13th July 2023 (6 Topics)
Context
In a major development, geologists have provided evidence of the beginning of the Anthropocene epoch — a proposed geological epoch that began when human activity started to have a significant impact on the Earth.
- Anthropocene epoch denotes the present geological time interval, in which the Earth’s ecosystem has gone through radical changes due to human impact.
|
As of now, at least officially, we’re in the Phanerozoic eon, Cenozoic era, Quaternary period, Holocene epoch and the Meghalayan age. |
Background
- Members of the Anthropocene Working Group (AWG), which has been working since 2009 to make the Anthropocene part of the planet’s time scale, the 35 geologists have estimated that the new epoch started sometime between 1950 and 1954.
- They revealed the findings after analysing the Crawford Lake in Canada, bottom sediments, which have over the years captured the fallouts of large-scale burning of fossil fuels, explosion of nuclear weapons and dumping of plastic and fertilisers on land and in water bodies.
What is the Anthropocene epoch?
- The Anthropocene epoch as a term was first coined by Nobel Prize-winning chemist Paul Crutzen and biology professor Eugene Stoermer in 2000 to denote the present geological time interval.
- In this period, the Earth’s ecosystem has gone through radical changes due to human impact, especially since the onset of the Industrial Revolution.
- There are numerous phenomena associated with this epoch, such as global warming, sea-level rise, ocean acidification, mass-scale soil erosion, the advent of deadly heat waves, deterioration of the biosphere and other detrimental changes in the environment.
How the Earth’s geological time scale is divided?
- The geological time scale (GTS) divides and chronicles earth’s evolutionary history into various periods from the beginning to the present based on definite events that marked a major change in earth’s physical, chemical and biological features.
- Major changes in earth’s physical and biological history stretch over several millions of years and hence in GTS all the divisions are expressed in ‘million years (mya – million years ago).’
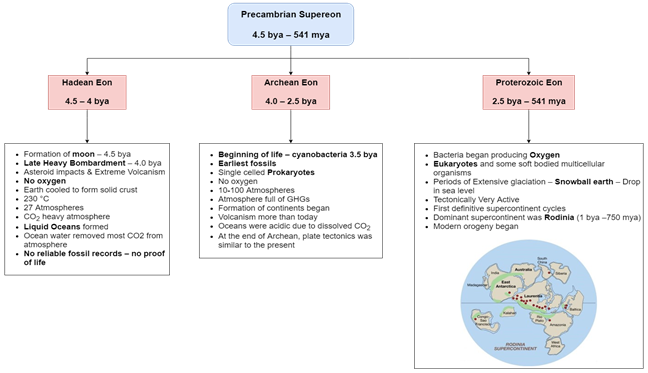
- The planet’s geological time scale is divided into five broad categories:” eons, epochs, eras, periods, epochs and ages. “
|
Eon ==> Era ==> Period ==> Epoch |
- While eon is the broadest category of geological time, age is the smallest category.
- Each of these categories is further divided into sub-categories.
- For instance, Earth’s history is characterised by four eons, including Hadeon (oldest), Archean, Proterozoic, and Phanerozoic (youngest).
How scientists able to identify these timelines?
- According to the New York-based Paleontological Research Institution, “Most of the boundaries on the geological time scale correspond to the origination or extinction of particular kinds of fossils.”
- This is also related to something called the principle of faunal succession, which states that different kinds of fossils characterise different intervals of time.