

17th November 2023 (11 Topics)
Context:
India is close to resolving its most contentious trade dispute, involving Information communications technology (ICT) products, with its second largest trade partner, the European Union (EU).
Background:
- New Delhi was been dragged in to the WTO’s dispute settlement mechanism in 2019 challenging its levying of import duty on a wide range of ICT products.
- They include mobile phones and components, base stations, integrated circuits and optical instruments claiming that the duty was inconsistent with global trade norms and was hurting 600 million Euros worth of its tech exports to India.
- The dispute assumes significance as it was feared to affect India’s efforts to boost electronic products manufacturing — a strategic sector in which India is trying to cut its reliance on
|
On April 17, 2023, the dispute settlement panel of the WTO, in three separate disputes filed by the EU, Japan and Chinese Taipei against India's import duties on certain ICT products, had ruled that the tariffs violated its commitment under multilateral trade rules and needed to be corrected. |
About the information: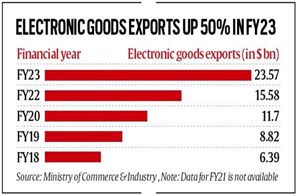
- The mutual settlement follows the high-level Trade and Tech Council (TTC) meeting between India and the EU that was set to discuss a number of outstanding issues between the two countries in the absence of a functional dispute resolution mechanism at the WTO.
- TTC with the EU assumes significance as the EU has a TTC only with the US.
- The council aims at forging technology partnerships with like-minded countries amid rising tensions with China
India-EU export duty on ICT products:
- India imposed higher duties on ICT products as it looks to boost the manufacturing of electronic products with the help of the production-linked incentive (PLI) scheme.
- The current strategy has also paid off as India’s electronic products have been on the rise even as broader goods exports have declined during the current fiscal.
|
What are ICT products?
|
WTO’s mechanism for resolution of trade disputes:
- Ideally disputes are resolved through negotiations. If this is not possible, WTO Members can request the establishment of a panel to settle the dispute.
- The panel will issue a report, which can subsequently be appealed before the WTO's Appellate Body on questions of law.
|
The Appellate Body is a standing body of seven persons that hears appeals from reports issued by panels in disputes brought by WTO members. |
- The Appellate Body can uphold, modify or reverse the legal findings and conclusions of a panel.
- If a WTO member does not comply with recommendations from dispute settlement, than trade compensation or sanctions, for example in the form of increases in customs duties.
- Many WTO members, including the EU, make active use of this system so that violations of trade rules are corrected. However, the EU only initiates a dispute settlement case where other ways of finding a solution have not been productive.


