Context
India and Saudi Arabia have joined the European Union and the United States in launching the Partnership for Global Infrastructure and Investment (PGII) and India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor.
About
India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor:
- In a bid to stimulate economic development through enhanced connectivity and economic integration, India, along with other members of the G20, has entered into a historic memorandum of understanding (MoU) to develop an India-Middle East-Europe economic corridor.
- The project is a part of the Partnership for Global Infrastructure Investment (PGII) — a West-led initiative for funding infrastructure projects across the world.
- Objective: The corridor aims to provide a reliable and cost-effective ship-to-rail transit network between Asia, Middle East and Europe.
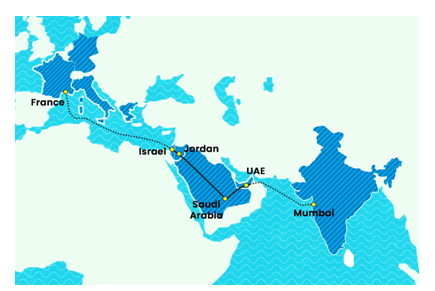
- Proposals: The corridor will comprise of two separate corridors,
- The Eastern corridor - will connect India to the Arabian Gulf.
- The Northern corridor- will connect the Arabian Gulf to Europe.
- Member Nations:Apart from India, the other participants will include Saudi Arabia, UAE, France, Germany, Italy, USA and the European Union.
- Components of the project:
- The arrangement will include a railway route that, upon completion, will provide a reliable and cost-effective cross-border ship-to-rail transit network to supplement existing maritime and road transport routes.
- This will enable goods and services to transit to, from, and between India, the UAE, Saudi Arabia, Jordan, Israel, and Europe.
- Along the railway track, the members want to lay a cable for clean hydrogen export.
- Key functions:
- This corridor will safeguard regional supply chains, boost trade accessibility, and enable a greater emphasis on environmental, social, and governance consequences.
- It will be designed to increase efficiencies, save costs, promote economic cohesion, create jobs, and reduce greenhouse gas emissions, leading to a radical integration of Asia, Europe, and the Middle East.
- Intended Timeline: As per the MoU, the members intend to meet within the next sixty days to develop and commit to an action plan with relevant timetables.
- However, although the memorandum sets forth political commitments of its participants, it does not create any rights or obligations under international law, which means that the members are not necessarily bound by it.
|
The EU, through its Global Gateway programme, has announced to activate 300 billion of investments in critical connectivity projects during the period 2021-2027. |
- Significance:
- It is seen as a counter to China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI).
- Key for connectivity of Global South.
- Strengthening supply chains amid Russia-Ukraine War.
|
Partnership for Global Infrastructure Investment (PGII):
|
Similar Initiatives:
- China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI): It was launched by China in 2013.
- The BRI consists of two main components:
- The Silk Road Economic Belt, which is a land-based network connecting China to Europe through Central Asia and the Middle East, and
- The 21st Century Maritime Silk Road, which is a sea-based network linking China to Southeast Asia, South Asia, Africa, and Europe via the South China Sea and the Indian Ocean.
- This initiative spans multiple continents, with projects in over 70 countries.
- India, however, opposed the BRI as it included the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor, which connected Kashgar in China with the Gwadar port in Pakistan via Pakistan-occupied Kashmir.