

21st April 2023 (7 Topics)
Context
The Ministry of Jal Shakti has released the report of the first census of water bodies.
Key highlights of the Census
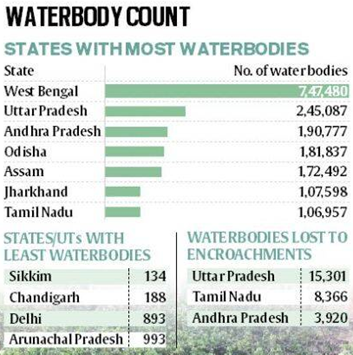
- India has 24.24 lakh water bodies like ponds, tanks and lakes, with West Bengal accounting for the most (7.47 lakh) and Sikkim the least (134).
- The report states, “24,24,540 waterbodies have been enumerated in the country, out of which 97.1% (23,55,055) are in rural areas and only 2.9% (69,485) in urban areas.”
- As per the report,
- 5 per cent (14,42,993) of waterbodies are ponds
- tanks (15.7 per cent i.e. 3,81,805)
- reservoirs (12.1 per cent i.e. 2,92,280)
- water conservation schemes/percolation tanks/check dams (9.3% i.e. 2,26,217)
- lakes (0.9% i.e. 22,361)
- others (2.5% i.e. 58,884)
|
What is a water body?
|
More Articles


