

10th September 2025 (16 Topics)
Context:
The Union Ministry of Tribal Affairs has sought a factual report from the Andaman and Nicobar administration after the Tribal Council alleged non-settlement of forest rights under the FRA, 2006, prior to diversion of land for the Great Nicobar Project.
Great Nicobar Project
Project Overview 
- Name: Great Nicobar Project
- Type: Multi-development initiative
- Timeline: Phased development over 30 years
- Clearance: Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC), Nov 2022
- Estimated Cost: ?72,000 crore
- Purpose: Strategic infrastructure development, economic growth, and enhanced security presence in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands
Strategic Importance
- Enhances India’s strategic presence in the southern Bay of Bengal.
- Counters expansionist activities by China in the Indo-Pacific region.
- Secures maritime interests and monitors illegal fishing/poaching (particularly by Myanmar).
- Supports India’s Look East/Act East Policy and maritime domain awareness.
Key Infrastructure Components
- International Container Trans-shipment Terminal – to handle global shipping traffic.
- Greenfield International Airport – dual-use (civilian and military) for strategic mobility.
- Township Development – supporting residential and commercial needs.
- Power Plant (450 MVA) – hybrid model: gas and solar-based.
- Transportation Networks – roads, ports, and logistic facilities.
Geographical and Ecological Context
- Location: Southernmost island of the Andaman and Nicobar group; near Indira Point (<150 km from Indonesia).
- Topography: Mountain ranges up to 650 m, tropical wet evergreen forests, coastal plains.
- Protected Areas: Two national parks and a biosphere reserve.
- Biodiversity: Home to endangered species like leatherback sea turtles, endemic flora and fauna.
Indigenous Tribes and Social Considerations 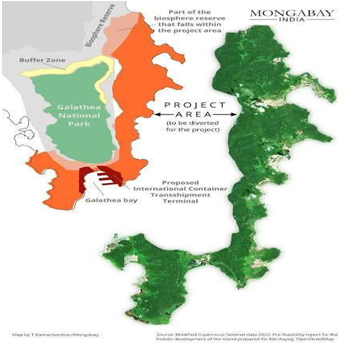
- Shompen Tribe: ~237 members, hunter-gatherers; reside in tribal reserve.
- Nicobarese Tribe: ~1,094 members; part of the tribal reserve.
- Land Impact: 84 sq km proposed for denotification out of 751 sq km tribal reserve.
- Concerns: Cultural displacement, loss of traditional livelihoods, protection of tribal rights under Scheduled Tribes and Other Traditional Forest Dwellers (Recognition of Forest Rights) Act, 2006.
Environmental Impacts
- Deforestation: 13,075 hectares (15% of island area); ~9.64 lakh trees to be cut.
- Ecosystem Risk: Threat to forests, mangroves, wildlife habitats, and endemic species.
- Mitigation: Environmental management plans, compensatory afforestation, biodiversity conservation measures.
Seismic and Disaster Considerations
- Seismicity: High-risk zone; 2004 earthquake (9.2 Richter) affected region.
- Risk Assessment: Major earthquakes unlikely for 400–750 years; smaller tremors expected.
- Structural Safety: All infrastructure will adhere to National Building Code (NBC) earthquake-resistant norms.
More Articles


