

30th December 2024 (12 Topics)
Context
With an eye on China developing a mega hydro project in the vicinity of Arunachal Pradesh, the Centre has accelerated the development of its colossal dam in the Siang upper valley, which will be the country’s biggest to date.
What is the Siang Upper Multipurpose Project (SUMP)?
- The proposed dam on the Siang river will be the largest hydropower project in India, with a capacity to generate 10-12 gigawatts (GW) of power. The total estimated cost of the project is approximately Rs 1 trillion.
- The dam will serve three primary objectives:
- Flood Management – To prevent flash floods in the region caused by irregular water flow.
- Water Flow Correction – To address changes in the flow patterns of the river, particularly those influenced by external factors.
- Power Generation – To generate significant hydropower as a by-product, which will be essential for meeting peak power demands in the region.
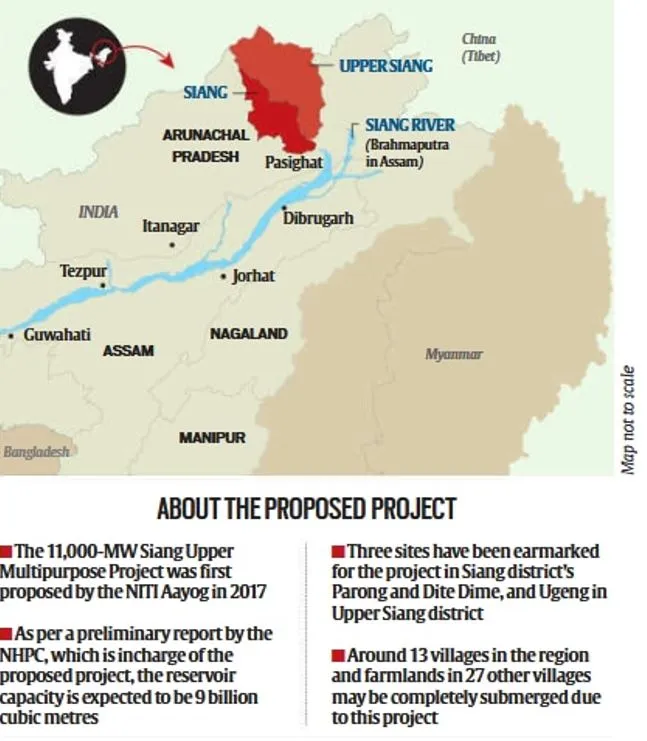
- The three sites earmarked for SUMP are Parong and Dite Dime in Siang district, and Ugeng in Upper Siang district.
- The project is being spearheaded by NHPC (National Hydroelectric Power Corporation), which has been tasked with developing the detailed project report (DPR) and project feasibility report (PFR) for the dam.
- While the project has received approval and funding, it continues to face hurdles due to local opposition (effect on aquatic life and the overall ecological balance) and logistical challenges.
- Need of the project: A major factor driving the urgency of the Siang valley project is the construction of a massive hydropower project by China on the Yarlung Tsangpo river, which flows into India as the Brahmaputra (Siang) river.
- The Chinese project, named the Motong Hydropower Station, has the potential to divert a significant amount of water from the Brahmaputra river system.
- Initial studies suggest that China’s project could reduce water flow to India by up to 80%, impacting regions like Arunachal Pradesh and Assam.
Fact Box: Siang
|
PYQQ: Which of the following is/are tributary/ tributaries of Brahmaputra? (UPSC 2016)
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
|
More Articles


