17th February 2025 (16 Topics)
Context
India and the United States have launched a transformative bilateral initiative called the Transforming Relationship Utilizing Strategic Technology (TRUST), aimed at boosting cooperation in the recovery and processing of critical minerals such as lithium and rare earth elements (REEs).
What is the TRUST Initiative?
- The TRUST Initiative aims to reduce barriers to technology transfer, address export controls, and enhance high-tech commerce.
- It will deepen the collaboration between India and the U.S. across various strategic sectors like defense, artificial intelligence (AI), semiconductors, quantum computing, and pharmaceuticals.
- The TRUST initiative will focus on the following aspects:
- Critical Minerals Supply Chains: The two countries will work together to establish strong supply chains for critical minerals such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel, which are essential for technologies in defense, renewable energy, and electric vehicles.
- Strategic Mineral Recovery and Processing: There will be an emphasis on the recovery and processing of strategic minerals, ensuring that these resources are sustainably managed and processed in both nations.
- Tech Transfer and High-Tech Commerce: TRUST aims to reduce barriers for technology transfer between the two nations, enhancing high-tech commerce across multiple sectors, including biotechnology and space exploration.
What is the need of the initiative?
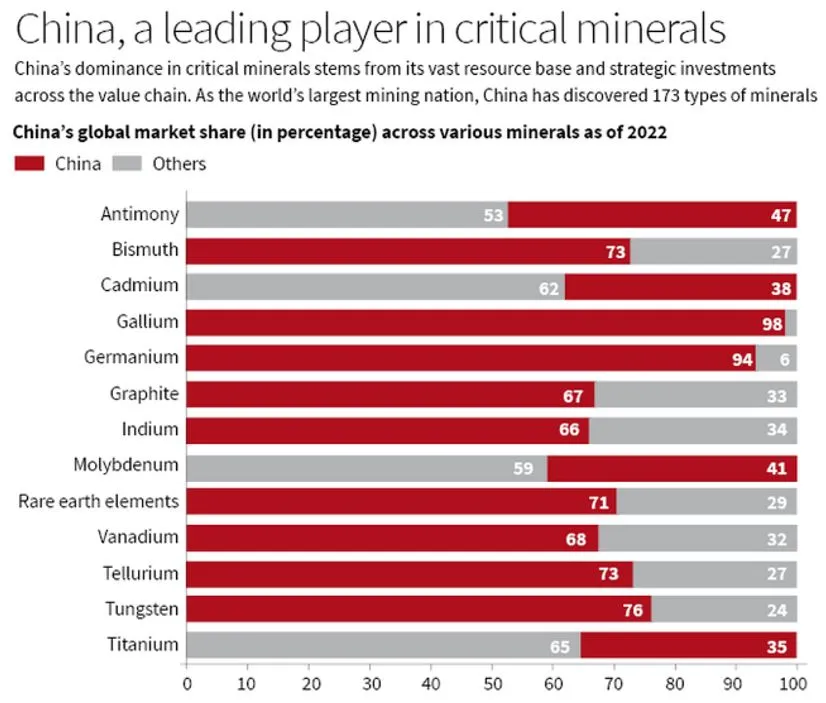
- The TRUST initiative comes at a time when the global supply chains for these critical minerals are heavily dominated by China, which controls nearly 70% of the global REE production and much of the processing infrastructure.
China’s dominance in critical minerals
|
- This dominance has raised concerns about technological sovereignty and national security, particularly for countries like India and the U.S., which rely on these minerals for military and high-tech applications.
Potential Benefits of TRUST
- Enhanced Innovation: TRUST will foster collaboration among governments, academia, and the private sector to drive innovation in areas such as defense, artificial intelligence, biotechnology, and energy.
- Boost to Strategic Industries: The focus on critical minerals will directly benefit industries that are foundational to national security and technological progress, including semiconductors, quantum computing, and space exploration.
- Strengthened Global Supply Chains: By diversifying sources of critical minerals, India and the U.S. can reduce dependency on a single country (China), ensuring more stable and secure access to resources.
- Strategic Importance: The strategic importance of critical minerals, especially lithium and REEs, cannot be overstated. These elements are vital for advanced technologies in key sectors such as:
- Defense: For manufacturing high-performance magnets used in missiles, fighter jets, and radar systems.
- Energy: Lithium, cobalt, and nickel are essential for battery storage technologies, especially in electric vehicles and renewable energy storage.
- Semiconductors and AI: Gallium and indium are crucial components in the development of semiconductors and AI hardware.
- Space: Heat-resistant alloys and lightweight materials such as scandium are critical for space exploration.
Challenges and Expectations
- Tax Benefits: Unlike Japan, which was granted tax benefits under the S. Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) for critical raw materials and battery components, Indian companies in the battery sector may not immediately benefit from such privileges.
- Technology Transfer: The success of the initiative will depend on reducing barriers to technology transfer, allowing Indian companies to leverage cutting-edge technologies in mineral processing and battery manufacturing.
What are Critical Minerals?
Previous Collaborations and National Programs
|
More Articles