

Context
The United States (US) shot down a Chinese surveillance balloon that has been spotted over US airspace for a couple of days.
China’s Balloon Incident:
- From January 28 to February 4, 2023, a large, white high-altitude balloon operated by China crossed North American airspace, passing over Alaska, western Canada, and the contiguous United States.
- Then, a U.S. jet shot it down over the Atlantic and U.S. ships raced to gather the debris.
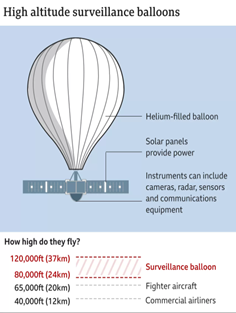
About
What is a Surveillance Balloon?
- About:
- Thesecheap, quiet and hard-to-reach balloons have been used for reconnaissance purposes, including in conflicts like the American Civil War.
- Thepractice became widespread during World War I and was used extensively during the Cold War when the US launched hundreds of balloons to gather intelligence on the Soviet Union and China.
- While their use hasdeclined with the rise of unmanned drones and satellites, many countries still employ spy balloons.
- The Purpose of Sending the Balloon:
- China has for decades complained about US surveillance by ships and spy planes near its own territory, leading to occasional confrontations over the years. According to China, the balloon was for research but got off track.
Uses:
- Close-range Monitoring:In the age of satellites, surveillance balloons which are typically advanced balloons equipped with high-tech, downward-pointing imaging gear offer close-range monitoring.
- Image Quality:The lower-flying balloons, which hover at about the same height as commercial airlines fly, can typically take clearer images than the lowest orbiting satellites.
- Satellites that rotate in sync with Earth capture continuous but hazier images due to farther orbit.
- Intercepting Communication:Surveillance balloons can also be capable of “gathering electronic signals” and intercepting communications.
|
Regulations in the US:
|
Who has sovereignty over the air?
- International law is clear with respect to the use of these balloons over other countries' airspace.
- Every country has complete sovereignty and control over its waters extending 12 nautical miles (about 22 kilometres) from its land territory.
- Every country likewise has "complete and exclusive sovereignty over the airspace above its territory" under international conventions.
- This means each country controls all access to its airspace, which includes both commercial and government aircraft.
- But the upper limit of sovereign airspace is unsettled in international law. In practice, it generally extends to the maximum height at which commercial and military aircraft operations, which is around 45,000 feet (about 13.7km).
- The supersonic Concorde jet, however, operated at 60,000 feet (over 18km).
- The Chinese balloon was also reported to be operating at a distance of 60,000 feet.
- International law does not extend to the distance at which satellites operate, which is traditionally seen as falling within the realm of space law.
- There are international legal frameworksin place that allow for permission to be sought to enter a country's airspace, such as the 1944 Chicago Convention on International Civil Aviation.
- The International Civil Aviation Organization has set an additional layer of rules on airspace access, including for hot air balloons, but it does not regulate military activities.
|
Prohibited Air Space:
Restricted Air Space:
|



