

16th June 2025 (10 Topics)
Context
Heightened tensions between Iran and Israel–U.S. have triggered renewed threats from Iran to block the Strait of Hormuz, a vital chokepoint through which approximately 20–21 million barrels of oil daily pass (~20–25% of global seaborne oil)
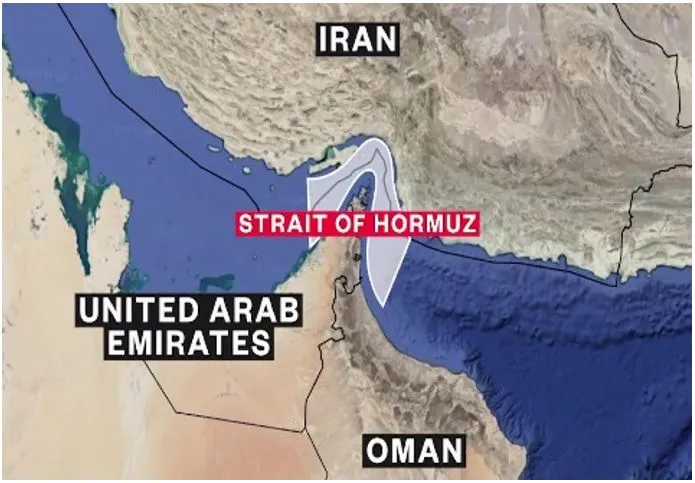
Strait of Hormuz
- Strategic Importance of the Strait
- Connects the Persian Gulf with the Gulf of Oman and Arabian Sea.
- Facilitates transit of ~1/5 of global oil and 1/3 of LNG Narrowest width ~21 nautical miles; shipping lanes just 3.2?km wide
- Iran’s Geopolitical Leverage
- Controls northern maritime approaches, with missiles, fast-attack boats, and mines enabling asymmetric power – the A2/AD doctrine
- Historical threats surfaced in 2012, 2019, and 2025 amid sanctions or attacks .
- UNCLOS stipulates “transit passage” rights, making total blockade illegal—though Iran could still disrupt shipping
- Global Consequences
- Even limited disruption could push crude prices above $100/barrel, raising global inflation and impacting energy security
- Surge in shipping insurance costs and rerouting, as seen with tanker avoidance and convoy measures
- Initiatives like the EMASoH coalition and strategic reserves may partially stabilize markets
- Iran’s Strategic Constraints
- Severe economic self-harm: oil revenue constitutes ~65% of Iranian government earnings; blockade could destabilize its economy and internal stability.
- Regional tensions: Oman and GCC nations may oppose such moves, with US-led naval deployments ready to reopen closure
More Articles


