Scientists have uncovered a new type of human brain cell, named asroseshipthat has never been seen in mice and other well-studied laboratory animals.
Context
Scientists have uncovered a new type of human brain cell, named asroseshipthat has never been seen in mice and other well-studied laboratory animals.
About
- The new finding is the result of collaboration between Allen Institute for Brain Science in Seattle and researchers at the University of Szeged in Hungary.
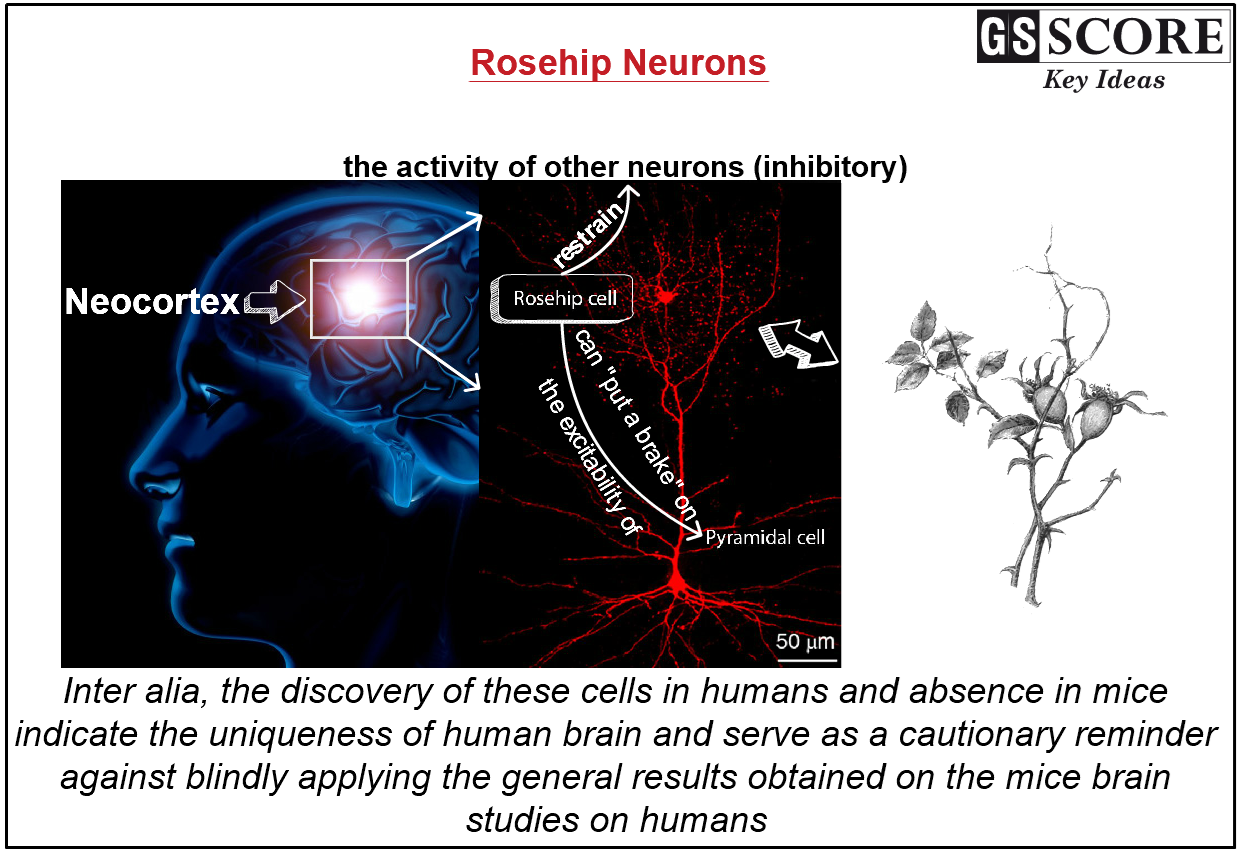
- The new neuron is named after the small, red fruits of a rose plant, called rosehips (defragmented rose).
- Distinctive shape:Rosehips have long branches called dendritesthat receive signals from other neurons. In the rosehip cells, these dendrites are very compact with lots of branch points, resembling a rosehip.

- Diverse connections with other neurons:It make up about 10% of the first layer of the neocortex — the most recently evolved part of the cortex that's involved in sight and hearing.They are alsoconnected to neurons called pyramidal cells, a type of excitatory neuron that makes up two-thirds of all the neurons in the cortex.
- Unique gene expression:Rosehip neurons act as inhibitory neurons, or those that restrain the activity of other neurons. They have the potential to sort of put the brakes on the excitability of pyramidal neurons.
Significance
- Human Cell Atlas: It is a significant contribution to the massive project to compile transcriptomic data on all the cells in the human body to understand how they organize into tissues, how they talk to each other, how they age, and how things can go wrong.
- Individuality of human brain: The absence of the rosehip neuron in mice brains might serve as a cautionary reminder that the results of some brain studies done on rats can't be translated to humans. Mice have been a wonderful model organismfor understanding how brains work in general and can help us understand how human brains work but finding a part of that circuit that is not seen in a mouse that points to needing to study actual human tissue.
- Future prospects: Finding cell types that are uniquely human helps the understanding of the physiological differences, that under higher cognitive abilities may help in treatment strategies for brain-related disorders.
Learning Aid
A visual overview of rosehip neurons :