14th February 2024 (11 Topics)
Context
The government announced the establishment of a Centre for Energy Transition in collaboration with The Energy and Resources Institute (TERI) at the 23rd World Sustainable Development held in New Delhi. This centre aims to lead the way in sustainable energy transition and innovation in renewable energy.
What is the current share of renewable energy?
- India ranks fourth in renewable energy installed capacity after China, the US and Brazil and third in renewable energy attractiveness after China and the US.
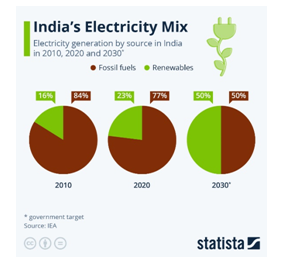
| Fossil fuels, including coal, continue to make up 75% of India’s power supply. |
- The share of renewable energy (wind, solar and other RE) increased to 30.1% in 2023 compared to 27.5% in 2022 with the share of coal-based power plants decreasing from 51.1% to 49.3%, marking a change in the energy supply mix.
- 44% of the nation's power generation capacity stems from non-fossil-fuel sources.
- With over 180 GW of renewable capacity out of a total of 427 GW, India stands at the forefront of renewable energy adoption.
- In its updated nationally determined contribution (NDC) to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change submitted in 2022, India put forth its goal of 50% installed power capacity from non-fossil sources.
- Already India’s non-fossil (including hydro and nuclear) installed capacity is around 43% of total installed capacity.
| India has surpassed its nationally determined contributions (NDCs) well ahead of schedule, positioning itself as the only major country whose energy transition aligns with limiting global temperature rise to sub-2 degrees. |
|
Major types of renewable energy |
|
|
Wind |
|
Solar (Photovoltaic)
|
|
Geothermal |
|
Hydropower |
|
Biomass
|
|
What is the need to transform the energy sector?
|
Energy transition refers to the energy sector’s shift from fossil-based systems of energy production and consumption — including oil, natural gas and coal — to renewable energy sources like wind and solar. |
- The world is at a decisive moment in the fight against climate change.
- India has the third largest energy demand in the world, with over 70% of its production coming from thermal power (primarily from coal, but also lignite, diesel and gas).
- India comprises 17% of the global population, while it is only responsible for only 3% of cumulative global carbon emissions.
- The share of renewable and non-fossil fuel sources has been steadily rising, but is still a small part of the overall mix.
- Given India’s growing economy and rising population, its energy needs are expected to quadruple in the coming decades.
- With greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions continuing to rise and average temperatures increasing, achieving net zero emissions by mid-century has become an urgent priority to avoid catastrophic climate impacts.
- To achieve net zero and limit future warming to 1.5C above pre-industrial levelsin line with the Paris Agreement, nothing less than a complete transformation of the global energy system is required.
|
The net-zero challenge
|
What government is doing for energy transition?
|
The government has also allocated INR 350 billion in the Union Budget 2023-24 towards energy transition, and announced a National Electricity Plan. |
- Net-Zero Emissions: At the UN Climate Change Conference held in Glasgow (COP26) in 2021, India committed to reaching net-zero emissions by 2070. This commitment was backed with other near-term targets for 2030, including
- achieving about 50 per cent cumulative electric power-installed capacity from non-fossil fuel-based energy resources
- reducing the emissions intensity of its GDP by 45 per cent from the 2005 level
- increasing its non-fossil electricity generation capacity to 500 GWs
- Energy Conservation Amendment Act 2022: The government has enacted the Energy Conservation Amendment Act 2022, which amended the Energy Conservation Act, 2001 and introduction of a carbon credit trading scheme.
- National Green Hydrogen Mission: In January 2023, India launched its National Green Hydrogen Mission to support production, use and exports of green hydrogen and its derivatives.
- PLI Scheme: Recently, the government concluded two tranches of allocations under the Production Linked Incentives (PLI) Scheme for high-efficiency solar photovoltaic (PV) modules.
- Electricity (Promoting Renewable Energy Through Green Energy Open Access) Rules 2022: The rules aim to promote the generation, purchase and consumption of green energy, including from waste-to-energy plants, through improving open access.
- National Framework for Promoting Energy Storage Systems a Viability Gap Funding (VGF) scheme: The scheme aims to boost the set-up of battery energy storage system (BESS) projects.
- FDI: Foreign investors are allowed to make 100 per cent investments in the renewable energy sector under the automatic route, without requiring prior government approval.
|
Other Government Initiatives for Solar Energy
|
- Push to rooftop solar: PradhanmantriSuryodayaYojana is a central government scheme which aims to provide electricity to low and middle-income individuals through solar rooftop installations, along with offering additional income for surplus electricity generation.
- Biomass-Based Schemes: GOBARdhan and SATAT
|
Global Biofuel Alliance (GBA) aims to expand the use of sustainable biofuels across various sectors, with a focus on reducing emissions and promoting cleaner energy alternatives. |
- GOBARdhan:Galvanizing Organic Bio-Agro Resources Dhan aims to convert cattle dung and agricultural residues into biogas, compressed biogas (CBG), and bio-compressed natural gas (CNG). It promotes circular economy principles and contributes to India’s climate goals.
- SATAT:The Sustainable Alternative Towards Affordable Transportation scheme focuses on setting up compressed biogas production plants. It enhances energy security, reduces emissions, and benefits both rural communities and women.
Pitfalls of the energy transition
- Ecological cost: While the commitment to reach 500 GW through ‘non-fossil-fuel’ and ‘renewable’ energy sounds positive, a very problematic part of this is that it includes large hydropower and nuclear plants. Both of these have enormous ecological, social and other costs.
|
Dam bursts in Uttarakhand, northern India, and most recently in Sikkim in north-east India are dramatic testimony to the dangers of massive infrastructure development in the fragile Himalaya. |
- Imbalance: 80% of the solar projects are reportedly in only 5 states (Rajasthan, Maharashtra, Gujarat, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh), creating further imbalances in the benefits that such projects could deliver.
- Effectiveness of EV: Electric vehicles (EVs) are government’s top focus. However,
- EV uses electricity produced by coal: Most of the electricity that EV will use is still being generated through coal (as is the case in India), they are hardly clean.
- Mining concerns: There is increasing concern about the impacts of related mining, e.g. of lithium and cobalt.
|
In India, lithium reserves have been found in Kashmir. However, it also raises concerns about serious ecological damage and social displacement. |
- Increase in coal mining and thermal power: New coal mining blocks continue to be given a green signal, including in some of the country’s most biologically diverse and socially sensitive (including indigenous/ Adivasi) areas.
- Unnecessary demand: Over the last few decades, luxury and wasteful demand and use has significantly grown (night-time glitz in India’s cities, extra cooling in malls and airports).
- Infrastructural issue Grids powered by renewable energy require a lot more effort to achieve stability in times of disruption than conventional energy sources, which can ramp up or down production as required. India's grid infrastructure requires a significant upgrade to adapt to the intermittent nature of renewable power.
- Operational issues: overloading of transmission lines at certain times, demand-supply disparities, frequency and voltage issues, losses of electricity transmission, a lack of coordination among state-level transmission planners and central planning agencies.
- Managing coal-dependent states: Indian states are highly dependent on coal. Managing the economy of coal-dependent states to steady the increasing share of renewable energy of some states is challenging.
- Troubled land acquisition: Land acquisition for large-scale renewable projects is cost-intensive with limited government support.
- Funding obstacles:Trillions of dollars will be required for transition – and flows of green finance are only about a quarter of what is needed now.
Major Renewable Solutions:
- Solar Power: India's solar power installed capacity was 73.32 GWAC as of 31 December 2023.
- Wind power generation capacity: As of 31 December 2023, the total installed wind power capacity was 44.736 gigawatts (GW), the fourth largest installed wind power capacity in the world.
- Hydrogen energy: India's current hydrogen consumption stands at an estimated 6 mmtpa, with specific figures fluctuating between 5 and 7 mmtpa.
- Nuclear energy: India has over 22 nuclear reactors in 7 power plants across the country which produces 6780 MW of nuclear power.
What measures are required?
- Power sector: Power generation is India’s largest source of GHG emissions because coal provides over 70% of the country’s electricity. It is unrealistic to rapidly reduce coal’s share in the fuel mix, even with richer countries providing support through initiatives such as the Just Energy Transition Partnership.
- Aging and inefficient coal plants can be phased out, while newer plants can be cleaned up to meet more stringent emissions standards.
- Deployment of renewables can also be stepped up significantly by establishing a domestic clean-energy supply chain.
|
Government Interventions for EV:
|
- Transport sector: Decarbonizing the transport sectorwill likely be more challenging than decarbonizing power. Though the sector has already start by electrifying two- and three-wheelers, which account for about two-thirds of India’s petrol demand. Mass transportation can also be fully electrified.
- Energy efficiency: A nationwide initiative to accelerate energy efficiency could pay significant dividends. Other expanding economies have shown that it is possible to slow growth in energy demand with efficiency measures, which then eases emissions. Energy savings would come from industry, buildings and transportation.
- Streamline demand & finances:National entities like the Solar Energy Corporation of India (SECI) and Indian Renewable Energy Development Agency (IREDA) can adopt the role of aggregator of demand for the sector at large. They can also play a role in supporting the financial process by providing payment security or leading partnerships to enable the same.
More Articles