

17th November 2023 (11 Topics)
Context:
High rainfall helped the survival of equatorial rainforests at a time when Earth was globally warm and atmospheric carbon dioxide concentration was a whopping more than 1000 ppmv, around 50 million years ago.
Background:
- The existing palaeo-climate data of mid- and high latitudes suggest large fluctuations in rainfall at around 50 million years ago.
- However, the quantification of terrestrial palaeoclimate data from the equatorial region was never attempted.
- Scientists are trying to explore the palaeoclimate data to probe the mysteries of survival under adverse conditions.
Paleoclimatic restructured simulations:
|
Paleoclimatology: It is the study of the climate history of Earth. This science helps people better understand the climate of Earth in the past and how it relates to the present and future climate on the planet. |
- Quantified Data: Scientists of Birbal Sahni Institute of Palaeosciences (BSIP), an autonomous institute of Department of Science and Technology, have quantified the terrestrial equatorial climate of around 50 million years ago using plant proxy.
- High rainfall and its effects: The scientists have estimated that the high rainfall, most likely, increased the plant’s water use efficiency and afforded resilience to survive and remain functional under extremely warm and elevated carbon dioxide concentration at around 50 million years ago.
- Global warming: It was earlier known that the Earth was around 13°C warmer than present and carbon dioxide concentration was more than 1000 ppmv during this time.
- Impact on Forest: This drastically affected the survival of mid- and high latitude forests due to changes in the hydrological cycle, but the equatorial forests survived successfully.
Significance of study:
- Low latitude regions forest study: The study has also helped focusing on developing a calibration file from the low-latitude regions which will be useful in the quantification of seasonal deep-time terrestrial climate.
- Blimatic and biotic changes: Tracing the mystery of the survival of the rainforests – the biodiversity hotspots of the world is the Key to understanding climatic and biotic changes occurring at present and in the future.
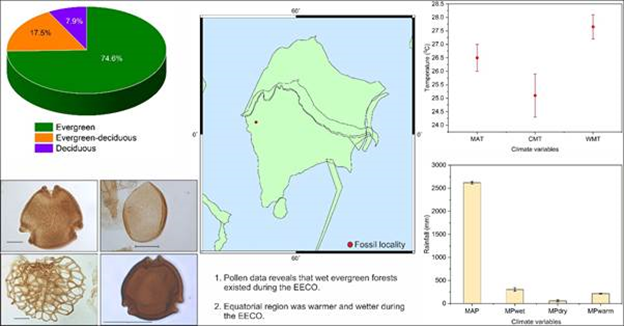
Analysis of Research:
- Geological Time Scale:
- Phanerozoic Eon – 543 mya - present
- Cenezoic Era – 65.5 mya - Present
- Paleogene Period - 5 mya – 23.0 mya
- Eocene Epoch – 55 mya – 34 mya - Early Eocene (56 million to 47.8 million years ago)
- Forest presence:
- Equatorial Forest: Due to high rainfall 50 mya, resulted in presence of around 75% of such forests.
- Evergreen-Deciduous Forest: The Evergreen-deciduous forest presence is around 17.5% over the globe.
- Deciduous Forest: The deciduous forest comprises of 7.9% which majorly lies in the transition of lower to mid-latitude regions of the Earth.
- Presence of India:
- India during this period was present near equator and was under the influence of equatorial type of climate.
More Articles


