Polity: Parliamentary Committees
Committees
- Broadly, parliamentary committees are of two kinds—Standing Committees and Ad Hoc Committees.
- The former are permanent (constituted every year or periodically) and work on a continuous basis, while the latter are temporary and cease to exist on completion of the task assigned to them.
Standing Committees
On the basis of the nature of functions performed by them, standing committees can be classified into the following six categories:
- Financial Committees
- Public Accounts Committee
- Estimates Committee
- Committee on Public Undertakings
- Departmental Standing Committees (24)
- Committees to Inquire
- Committee on Petitions
- Committee of Privileges
- Ethics Committee
- Committees to Scrutinize and Control
- Committee on Government Assurances
- Committee on Subordinate Legislation
- Committee on Papers Laid on the Table
- Committee on Welfare of SCs and STs
- Committee on Empowerment of Women
- Joint Committee on Offices of Profit
- Committees Relating to the Day-to-Day Business of the House
- Business Advisory Committee
- Committee on Private Members’ Bills and Resolutions
- Rules Committee
- Committee on Absence of Members from Sittings of the House
- House-Keeping Committees or Service Committees (i.e., Committees concerned with the Provision of Facilities and Services to Members):
- General Purposes Committee
- House Committee
- Library Committee
- Joint Committee on Salaries and Allowances of Members
Committees in Detail:
Public Accounts Committee
- This committee was set up first in 1921 under the provisions of the Government of India Act of 1919 and has since been in existence.
- At present, it consists of 22 members (15 from the Lok Sabha and 7 from the Rajya Sabha).
- The members are elected by the Parliament every year from amongst its members according to the principle of proportional representation by means of the single transferable vote.
- The term of office of the members is one year.
- A minister cannot be elected as a member of the committee.
- The chairman of the committee is appointed from amongst its members by the Speaker.
- The chairman of the committee is selected from the Opposition.
- The function of the committee is to examine the annual audit reports of the Comptroller and Auditor General of India (CAG).
- The CAG submits three audit reports to the President, namely, audit report on appropriation accounts, audit report on finance accounts and audit report on public undertakings.
- The committee examines public expenditure not only from legal and formal point of view to discover technical irregularities but also from the point of view of economy, prudence, wisdom and propriety to bring out the cases of waste, loss, corruption, extravagance, inefficiency and nugatory expenses.
- Its recommendations are advisory and not binding on the ministries.
Estimates Committee
- The origin of this committee can be traced to the standing financial committee set up in 1921.
- It consists of 30 members.
- All the thirty members are from Lok Sabha only.
- The chairman of the committee is appointed by the Speaker from amongst its members and he is invariably from the ruling party.
- The term of office is one year.
- It examines every year only certain selected ministries and departments. Thus, by rotation, it would cover all of them over a number of years.
- Its recommendations are advisory and not binding on the ministries.
- Its work is in the nature of a post-mortem.
Committee on Public Undertakings
- This committee was created in 1964 on the recommendation of the Krishna Menon Committee.
- It has 22 members (15 from the Lok Sabha and 7 from the Rajya Sabha).
- Its members are elected according to the principle of proportional representation by means of a single transferable vote.
- The term of office of the members is one year.
- The chairman of the committee is appointed by the Speaker from amongst its members who are drawn from the Lok Sabha only.
- They examine the reports of the Comptroller and Auditor General on public undertakings.
- The committee is not to examine and investigate any of the following:
- Matters of major government policy as distinct from business or commercial functions of the public undertakings
- Matters of day-to-day administration
- Matters for the consideration of which machinery is established by any special statute
Departmental Standing Committees
- On the recommendation of the Rules Committee of the Lok Sabha, Departmentally-Related Standing Committees (DRSCs) were set up in the Parliament in 1993.
- The main objective of the standing committees is to secure more accountability of the Executive to the Parliament, particularly financial accountability.
- The 24 standing committees cover under their jurisdiction all the ministries / departments of the Central Government.
- Each standing committee consists of 31 members (21 from Lok Sabha and 10 from Rajya Sabha).
- Out of the 24 standing committees, 8 work under the Rajya Sabha and 16 under the Lok Sabha.
- They consider the demands for grants of the concerned ministries / departments before they are discussed and voted in the Lok Sabha.
- Its report should not suggest anything of the nature of cut motions.
- They should not consider the matters of day-to-day administration of the concerned ministries / departments.
Consultative Committees
- Consultative committees are attached to various ministries / departments of the Central Government.
- They consist of members of both the Houses of Parliament.
- The Minister / Minister of State in charge of the Ministry concerned acts as the chairman of the consultative committee of that ministry.
- These committees are constituted by the Ministry of Parliamentary Affairs.
- These committees provide a forum for informal discussions between the ministers and the members of Parliament on policies and programmes.
- The maximum membership of a committee is 30 and the minimum is 10.
- These committees shall stand dissolved upon dissolution of every Lok Sabha and shall be reconstituted upon constitution of each Lok Sabha.
- In addition, separate Informal Consultative Committees of the members of Parliament are also constituted for all the Railway Zones.
- Unlike the Consultative Committees attached to various ministries / departments, the meetings of the Informal Consultative Committees are to be arranged during the session periods only.
Comptroller and Auditor General of India
- Article 148 provides for an independent office of the Comptroller and Auditor General of India (CAG).
- He is the head of the Indian Audit and Accounts Department.
- He is the guardian of the public purse and controls the entire financial system of the country at both the levels—the Centre and the state.
- He is one of the bulwarks of the democratic system of government in India; the others being the Supreme Court, the Election Commission and the Union Public Service Commission.
- The CAG is appointed by the president of India by a warrant under his hand and seal.
- He holds office for a period of six years or up to the age of 65 years, whichever is earlier.
- He tables his resignation letter to the President.
Duties and Powers
- He audits the accounts related to all expenditure from the Consolidated Fund of India, consolidated fund of each state and consolidated fund of each union territory having a Legislative Assembly.
- He audits all expenditure from the Contingency Fund of India and the Public Account of India as well as the contingency fund of each state and the public account of each state.
- He compiles and maintains the accounts of state governments. In 1976, he was relieved of his responsibilities with regard to the compilation and maintenance of accounts of the Central Government due to the separation of accounts from audit, that is, departmentalization of accounts.
- He audits the accounts of any other authority when requested by the President or Governor.
- He advises the President with regard to prescription of the form in which the accounts of the Centre and the states shall be kept (Article 150).
- He submits his audit reports relating to the accounts of the Centre to President, and reports relating to state to Governor.
Audit reports submitted by CAG to the President:
- Audit report on appropriation accounts;
- Audit report on finance accounts; and
- Audit report on public undertakings;
- When President lays these reports before both houses of the Parliament, the Public Accounts Committee examines them and reports its findings to the Parliament
Accessible India Campaign
Context
- The Accessible India Campaign also known as the Sugamya Bharat Abhiyan was launched in 2015 by Prime Minister.
- The project that aimed to make the country accessible for people with disabilities is yet to meet its target.
- The government has announced that deadline of Accessible India campaign has been extended.
About
- Accessible India Campaign (Sugamya Bharat Abhiyan) is a nation-wide Campaign launched by Department of Empowerment of Persons with Disabilities (DEPwD) of Ministry of Social Justice & Empowerment to provide universal accessibility to persons with disabilities.
- The campaign aims at providing equal opportunity to persons with disabilities to participate in all the aspects of life and live independently. The Sugamya Bharat Abhiyan focuses on developing accessible physical environment, transportation system and Information & communication ecosystem.
- The Government of India with firm commitment towards socio-economic transformation of the persons with disabilities is making efforts to create mass awareness for universal accessibility.
- India is a signatory to the UN Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities (UNCRPD).
Components of Accessible India Campaign
- Built Environment Accessibility
- Transportation System Accessibility
- Information and Communication Eco-System Accessibility
Serious Fraud Investigation Office
Context
- In a bid to prevent big economic offenders like Vijay Mallya and Nirav Modi from fleeing the country, the government has empowered PSU banks to request Lookout Circulars (LOCs) against wilful defaulters and fraudsters.
- The Home Ministry has also authorised the Serious Fraud Investigation Office (SFIO), a statutory corporate fraud investigation agency, to request LOCs if it feels the suspect may escape from India.
About
Serious Fraud Investigation Office
- It is not a statutory body, as it was established through an executive resolution, which inter alia stated the responsibilities and functions of the SFIO.
- It is under the ministry of Corporate Affairs.
- The SFIO makes investigations under the provisions of the Companies Act, 1956 and also forwards the investigated reports on violations of the provisions of other acts to the concerned agencies for prosecution/appropriate action.
- The SFIO is a multi-disciplinary organisation consisting of experts in the field of accountancy, forensic auditing, law, information technology, investigation, company law, capital market and taxation for detecting and prosecuting or recommending for prosecution white collar crimes/frauds.
- The SFIO normally take up only such cases for investigation, which are characterized by:
- complexity and having inter-departmental and multi- disciplinary ramifications;
- substantial involvement of public interest to be judged by size, either in terms of monetary;
- the possibility of investigation leading to or contributing towards a clear improvement in systems, laws or procedures.
- SFIO may also take up cases on its own; it investigates serious cases of fraud received from Department of Company Affairs.
- Whether an investigation should be taken up or not, is decided by the Director SFIO, who will be expected to record the reasons in writing. This decision is further subject to review by a coordination committee.
- It was set up in 2003, on the recommendation of Naresh Chandra Committee, and in the backdrop of stock market scams resulting in huge financial loss to the public.
E-Sahaj Portal
Context
- Union Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) has recently launched e-Sahaj portalto facilitate individuals and private companies in seeking security clearance for setting up businesses in certain sensitive sectors.
About
- e-Sahaj: On the portal, applicants can submit their applications and view its status online from time to time. This will bring greater transparency in according security clearances to business proposals relating to sensitive sectors and geographical locations.
- Security Clearance: The objective of national security clearance is to evaluate potential security threats, including economic threats and provide risk assessment before clearing investment and project proposals in key sectors. Thus, it is essential for maintaining healthy balance between ensuring national security and facilitating ease of doing business.
- MHA: It is the nodal authority for granting security clearances in certain sensitive sectors before licence, permit, permission, contract etc. is issued to companies, bidders, individuals by respective administrative ministry.
Significance
- With its introduction, the process has now become standardised, making the process faster, transparent and easier to monitor.
- It will thus help in facilitating ease of doing business and promoting investment in the country.
Repurpose Used Cooking Oil (RUCO)
.jpg)
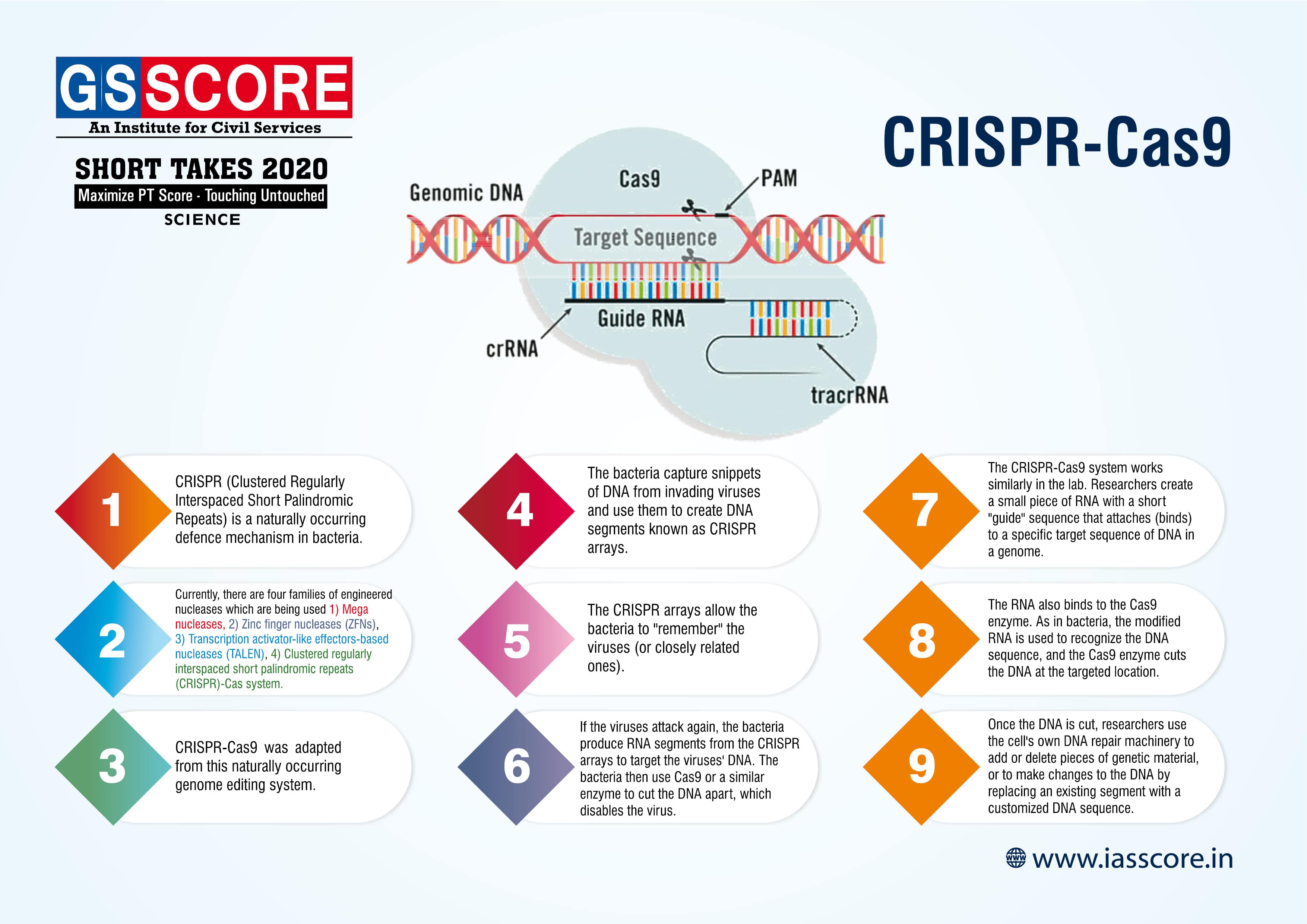
CRISPR-Cas9
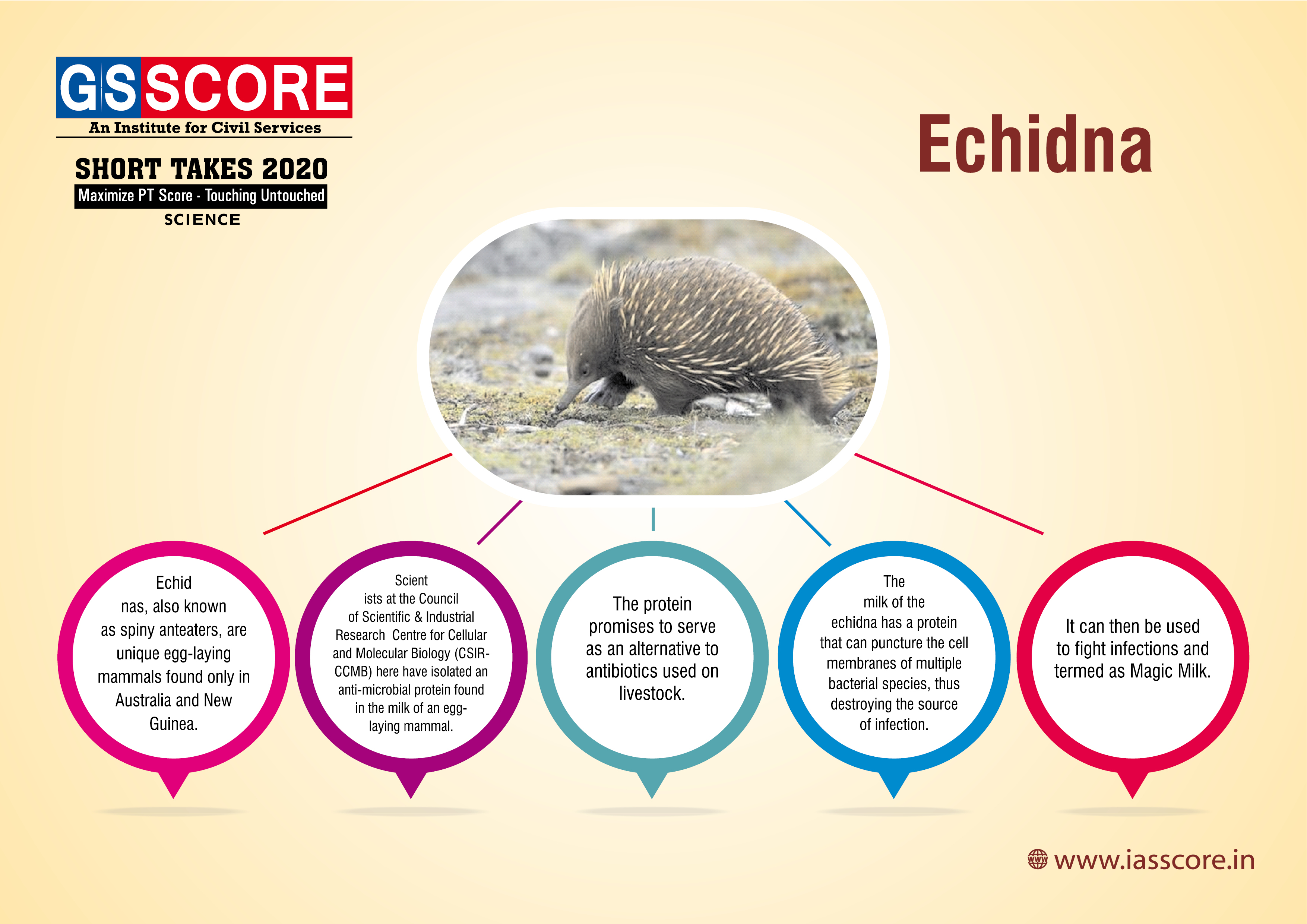
Echidna
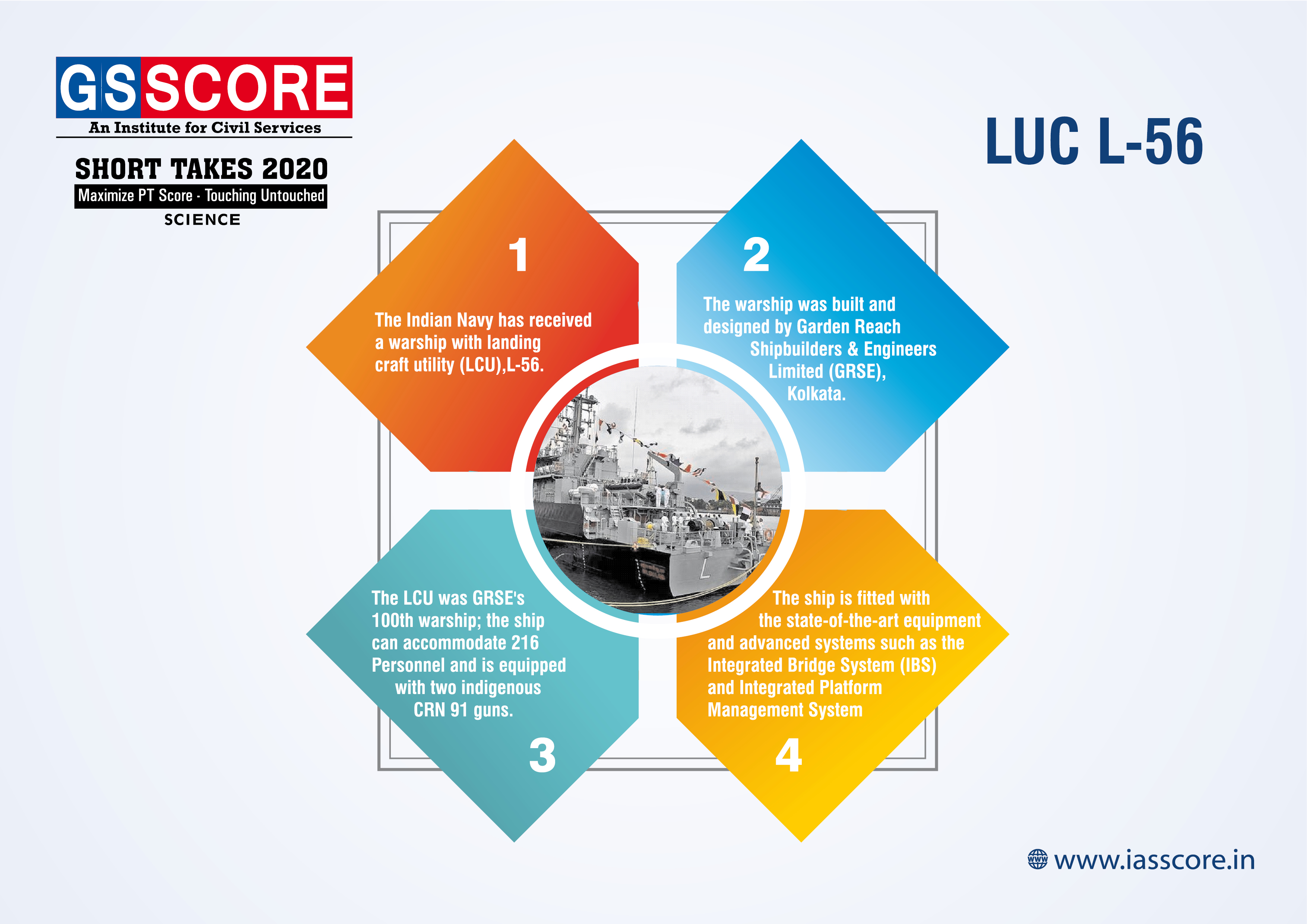
LUC L-56
Facebook launches tools to boost Electoral Process
-min.jpg)


