

8th September 2025 (12 Topics)
Context:
The Government of India launched the National Critical Minerals Mission (NCMM) in 2025 to secure long-term domestic and global supply chains of strategic minerals essential for clean energy, advanced technologies, and national security.
Critical Minerals: The Strategic Foundation of India’s Energy and Economic Future
Introduction
- Critical minerals are essential for clean energy, advanced electronics, defence, and digital infrastructure.
- India released a list of 30 critical minerals in 2023, including lithium, cobalt, nickel, rare earths, tungsten, vanadium, etc.
- With the launch of NCMM (2024–25 to 2030–31), India aims to strengthen exploration, extraction, processing, recycling, and global partnerships.
Key Features of National Critical Mineral Mission (NCMM)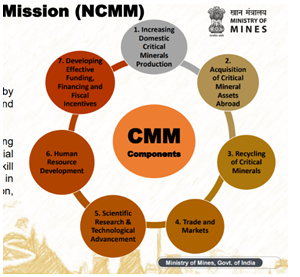
- Scope and Expenditure
- Duration:7 years (2024–25 to 2030–31)
- Outlay:?16,300 crore (government) + ?18,000 crore PSU/stakeholder investment
- Targets
- 1,000 patents by 2030 in mineral R&D
- 7 Centres of Excellence (CoEs) in IITs & research institutions
- 270 kilo ton annual recycling capacity by 2030
- 40 kilo ton production of minerals from recycling
- Job creation:~70,000 direct jobs
- Institutional Mechanism
- Amendment of MMDR Act: Centre empowered to auction 24 of 30 minerals.
- Pilot projects: ?100 crore for recovery from fly ash, mine tailings, red mud.
- Incentive scheme: ?1,500 crore for recycling e-waste, battery scrap, end-of-life vehicles.
Critical Minerals in India’s Clean Energy Transition
- Solar Energy
- Reliance on silicon, gallium, tellurium, indium for photovoltaic cells.
- India’s solar capacity: 64 GW (2025), target 280 GW+ by 2030.
- Wind Energy
- Neodymium, dysprosium crucial for permanent magnets in turbines.
- India’s target: 140 GW wind capacity by 2030.
- Electric Mobility
- Lithium, cobalt, nickel for EV batteries.
- Target: 30% EV penetration by 2030.
- Energy Storage
- Lithium-ion systems critical for renewable grid integration.
- Strategic stockpiles planned for ensuring energy security.
Innovation and R&D Push
- Patent Ecosystem: 62 patents filed in May–June 2025, 10 granted.
- Focus on battery materials, advanced alloys, nanotechnology.
- Centres of Excellence: IIT Bombay, IIT Hyderabad, IIT Roorkee, IIT-ISM Dhanbad, CSIR labs (IMMT, NML), NFTDC Hyderabad.
Strategic and Geopolitical Dimension
- Global race for critical minerals: dominated by China, U.S., EU, Australia.
- India’s strategy: domestic exploration + overseas asset acquisition.
- Enhances supply chain resilience, reduces import dependency.
- Aligns with Atmanirbhar Bharat and India’s net-zero target by 2070.
Global Partnerships
- Mineral Security Partnership (MSP): 14 countries + EU, chaired by South Korea; India exploring 32 global projects.
- iCET (India–US Initiative on Critical & Emerging Technologies): joint projects in exploration and R&D.
- Indo-Pacific Economic Framework (IPEF): India presented CM initiatives in 2024.
- India–UK Technology and Security Initiative (TSI): collaborative R&D.
- Quad Clean Energy Principles (2023): focus on resilient supply chains.
- Bilateral MoUs: with Australia, Argentina, Chile.
Challenges
- Limited domestic reserves of minerals like lithium and cobalt.
- High dependence on imports from geopolitically sensitive regions.
- Environmental and social risks from intensive mining.
- Need for advanced refining and processing technologies.
Way Forward
- Strategic Partnerships: Deepen collaborations with resource-rich countries (Australia, Chile, Argentina, Africa).
- Technology Development: Invest in indigenous refining, advanced metallurgy, and battery recycling.
- Environmental Safeguards: Balance extraction with sustainability through circular economy models.
- Skill Development: Establish academic–industry partnerships for human capital in mining and processing.
- Global Role: Position India as a critical minerals hub by leveraging International Solar Alliance (ISA) and new supply chain coalitions.
More Articles


