12th December 2024 (13 Topics)
Context
The case of Bengaluru Techie who died by suicide citing alleged harassment by his estranged wife has opened up a debate on misuse of anti-dowry law. The Supreme Court expressed concern over the rampant misuse of Section 498A of the Indian Penal Code (IPC), which penalises cruelty by husbands and their relatives against married women.
Purpose of Laws
- India has made significant progress in protecting women's rights through various laws. These laws aim to promote gender equality, and ensure social, political, and economic justice for women.
- However, some women misuse these laws for personal gains, leading to serious concerns about the misuse of the legal system.
- This misuse is referred to as the "weaponization of laws."
- Laws Misused: Several laws meant to protect women have been misused:
- Dowry Laws (Section 498-A of IPC): These laws aim to stop dowry-related harassment but have been misused for extortion and false accusations against husbands and their families.
- Domestic Violence Act: Although meant to protect women from domestic abuse, it has been used to harass innocent family members, including elderly relatives, during family disputes.
- Sexual Harassment at Workplace (POSH) Act: Some women have falsely accused colleagues or superiors to settle personal scores.
- Rape Laws: There are cases where women have falsely accused men of rape to gain personal benefits or seek revenge.
- Child Custody Laws: Some women misuse these laws in divorce cases to gain sole custody of children, even when it's not in the child's best interest.
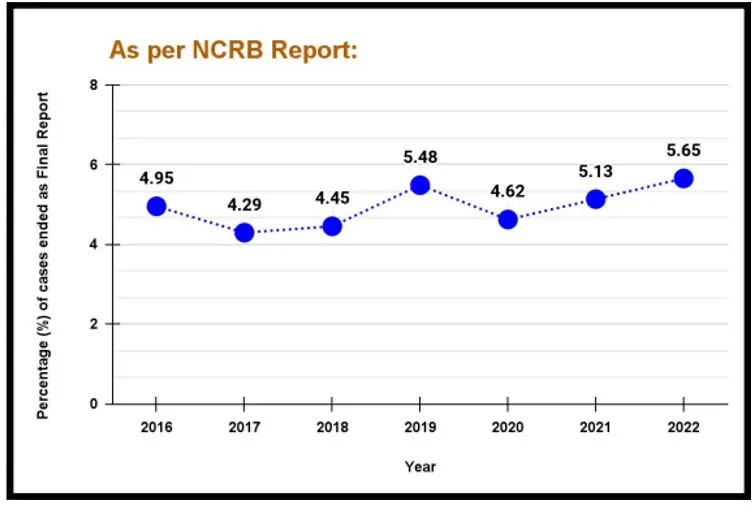
NCRB Data on False Cases
According to the National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB), a significant number of cases are found to be false:
- In 2022, out of 650,033 cases investigated, 36,715 (5.65%) were found to be false.
- The false cases were particularly high in certain categories:
- Rape: 9.69% of rape cases were false.
- Attempt to Commit Rape: 15.23% were false.
- Assault on Women with Intent to Outrage Modesty: 5.93% were false.
Factors Behind Misuse
Several factors contribute to the misuse of laws:
- Lack of Legal Consequences: There's often no severe punishment for those who file false cases, making it easy for them to misuse the system.
- Societal Pressure: There’s societal pressure on authorities to favor women in such cases, leading to bias against the accused.
- Economic Motives: In some cases, women misuse laws for financial gains, such as seeking alimony or property.
- Emotional Turmoil: Disputes, particularly in family matters, can drive people to misuse legal provisions out of anger or revenge.
- Difficulty for Accused to Prove Innocence: The person accused in a false case often struggles to prove their innocence due to the burden of proof being on them, causing them to suffer financially, emotionally, and mentally.
Impact on Men
The psychological toll on men falsely accused of crimes is immense. It can ruin their reputation, harm their mental health, and even lead to acts of revenge. The social stigma that comes with being falsely accused can last for a long time, affecting not just the individual but also their family and future generations.
Key ethical aspects related to the misuse of laws:
- Moral Responsibility of Individuals: The act of filing false cases or misusing the legal system is not only legally wrong but also ethically irresponsible. Ethics emphasizes personal responsibility and honesty. Misuse of laws to harass innocent people violates moral principles of fairness and justice.
- Trust in Legal Systems: For a society to function ethically, the rule of law must be upheld with integrity. The misuse of laws erodes public trust in the legal system, causing long-term societal harm. Ethical governance requires ensuring that laws are applied correctly and that those who misuse them are held accountable.
- Ethical Dilemmas of False Allegations: When false accusations are made, they lead to ethical dilemmas for all involved—judges, police, and society at large. Legal professionals are ethically bound to ensure justice is done, but false claims complicate their ability to do so. This puts them in situations where they must balance empathy for the victim with a duty to protect the accused.
- Prevention of Abuse of Power: Misuse of laws is also an abuse of power. Ethical governance requires checks and balances to prevent individuals from using their power within the legal system for personal or malicious purposes.
- Equity vs. Equality: While laws protecting women’s rights are essential for gender equality, misuse of these laws presents a conflict between equity and equality. Ethical principles highlight the need to balance the protection of vulnerable groups with fairness to all individuals, regardless of gender. Misuse of laws for personal gain undermines the very principles of gender equality that such laws are meant to protect.
- Empathy and Compassion: Ethics also stresses the importance of empathy and compassion in handling sensitive issues like domestic violence or sexual harassment. While the law is meant to protect, it should also be used in a manner that fosters genuine concern and empathy for those who truly need help, rather than being manipulated for personal motives.
|
Crimes Identified Under the Indian Penal Code (IPC) Obscenity
Dowry Death
Acid Attack
Outraging the modesty of a women
Rape and Sexual Assault
Cruelty
|