3rd May 2024 (14 Topics)
Context
Following a complaint from the State of West Bengal against the Central Bureau of Investigation's (CBI) "unilateral right" to look into offenses committed by CBI officials within State jurisdiction, the Supreme Court said unequivocally that “law and order is a State subject”. The decision emphasized the division of powers between the central and state authorities.
1: Dimension- State Subject Status of Law and Order:
- Constitutional Division of Powers: The Constitution of India delineates the distribution of powers between the central government and state governments, with law and order falling within the domain of the latter.
- Autonomy of State Governments: States possess the authority to enact laws, maintain public order, and ensure the safety and security of citizens within their jurisdictions.
- Supreme Court's Clarification: The recent statement by the Supreme Court reaffirms the principle that matters concerning law and order primarily fall under the purview of state governments, underscoring their autonomy and responsibility in this regard.
2: Dimension- Implications of SC's Assertion:
- Clarity on Jurisdiction: The SC's clarification provides clarity on the division of powers between the central and state authorities, preventing potential conflicts and ensuring effective governance.
- State Government Accountability: Emphasizing law and order as a state subject highlights the accountability of state governments in addressing issues related to public safety and security.
- Role of Central Government: While law and order is primarily the responsibility of state governments, the central government may intervene in exceptional circumstances, such as maintaining constitutional integrity or combating threats to national security.
|
Fact Box: About Schedule VII
|


Context
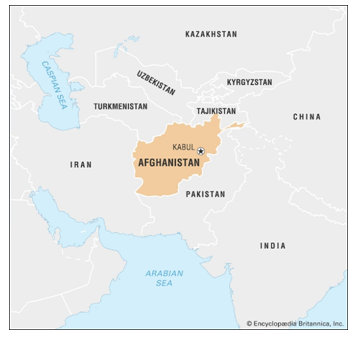
The Taliban (who govern Afghanistan) is working with Kazakhstan and Turkmenistan to create a regional energy trade hubin western Afghanistan that would facilitate oil sales from Russia to South Asia. It marks a strategic move by the Taliban to leverage Afghanistan's geographical location and revive its economy through regional energy trade.
1: Dimension-Significance of the Agreement
- Strategic Location: Afghanistan's geographical location, situated between South and Central Asia and sharing borders with China and Iran, makes it strategically positioned for trade routes. Historically, Afghanistan served as a crucial point along the ancient Silk Road trade route.
- Multi-Modal Services: It will allow for the development of multi-modal services by consolidating truck shipments in the dry port where they will be sorted and sent along railroads on the North-South corridor to sea ports in the Gulf, Pakistan, and Indian Ocean, towards India.
- Development in Herat Province: The establishment of a logistics center in Herat province holds significance as it can serve as a pivotal link connecting northern regions to South Asia. This infrastructure development has the potential to boost economic activity and trade flows in the region.
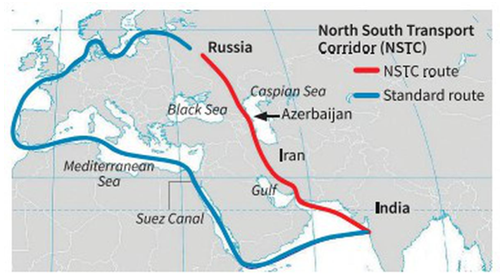
- The trio noted that the eastern branch of the International North South Transport Corridor (INSTC) had gained new impetus to become a key route for transporting goods from Russia and Belarus through Kazakhstan and Turkmenistan to Afghanistan, India, and West Asia.
2: Dimension-Implication of the development
This initiative has implications not only for Afghanistan but also for neighboring countries and broader regional dynamics.
- Emerging as key player: The agreement to build a logistics hub signifies the Taliban's efforts to establish Afghanistan as a key player in regional trade, particularly in the energy sector.
- Diversification: By fostering partnerships with neighboring countries like Kazakhstan and Turkmenistan, the Taliban seeks to diversify Afghanistan's economy and reduce reliance on external aid.
- Benefit for Kazakhstan: The country is eyeing the development of roads and a railway through Afghanistan to have connections with the Gulf and South Asia. Currently, Kazakhstan’s crude oil exports are dependent on logistics in Russia and Russian ports on the Black Sea.
- Challenges:
- Security situation in Afghanistan remains fragile
- Concerns about the feasibility of infrastructure development projects.
- Geopolitical rivalries and regional dynamics
3: Dimension- Impact on India
- Economic Opportunities: Increased connectivity and trade facilitation could open up new economic opportunities for Indian businesses, especially in sectors such as energy, infrastructure development, and logistics.
- Energy Security: The development could contribute to India's energy security objectives. Access to energy resources from Central Asia and Russia via Afghanistan could diversify India's energy sources and reduce dependency on traditional suppliers.
- Connectivity and Regional Integration: Enhanced connectivity through the logistics hub could bolster India's efforts towards INSTC.
|
Fact Box: About INSTC
|


Context
A recent study discovered the deepest blue hole in the world-the TaamJa' Blue Hole, located in Mexico's Chetumal Bay.
About TaamJa' Blue Hole
- Mexico's TaamJa' Blue Hole is the deepest known underwater sinkhole in the world,
- Depth:1,380 feet (420 meters) below the surface.
- It outshines the previous record holder, the SanshaYongle Blue Hole (Dragon Hole) in the South China Sea, by 480 feet.
|
Fact Box: Blue Hole (Karst Formations)
|


Context
The 26th Meeting of the Committee for Environmental Protection (CEP 26) and the 46th Antarctic Treaty Consultative Meeting (ATCM 46) will be held in Kochi, Kerala, by the Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES) in collaboration with the National Centre for Polar and Ocean Research (NCPOR).
About
- The Antarctic Treaty was signed in 1959 and came into effect in 1961.
- It designates Antarctica as an area committed to environmental preservation, scientific collaboration, and peaceful objectives.
- More than 56 of the nations are currently parties to the Treaty.
- With the intention of advising the ATCM on environmental conservation and protection in Antarctica, the Committee for Environmental Protection was founded in 1991 under the auspices of the Madrid Protocol, which established the Protocol on Environmental Protection to the Antarctic Treaty.
- India joined the Antarctic Treaty in 1983 as a Consultative Party.


Context
The first-ever India-Indonesia Defense Industry Partnership was held in Jakarta that marked the importance of bilateral defense cooperation in the 75th year of diplomatic ties between the two nations.
Key-highlights of India-Indonesia Relations
- Formal diplomatic relations established in: 1951
- Trade relations established in: 1978
- In 2018, India and Indonesia elevated their relationship to a "Comprehensive Strategic Partnership".
- The duo also agreed on the "Shared Vision of India-Indonesia Maritime Cooperation in the Indo-Pacific".
- Factors fostering peaceful relations: Geographical proximity, history of collaboration in international forums like the Non-Aligned Movement
- Key areas of cooperation:Energy sector, Technology and medicine, Food security and agriculture.
- Exports from India to Indonesia: motor vehicles and cars, sugar, ships, boats, and floating structures and iron and steel
- Imports from Indonesia: coal, coke, and briquettes, vegetable oils, iron and steel, bulk minerals and ores and cosmetics and toiletries
- Indonesia is viewed by India as a crucial ASEAN member.
- Indo-Indonesia Joint Commission (JCM) was formed in 2003
- The Double Taxation Avoidance Agreement (DTAA) was endorsed in 2012.
- Bilateral Exercises
- The 42nd India-Indonesia Coordinated Patrol (IND-INDO CORPAT) is scheduled to take place in May.
- Military exercise Garuda Shakti
- Naval exercise Samudra Shakti


Context
Attempts are being made to contain the largest Mpox outbreak in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC). Researchers have shown that a new form of the disease that was found in a mining community may be more contagious.
About Monkeypox:
- The monkeypox virus is the infectious agent that causes mpox, often known as monkeypox.
- It may result in fever, swollen lymph nodes, and an excruciating rash.
- The virus that causes mpox, also known as monkeypox, is the enveloped double-stranded DNA virus of theOrthopoxvirus genus in the Poxviridae family, which also includes vaccinia, cowpox, variola, and other viruses.
- Clades I and II, the virus's two genetic clades, are native to Central and West Africa and are related to
- Clade 1:Up to 10% of those infected can die from Clade 1, which is more severe.
- Clade 2:The 2022 outbreak was started by Clade 2, and over 99% of those infected recovered.
- Transmission:The mpox can spread from person to person by direct contact with infected skin or other lesions including those on the mouth or genitalia.
- In July 2022, the global mpox outbreak was classified as a public health emergency of international significance (PHEIC) by


Context
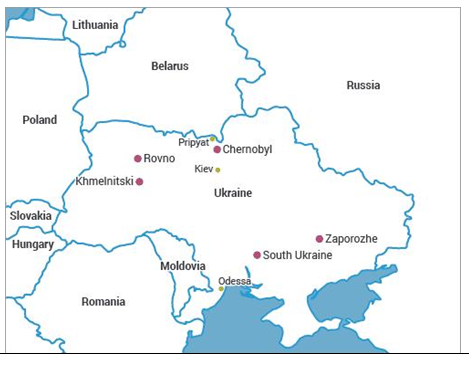
Approximately 50% ofUkraine's power output is still produced by the nuclear industry, 38 years after the Chernobyl Disaster.
Key-highlights:
- Share of energy output:Following Slovakia and France, Ukraine has the third-highest nuclear energy output percentage globally.
- After the seizure of the Zaporizhzhia plant (largest nuclear power plant in Europe) by Russian forces in 2022, the other three Soviet-era nuclear power plants remain under Ukrainian control. They are:
- Pivdennoukrainsk (South Ukraine)
- Khmelnytskyi
- Rivne
|
Chornobyl Disaster
|


Context
According to a study, removing alien plants from forested areas will assist ensure that wild elephants at Munnar'sChinnakkanal have food.
What are Invasive species?
- An organism that is not native or indigenous to a certain location is referred to as an invasive species.
- Pathways: Oceangoing ships' ballast water, purposeful and inadvertent discharges of aquaculture species, aquarium specimens or bait, and other methods can all introduce an invasive species into a new location.
- The majority of food crops cultivated in the US, such as popular types of rice, tomatoes, and wheat, are not indigenous to the area.
- A species needs to be able to readily adapt to its new environment in order to qualify as invasive.
- It needs to proliferate rapidly.
- It has to damage property.
List of invasive flora and fauna in India
|
Name |
State / Region |
Native to |
|
African apple snail |
Andaman and Nicobar |
|
|
Papaya Mealy Bug |
Assam |
Mexico and Central America, |
|
Cotton Mealy Bug |
Deccan |
North America |
|
Amazon sailfin catfish |
West Bengal |
|
|
Black Wattle |
Western Ghats |
South East Australia |
|
Water Hyacinth |
It is found throughout India |
Tropical America |
|
Black Mimosa |
Himalaya, Western Ghats |
Tropical North America |
|
Parthenium/ Congress grass, Parthenium |
It is found throughout India |
Tropical North America |
|
Cannibal Snail / Rosy wolf snail |
– |
Native to the southeastern United States. |
|
Indian Bullfrog |
Andaman and Nicobar |
Afghanistan, Bangladesh, India, Myanmar, Nepal, Pakistan |
|
Lantana camara |
In the Bandipur National Park, Karnataka |
South America |


Context
The Reserve Bank of India has granted payment aggregator (PA) licences to numerous payment providers and big merchant organizations in recent monthsWhat is a PA business?
- PA businesses are companies that help online retailers and e-commerce sites accept different payment methods from clients to fulfill their payments without requiring the merchants to set up their own infrastructure.
- Key-examples: Amazon Pay, PayPal, Stripe, others.
- PAs enable their clients to accept various payment methods such as UPI, debit cards, credit cards, cardless EMIs, bank transfers, e-wallets.
- After receiving payments from clients, PAs combine them and send them to the retailers.
- Requirement:A company that submitted an application for a PA license had to have had a net value of Rs. 15 crore as of March 31, 2021, and Rs. 25 crore as of March 31, 2023.
- Features:
- Seamless Onboarding, Integration and Sub-Merchant Account
- Secure Payment Processing
- Fraud Detection and Prevention
- Multiple Payment Options
- Fast Settlements and Customer Support
- Significance:
- For organisations:In addition to these organizations' expansion and significance
- For RBI and economy: RBI can keep an eye on the businesses that manage or transfer substantial sums of money. The RBI is able to monitor any suspected money laundering activities and high-value suspicious transactions by licensing these companies and placing them under its direct supervision.


Context
The investment cap for passive funds in sponsor group companies has been raised by SEBI in an effort to boost the effectiveness and competitiveness of these funds in India.
About passive exchange-traded fund (ETF)
- An investment tool called a passive exchange-traded fund (ETF) aims to mimic the performance of either a particular industry or trend or the larger equity market.
- ETFs replicate the holdings of an index, which is a group of tradable securities that are thought to be typical of a specific market or industry.
- They are available for purchase and sale at any time during the trading day, just like stocks on a major exchange.


|
S.No. |
Term |
About |
|
1. |
Blue holes |
Blue holes are huge underwater sinkholes that appear on the seafloor when the limestone bedrock collapses. |
|
2. |
Public Health Emergency of International Concern (PHEIC) |
PHEIC is a formal designation, giving a special status for an emergency caused by an infectious disease outbreak from the World Health Organization (WHO), tied to international law through the International Health Regulations (IHR). |
|
3. |
Trading securities |
Trading securities are securities purchased by a company for the purpose of realizing a short-term profit. |
|
4. |
Xenophobia |
Xenophobia is the dislike or hatred of people because they are unlike people in one's culture or society. |


Context:
The issue of menstrual leave has gained prominence in India.
Progressive Changes in India and Asia
- Progressive Indian States: States like Kerala and Bihar have a history of recognizing the need for menstrual leave, with Kerala introducing menstrual and maternity leave for students above 18 in 2023.
- International Comparison: Several Asian countries, including Japan, Indonesia, and South Korea, have implemented menstrual leave policies, while India's progress in this regard remains limited.
- Global Initiatives: International organizations like the International Labour Organization and the World Health Organization have advocated for menstrual leave as a women's right, but India's recent Social Security Code does not include provisions for menstrual leave.
Greater Gender Sensitivity Needed:
- Supreme Court's Response: The Supreme Court of India declined to entertain a public interest litigation on menstrual leave, stating that it falls within the policy domain of the government.
- Addressing Gender Inequalities: Policy solutions addressing gender inequalities, including menstrual leave, are essential for promoting equity and challenging socio-cultural taboos.
- Impact on Women Laborers: Lack of menstrual leave can have adverse effects on women laborers' health and livelihoods, highlighting the need for legislative reforms to protect their rights.


Context
The discourse on India's foreign policy and its role in shaping the nation's development trajectory is highlighted in a recent commentary.
Vision for Viksit Bharat:
- Political Stability and Policy Continuity: Achieving the goal of Viksit Bharat requires political stability and continuity to implement long-term policy prescriptions.
- "Bharat First" Foreign Policy: India's foreign policy has shifted towards prioritizing national interests, promoting multi-vector diplomacy, and asserting relevance on the global stage.
- Importance of Manufacturing and Technology: Deepening national strengths, particularly in manufacturing and emerging technologies, is crucial for India's development, requiring strong international collaboration and effective diplomacy.
International Collaboration and Diplomacy:
- Strategic Autonomy and National Development: In a post-Covid world, nations are seeking strategic autonomy and self-reliance, emphasizing the significance of initiatives like "Make in India" for economic growth and national security.
- Global Engagement and Talent Mobility: India aims to become a global hub for research, design, and innovation, facilitated by international partnerships and mobility agreements to harness Indian skills and talent.
- Connectivity and Security: India's foreign policy also focuses on enhancing connectivity and political balances in a changing world, exemplified by initiatives like the IMEC corridor and engagement in multilateral forums like Quad and BRICS.


Context:
A potential crisis regarding the use of Standard Essential Patents (SEPs) by certain technology companies against India's telecom manufacturing sector has emerged, highlighting the complexities of policy regulation in this area.
Importance of Standard Essential Patents (SEPs):
- Role of SEPs in Industry Standards: SEPs cover technologies adopted as industry standards, ensuring interoperability among different brands of cellular phones.
- Privatized Standard Setting Organizations (SSOs): Standard setting processes, largely controlled by private technology companies, limit India's influence in setting standards and licensing SEPs.
- Patent Holdup Problem: SEP owners can demand excessive royalties, leading to anti-competitive practices and hindering market competition, despite the expectation of fair, reasonable, and non-discriminatory (FRAND) licensing.
Effect of Judicial Lethargy and Activism:
- Judicial Delay in Competition Law Issues: Indian judiciary's delayed response to investigating potentially abusive licensing practices of SEP owners, leading to prolonged litigation and absence of regulatory oversight.
- Interim Remedies by Delhi High Court: The Delhi High Court's granting of interim orders, such as requiring manufacturers to deposit money during trials, creates financial burdens and undermines defendants' rights.
- Negative Impact on Manufacturing Sector: Judicial activism and delays adversely affect government initiatives to attract investment in the manufacturing sector, hindering India's progress towards becoming a manufacturing hub.
Case of Europe and Need for Regulation:
- European Parliament's Regulation: The European Parliament has enacted measures to regulate SEPs, setting a precedent for addressing similar issues.
- India's Strong Case for Regulation: India, lacking influence in SEP selection but obligated to enforce patents of foreign technology companies, needs regulatory measures to safeguard its manufacturing sector's interests.