

17th November 2023 (11 Topics)
Context:
The research was led by Scientists from IIT Guwahati and U R Rao Satellite Centre (URSC) has discovered that X-Ray Polarization in Extragalactic black hole.
What is a Black Hole?
- A black hole is formed when stars collapse, leading to a space in the universe with an escape velocity — the speed at which an object must travel to override a planet or an object’s gravitational force.
- Because light cannot get out, black holes are invisible and can only be tracked with the help of spatial telescopes and special tools.
- The light cannot go out because the gravity inside a black hole is very strong as a result of a lot of matter being squeezed into a small space.
|
Extragalactic black hole:
|
About the Study:
- Polarized emissions: For the first time, a team of researchers from the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Guwahati and the UR Rao Satellite Centre of the Indian Space Research Centre (ISRO) have detected polarized emissions from a black hole source that exists beyond our Milky Way Galaxy.
- Black hole sources: These findings open a new window to investigate and understand the nature of astrophysical black hole sources.
- Large Magellanic Cloud X-3 (LMC X3): It is a binary star system consisting of a black hole and a ‘normal’ star that is "much hotter, bigger, and more massive than the Sun.
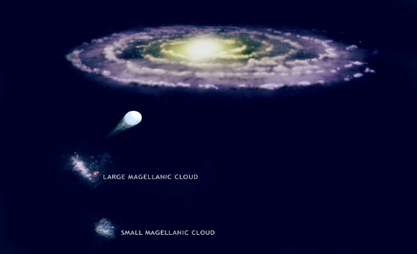
- Location: The system is located in a satellite galaxy of the Milky Way, nearly 2,00,000 light years away from planet Earth.
- Satellite galaxy of Milky Way: Since its discovery in 1971, it has been observed by various satellites. However, there has been a gap in understanding the polarization properties of X-rays emitted by highly energetic objects like stellar mass black holes in the universe.
- The Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer (IXPE): The researchers studied LMC X-3 using ‘The Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer (IXPE)’, NASA’s first mission to study polarization of X-rays from celestial objects.
- Additional Data: They also used simultaneous broad-band coverage of the Neutron Star Interior Composition Explorer (NICER) Mission and the Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR) Mission to constrain the spin of LMC X-3.
Significance of the Study:
- X-ray polarimetry: It is a unique observational technique to identify where radiation comes from near black holes.
- Powerful X-rays: LMC X-3 emits X-rays that are 10,000 times more powerful than those from the Sun.
- Changes the polarization characteristics: When these X-rays interact with the material around black holes, specifically when they scatter, it changes the polarization characteristics, i.e. degree and angle.
- Behavior of matter drawing towards black hole: This helps in understanding how matter is drawn toward black holes in the presence of intense gravitational forces
More Articles


