17th April 2024 (12 Topics)
Run-up to Ottawa: Arctic a ‘hemispheric sink’ for chemicals & plastics; 13 million people in region at risk, says report
Context
A report released ahead of negotiations for a Global Plastic Treaty in Ottawa, Canada, highlights the Arctic's alarming status as a repository for chemicals and plastics. The region's 13 million inhabitants face significant risks due to this environmental crisis.
Key-highlights of the Report
- Report Title: 'The Arctic’s Plastic Crisis: Toxic Threats to Health, Human Rights, and Indigenous Lands from the Petrochemical Industry'
- Launching Organizations: Alaska Community Action on Toxics (ACAT) and the International Pollutants Elimination Network (IPEN)
- Advocacy: Urgent need for a Just Transition framework to shift from an extractive to a regenerative economy in the Arctic and globally.
- Intergovernmental Negotiating Committee: Scheduled session in Ottawa, Canada, from April 23-29, 2024, preceding regional consultations on April 21.
1: Dimension- Interconnected Challenges
- Sources: The report identifies plastics, toxic chemicals, and climate change as interconnected challenges in the Arctic.
- Pollution Origins: Both local exploitation and global emissions contribute to Arctic pollution, with pollutants transported via atmospheric and oceanic currents.
- Climate Impact: Arctic warming occurs at a rate four times faster than the global average, exacerbating environmental degradation and threatening indigenous communities.
2: Dimension- Petrochemical Industry's Role
- Historical Exploitation: The Arctic has a long history of colonization and resource extraction, with multinational corporations often disregarding environmental consequences.
- Current Threats: Despite global shifts towards renewable energy, the fossil fuel industry aims to increase petrochemical production, intensifying environmental risks for Arctic communities.
- Indigenous Impact: Indigenous peoples face displacement, loss of traditional lands, and threats to cultural practices due to climate-induced changes and pollution.
3: Dimension- Recommendations for Action
- End Fossil Fuel Subsidies: Governments should halt subsidies to the fossil fuel and petrochemical industries and transition to renewable energy sources.
- Sustainable Practices: Emphasize clean, renewable energy and promote a toxics-free materials economy to mitigate further environmental damage.
- Indigenous Involvement: Support initiatives led by indigenous communities to restore traditional values and foster post-extractive futures.
|
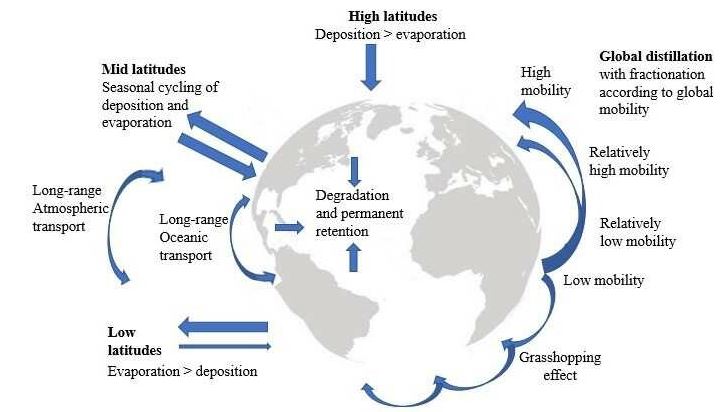
Grasshopper Effect
|
Mains Practice Question
Q: “The Arctic's plight underscores the urgent need for global environmental cooperation.” Discuss.