WHAT IS MEANT BY “HUNGER”?
The problem of hunger is complex, and different terms are used to describe its various forms:
Hunger: Hunger is usually understood to refer to the distress associated with a lack of sufficient calories. The Food and Agriculture Organization defines food deprivation, or undernourishment, as the consumption of too few calories to provide the minimum amount of dietary energy that each individual requires to live a healthy and productive life, given that person’s sex, age, stature, and physical activity level.
Undernutrition: Undernutrition goes beyond calories and signifies deficiencies in any or all of the following: energy, protein, and/ or essential vitamins and minerals. Undernutrition is the result of inadequate intake of food in terms of either quantity or quality, poor utilization of nutrients due to infections or other illnesses, or a combination of these factors. These, in turn, are caused by a range of factors, including household food insecurity; inadequate maternal health or childcare practices; or inadequate access to health services, safe water, and sanitation.
Malnutrition: Malnutrition refers more broadly to both undernutrition (problems caused by deficiencies) and overnutrition (problems caused by unbalanced diets, such as consuming too many calories in relation to requirements with or without low intake of micronutrient-rich foods).
How are the GHI scores calculated?
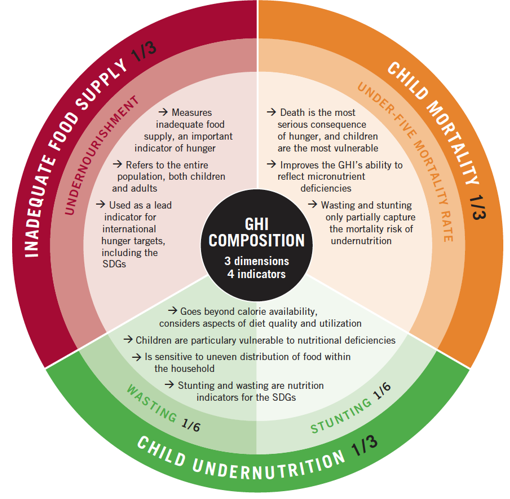
GHI scores are calculated using a three-step process that draws on available data from various sources to capture the multidimensional nature of hunger.
First, for each country, values are determined for four indicators:
- UNDERNOURISHMENT: the share of the population that is undernourished (that is, whose caloric intake is insufficient);
- CHILD WASTING: the share of children under the age of five who are wasted (that is, who have low weight for their height, reflecting acute undernutrition);
- CHILD STUNTING: the share of children under the age of five who are stunted (that is, who have low height for their age, reflecting chronic undernutrition); and
- CHILD MORTALITY: the mortality rate of children under the age of five (in part, a reflection of the fatal mix of inadequate nutrition and unhealthy environments).
Second, each of the four component indicators is given a standardized score on a 100-point scale based on the highest observed level for the indicator on a global scale in recent decades.
Third, standardized scores are aggregated to calculate the GHI score for each country, with each of the three dimensions (inadequate food supply; child mortality; and child undernutrition, which is composed equally of child stunting and child wasting) given equal weight. This three-step process results in GHI scores on a 100-point GHI Severity Scale, where 0 is the best score (no hunger) and 100 is the worst.
Related Articles