bivalves, hermit crabs, polychaetes and small fishes.
- IUCN Status: Least Concern
Flood in UAE
Context
UAE receives its highest rainfall in 75 years, with 1.5 year’s worth of rain falling over Dubai in 24 hours.
About
- The UAE witnessed the largest amount of rainfall during the past 75 years.
- Dubai is experiencing major flooding as 1.5 year’s worth of rain just fell in a single day. Nearly 5 inches (127 mm) fell in 24 hours,”
- Dubai and UAE are situated in the Arabian Peninsula (AP), which has an extremely arid and dry climate.
- A study published in 2020 noted that there will be “a robust increase in annual mean precipitation over the southern AP, and a decrease over the northern AP”.
- It was also the driest year on record, with the country’s annual total rainfall in deficit, compared with the long-term average (2003-2022).
Green Bonds
Context
Government of India is likely to issue 20000 cr- 25000 cr of green bonds for which it has allowed Foreign institutional Investors (FIIs) to invest in it.
About
- Green bonds are a type of fixed-income investment used to fund projects with a positive environmental impact.
- Like traditional bonds, green bonds offer investors a stated return and a promise to use the proceeds to finance or refinance sustainable projects, either in part or whole.
- They follow the Green Bond Principles stated by the International Capital Market Association (ICMA).
- Issues: Transparency and reporting, some bonds may have lower liquidity than traditional ones, greenwashing.
|
Blue Bonds
|
Imported Inflation
Context
The Asian Development Bank recently warned that India could face imported ination as the rupee could depreciate amid the rise in interest rates in the West.
About
- Imported inflation refers to the rise in the prices of goods and services in a country that is caused by an increase in the price or the cost of imports into the country.
- It is believed that a rise in input costs pushes producers to raise the price they charge from their local customers, thus boosting inflation.
- When a country’s currency depreciates, people in the country will have to shell out more of their local currency to purchase the necessary foreign currency required to buy any foreign goods or services, which in turn means that they will effectively be paying more for anything that they import.
- A rise in interest rates in the West tends to cause the currencies of developing countries to depreciate against western currencies, which in turns can lead to higher import costs for these countries.
- A rise in import costs even without depreciation in the value of a country’s currency is also believed to lead to import inflation.
TERM OF THE DAY
|
S. No. |
Term |
About |
|
1. |
Greenwashing |
Greenwashing is a marketing technique that deceives the public into believing that a company's products, policies, or aims are environmentally friendly. It's also known as green sheen, and is a combination of the words "whitewash" and "green". |
|
2. |
Grasshopper Effect |
The grasshopper effect, also known as global distillation, is a geochemical process that transports certain chemicals from warmer to colder regions of the Earth. |
|
3. |
Prepaid Payment Instrument (PPI) |
A prepaid payment instrument (PPI) is a digital payment solution that allows users to store money electronically and use it for a variety of transactions, including online shopping, bill payments, and money transfers. PPIs can be used to purchase goods and services at a group of merchant locations that have a contract with the issuer to accept PPIs as payment instruments. PPIs can be issued as cards or wallets. |
|
4. |
RCS (Rich Communication System) |
RCS (Rich Communications Services or Suite) provides customers with voice and SMS services such as, instant messaging, files sharing, or live video over a network to provide a more effective communication experience. |
|
5. |
Blue Holes |
Blue holes are large, underwater sinkholes or caves characterized by their deep blue color and unique ecosystem. These formations typically occur in coastal regions or in underwater cave systems. Over time, blue holes form as limestone or other soluble rock erodes, creating a depression or cavity that extends below the water surface. |
|
6. |
wokeism |
Wokeism is a set of theories that revolve around gender, race, and identity. It is a promotion of liberal progressive ideology and policy as a way of expressing sensitivity to systemic prejudices and injustices. |
|
7. |
Star Campaigner |
A star campaigner is a celebrity vote seeker in an election for a party. This person can be anyone, a politician or even a film star. A ‘recognised’ National or State party declared as such by the ECI can nominate a maximum of 40 star campaigners. An unrecognised political party can nominate a maximum of 20 star campaigners. |
Editorial
Navigating life as a consumer with disability
Context
Despite the annual observance of World Consumer Rights Day, the challenges faced by consumers with disabilities in accessing goods and services remain largely overlooked, highlighting the need for enhanced awareness and policy measures to ensure inclusivity in the marketplace.
Challenges of Accessibility for Consumers with Disabilities:
- Lack of Access to Goods and Services: Consumers with disabilities often face barriers in accessing goods and services due to pervasive inaccessibility in the market. For instance, the absence of accessible transportation apps, lack of tactile pavements in buildings, and inaccessible customer support options hinder their ability to engage independently in consumer activities.
- Responsibility of Businesses: Businesses typically overlook persons with disabilities as their target consumers, resulting in inaccessible offerings. However, considering that persons with disabilities constitute a significant portion of the population (5-8% in India), businesses could enhance their consumer experience by making their offerings accessible, thus broadening their customer base.
- Role of Government: Government interventions through effective policy measures can bridge the gap in sensitization among businesses. Initiatives like issuing advisories for incorporating accessibility features, such as QR codes for product information, can significantly empower consumers with disabilities to access essential information independently. Comprehensive accessibility guidelines for all goods and services, inspired by global best practices, can further ensure inclusivity in the market.
Legal Reforms to Safeguard Consumer Rights:
- Rights of Persons with Disabilities Act (RPWDA), 2016: The RPWDA grants various rights to persons with disabilities, including the rights to equality, accessibility, and reasonable accommodation. Provisions for universally designed consumer goods and accessible services aim to ensure inclusivity in the market. However, the effectiveness of enforcement mechanisms, such as Disability Commissions, needs improvement to provide adequate redress for violations.
- Consumer Protection Act (CPA), 2019: The CPA empowers Consumer Commissions to address consumer grievances and impose penalties against violations. While consumers with disabilities have successfully obtained remedies under the CPA, the lack of dedicated rights for them may deter them from filing complaints. Aligning the CPA with the RPWDA is crucial to ensure comprehensive protection for consumers with disabilities.
- Awareness and Advocacy: Raising awareness about existing rights and resources available to consumers with disabilities is essential. Despite efforts like the Jago Grahak Jago Campaign, attention to the rights of consumers with disabilities has been lacking. Advocacy efforts should focus on ensuring that consumers with disabilities are adequately represented and supported in consumer protection initiatives.
Editorial
The world is still on fire, sadly, as the multilateral system looks on
Context
The current global scenario is marred by a plethora of challenges, including economic instability, rising debt burdens on developing nations, and the exacerbation of the climate crisis. Despite numerous pledges and plans by world leaders, concrete actions to address these issues have fallen short, leading to a dire situation in many parts of the world.
Challenges in Global Development:
- Debt Burden on Developing Nations: Developing countries, especially the poorest among them, are grappling with crippling debt burdens exacerbated by higher interest rates and economic downturns. Many of these nations have yet to recover from the impact of the pandemic, further widening the economic disparities.
- Climate Crisis Mitigation Efforts: Despite promises to prioritize climate action, international financial institutions and assistance agencies have failed to deliver significant support to developing countries for climate change mitigation and adaptation. The failure to mobilize sufficient resources has hindered efforts to address the escalating environmental crisis.
- Humanitarian Crisis and Governance Failures: Humanitarian disasters, exacerbated by conflicts, inflation, and poor governance, have pushed vulnerable populations to the brink of famine in several countries. The international response to these crises has been sluggish, highlighting a broader failure of the global community to address urgent humanitarian needs effectively.
Proposed Solutions for Effective Global Development:
- Reversing Capital Flows and Expanding Support: Immediate measures should focus on redirecting capital flows to provide more support to the lowest-income countries. This can be achieved through innovative financial tools and increased contributions from shareholders, including legislative approval for capital increases in multilateral development banks.
- Transformation of Multilateral Development Banks: Multilateral development banks need to adopt more ambitious and risk-taking approaches, particularly in addressing climate-related challenges. Wealthy countries must provide political support to scale up these efforts and prioritize climate-focused investments.
- Full Funding for International Development Association (IDA): Ensuring adequate funding for the IDA, a vital institution supporting the poorest countries, is essential. A substantial replenishment from donors is necessary to meet the growing challenges faced by low-income nations.
- Addressing Food Insecurity: Adequate funding to address food security issues is imperative to prevent a humanitarian catastrophe. International donors must step up their contributions to alleviate hunger and demonstrate the efficacy of the international system in responding to urgent humanitarian needs.
Editorial
Pulses need a production boost
Context
India's persistent shortage in pulses production has led to significant challenges in ensuring food security and managing inflation in the 'pulses and products' group. The recent decline in output, coupled with increased imports, highlights the urgent need to address the underlying factors affecting pulses cultivation and production.
Challenges in Pulses Production:
- Declining Output and Rising Prices: Despite efforts to increase domestic production, India continues to face a deficit in pulses production, leading to inflationary pressures in the market. The recent drop in cultivation and output of major pulses, such as moong and urad, has exacerbated the situation, particularly due to deficit rainfall in key producing regions.
- Dependency on Imports: India heavily relies on imports to meet the growing demand for pulses, further straining its economy. Limited import sources and fluctuations in international prices pose challenges in stabilizing domestic supplies and prices, adversely affecting consumers, especially the poor.
- Structural Issues in Agriculture: Structural constraints, including the shift in cropping patterns towards cereal-cereal cultivation and inadequate irrigation facilities for pulses, contribute to low yields and output. The lack of post-harvest management and market linkages further impedes the growth of pulses production.
Strategies for Enhancing Pulses Production:
- Promoting Cultivation in Fertile Regions: Immediate measures should focus on promoting pulses cultivation in fertile and irrigated areas, providing input incentives, and ensuring remunerative prices for farmers. This would encourage farmers to prioritize pulses cultivation and contribute to increasing domestic production.
- Adoption of High-Yielding Varieties and Technologies: Enhancing pulses production requires the adoption of high-yielding varieties and modern agricultural technologies. Investments in research and development, coupled with extension services, can facilitate the dissemination of best practices among farmers and improve productivity.
- Sustainable Agriculture Practices: Cultivation of pulses not only addresses food security concerns but also promotes sustainable agriculture practices. Encouraging pulses cultivation can help enrich soil fertility, conserve water, and mitigate the adverse effects of climate change, contributing to long-term agricultural sustainability.

 5 Questions
5 Questions 5 Minutes
5 Minutes




