

18th July 2023 (6 Topics)
Context
- The Rashtriya Sarokar and Samanwaya Samiti — a committee of the upper house of Nepal Parliament that looks after issues of national concern and coordinates with the government has mentioned that India-Nepal borders are facing security threats, due to porous nature.
About the concern highlighted:
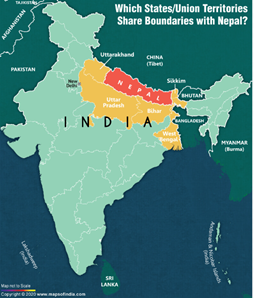
- Nepal shares a 1,850-km border with India with no travel restrictions to citizens of either side.
- The open border has contributed to human and drug trafficking, smuggling of arms and weapons besides fugitives crossing the border and taking refuge in Nepal.
Border Management between India and Nepal:
- Indo-Nepal border is governed under Sagauli Treaty 1816.
- India and Nepal have shared an open border since 1950. The conception of such a border can be found in the Treaty of Peace and Friendship that the two countries signed that year.
- Provisions in the treaty, wherein citizens of both countries are given equal rights in matters of residence, acquisition of property, employment and movement in each other’s territory, provide for an open border between the two countries.
- Free movement of people across the border and strong people to people tie-up. This base of this good relationship is due friendship treaty of 1950.
Points of Dispute:
- Open border has been a great facilitator of strong and unique bilateral relations. At the same time, it has given rise to many irritants and problems that raise serious concerns.
- Allegations of excesses such as intimidation and forcible grabbing of land by either side along the disputed border also surface from time to time.
- There are dispute over the some areas due to shifting course of Himalayan River. Kalapani and Susta disputes.
- Many terrorist organisations and Naxalites have fully exploited open borders with Nepal.
- Open border with Nepal facilitated movement of terrorists and insurgents which created instability in the country fuelling the separatist movement in Kashmir and insurgency problem in north-east.
- Many criminals from both sides escape the countries.
- ISI and other terrorist’s organizations are using Nepal as a transit route and operate from the soil of Nepal.
Government Interventions:
- Establishment of a new intelligence section in SSB at Indo-Nepal and Indo- Bhutan border to ensure better operational efficiency.
- Establishment of Border District Coordination Committee at the level of district officials of the two countries to discuss issues of mutual concern.
- The Government of India has approved construction of 1377 km of roads along Nepal border.
- Development aid to Nepal to prevent human trafficking owing to lack of employment opportunities there
- 200 bed Nepal Bharat Maitri Emergency and Trauma Centre in Kathmandu.


