15th September 2025 (15 Topics)
Context
New scientific studies indicate that mosquitoes are adapting to climate change, expanding their geographical range, and increasing the global risk of mosquito-borne diseases such as malaria and dengue.
Mosquitoes as Disease Vectors:
- The CDC calls mosquitoes the “world’s deadliest animals” as they cause over 1 million deaths annually.
- Diseases spread: Malaria (Plasmodium parasite via Anopheles), Dengue, Chikungunya, Zika, Yellow Fever (Aedes aegypti), West Nile virus, Japanese Encephalitis.
Climate Change Link:
- Rising global temperatures and humidity extend mosquito habitats beyond traditional tropical zones.
- UC Berkeley (2025) study: genetic variations help mosquitoes tolerate heat, expanding their survivability.
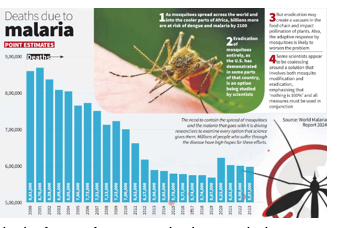
- WHO World Malaria Report 2024: 597,000 malaria deaths in 2023; decline in malaria deaths has stagnated since 2015 due to resistance.
Control & Eradication Approaches:
- Traditional: Insecticides like DDT (banned due to ecological harm; Rachel Carson’s Silent Spring 1962 highlighted eggshell thinning in birds).
- Sterile Insect Technique (SIT): Used against New World Screwworm Fly (Cochliomyia hominivorax). Sterile male release reduces populations.
- Genetic Modification (CRISPR-Cas9): Produces sterile or male-biased offspring in mosquitoes.
- Biological Control:
- Wolbachia bacteria in Aedes aegypti blocks dengue, Zika, chikungunya, yellow fever transmission (successful field trials in Australia, Brazil, Colombia).
- New bacterial strains discovered that block Plasmodium parasite in Anopheles mosquitoes.
- Drug Repurposing: Nitisinone drug found effective in killing Anopheles gambiae mosquitoes, even those resistant to insecticides.
Challenges:
- Resistance development in mosquitoes to insecticides.
- Ecological concerns — out of 3,000+ mosquito species, only a few spread diseases, but eradication of all could disrupt food webs and pollination.
- Need for integrated vector management (IVM) combining vaccines, treatment, biological, genetic, and chemical methods.
More Articles