

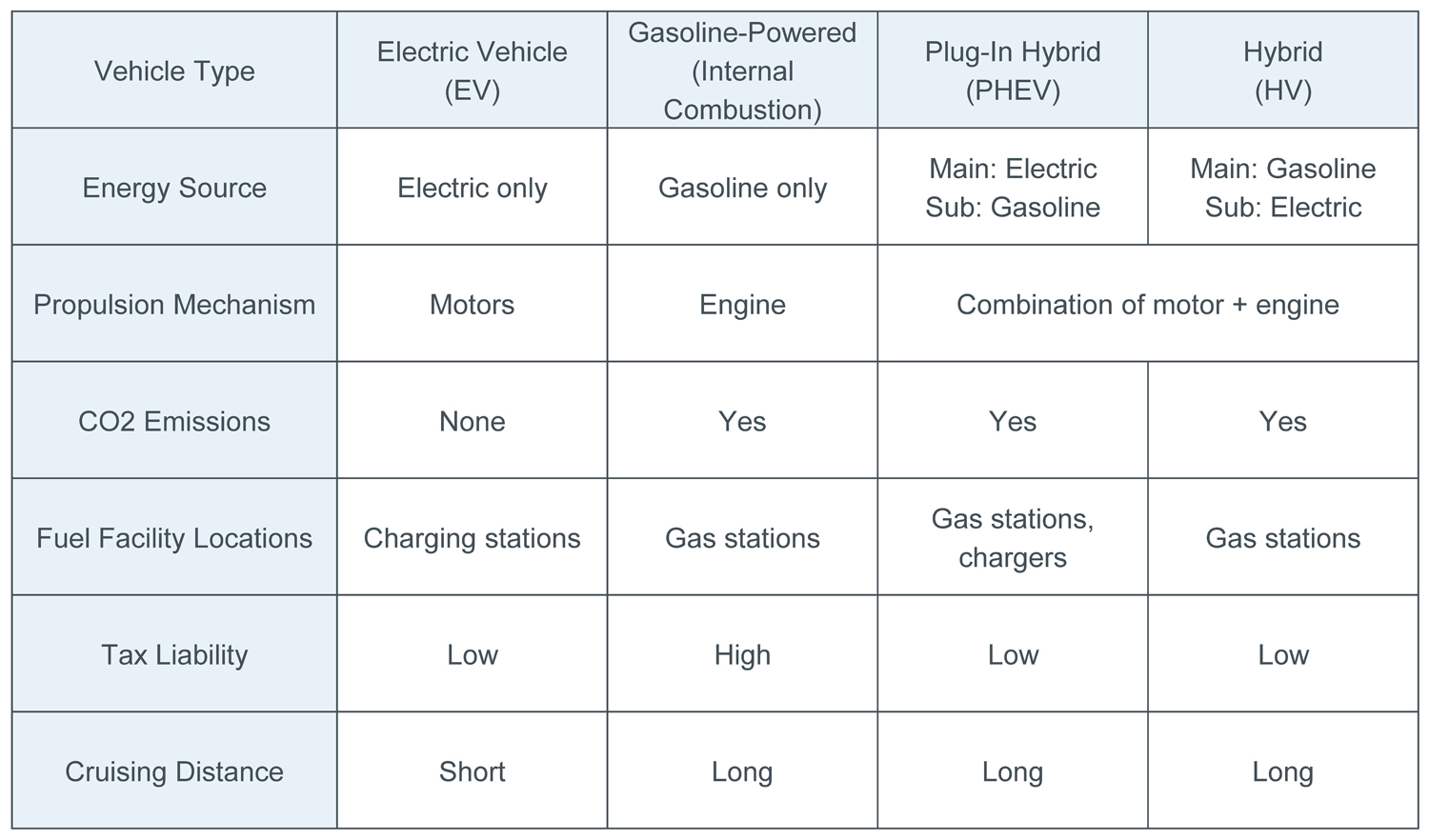
- The biggest difference is Source of power; EV’s use motor and conventional vehicles use fuel powered engines.
An electric vehicle (EV) is one that operates on an electric motor, instead of an internal-combustion engine that generates power by burning a mix of fuel and gases
There are 4 types of electric vehicles (EV);
- BEV ( Battery electric vehicles)
- PHEV(Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles)
- Conventional Hybrids
- FCEV(Full Cell Electric vehicle)
EVs are typically comprised of 4 main elements.
- An onboard charger that converts household AC power to DC
- Batteries that store the charged electricity
- An inverter for controlling the flow of electricity from the battery to the motor
- Motors that convert the electricity into propulsion power
Conventional cars are equipped with an engine that runs on energy generated by burning fossil fuel. EVs replace the gas and engine with electricity and motors.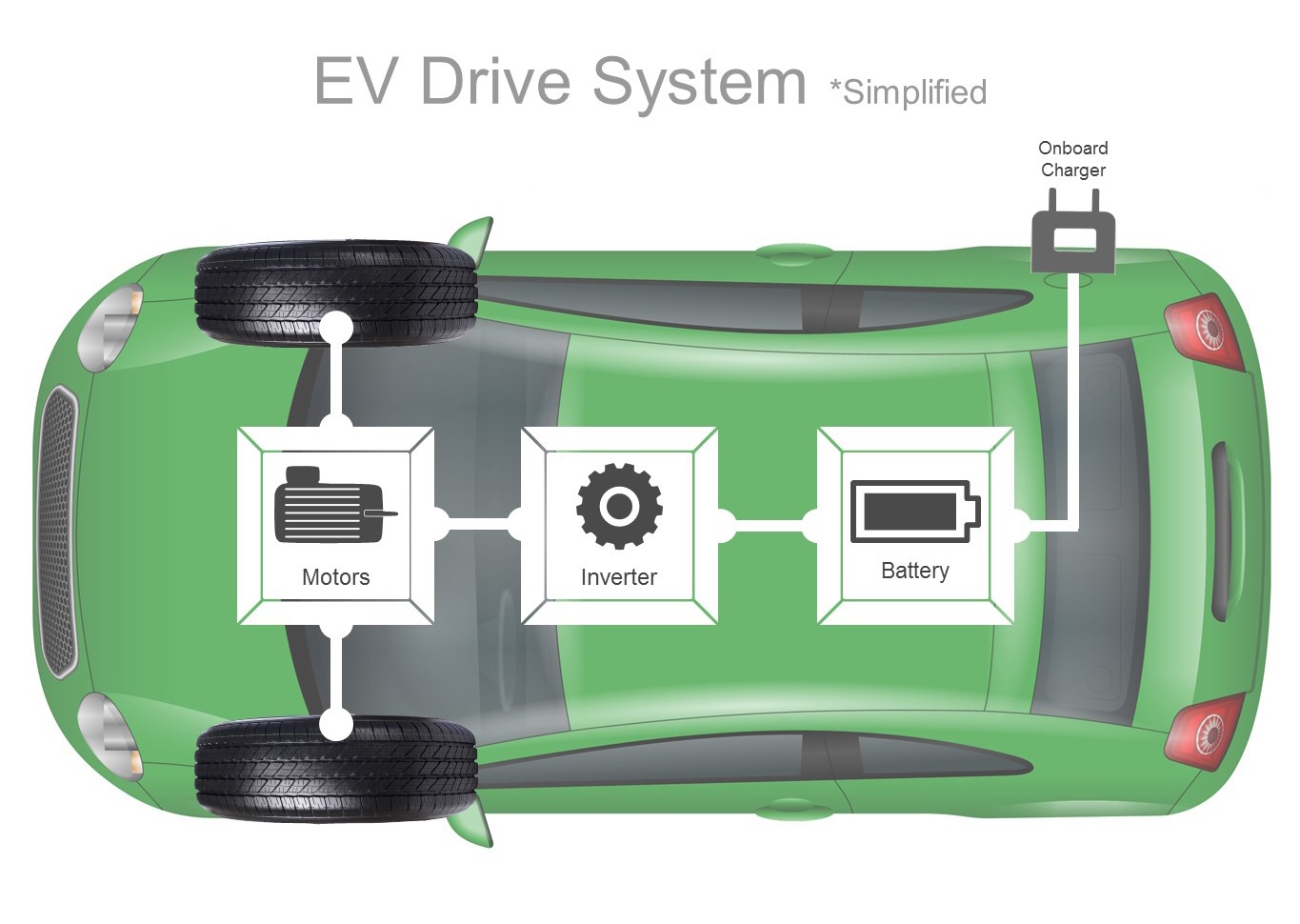
“Electric Vehicle Initiative” is a multi-governmental policy forum established in 2010 under the Clean Energy Ministerial (CEM). Recognising the opportunities offered by EVs, the EVI is dedicated to accelerating the adoption of EVs worldwide. Facilitate exchanges between governments aiming at support and development of EV’s. The International Energy Agency (IEA) serves as the co-ordinator to support the EVI member governments in this activity.
The EVI also helps to raise the ambition levels for electric mobility worldwide through the linked CEM campaigns of EV30@30 and Global Commercial Vehicle Drive to Zero Campaign, each endorsed by different members.
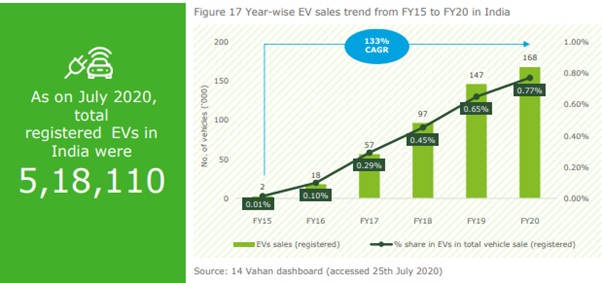
- According to IEA’s (International Energy Agency) Global EV Outlook 2021, The EV market across globe rose to 10 million mark in 2020, a 43% increase over 2019, and representing a 1% stock share. Battery electric vehicles (BEVs) accounted for two-thirds of new electric car registrations and two-thirds of the stock in 2020. China, with 4.5 million electric cars, has the largest fleet.
- The International Energy Agency predictsthat the number of electric cars, buses, vans and heavy trucks on roads is expected to hit 145 million by 2030.
- In India, the first concrete decision to incentivise electric vehicles was taken in 2010. According to an Rs 95-crore scheme approved by the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE), the government announced a financial incentive for manufacturers for electric vehicles sold in India.
- In 2013, India unveiled the 'National Electric Mobility Mission Plan (NEMMP) 2020' to make a major shift to electric vehicles and to address the issues of national energy security, vehicular pollution and growth of domestic manufacturing capabilities. But settled down to papers only.
- Union Budget for 2015-16 in Parliament, then finance minister Arun Jaitley announced “Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Electric Vehicles (FAME)”, with an initial outlay of Rs 75 crore. The scheme was announced with an aim to offer incentives for clean-fuel technology cars to boost their sales to up to 7 million vehicles by 2020.
- In 2017, Transport Minister Nitin Gadkari made a statement showing India’s intent to move to 100 per cent electric cars by 2030. But criticism aroused and resulted bringing down number to 30%.
- In February 2019, the Union Cabinet cleared an Rs 10,000-crore programme under the FAME-II scheme. The main objective of the scheme is to encourage a faster adoption of electric and hybrid vehicles by offering upfront incentives on purchase of electric vehicles and also by establishing necessary charging infrastructure for EVs.
- In 2019, cabinet approved setting up National Mission on Transformative Mobilityand Battery Storage' to promote clean, connected, shared, sustainable and holistic mobility initiatives. As India committed to cutting down GHG emission by 33% to 35% below 2005 levels by 2030.
- Report by Indian Energy Storage Alliance (IESA)projects that the Indian EV market will grow at a CAGR of 36 percent till 2026. The EV battery market is also projected to grow at a CAGR of 30 percent during the same period.
- Recently government approved bids for companies under PLI scheme (Production Linked Incentive) for manufacturing of ACC (Advanced chemistry Cell) under NPACC (National programme on Advanced Chemistry Cell). Where ACC’s can store electric energy, either as electrochemical or as chemical energy, and convert it back to electric energy as and when required. They will cater not only to electric vehicles but also to the consumer electronics industry, solar rooftops, and electricity grids.
- NITI Aayog’s Draft on Battery Swapping, where discharged batteries are replaced with fully charged one which helps in search for charging facilities.
Challenges:
- Range Anxiety, Indian customers concern about the range where lack of EV infrastructure forcing people to go for conventional vehicles.
- Scarce battery technology, India relies on import of Li-ion batteries resulting in high price of components.
- Lack of products, Less products are available in the Indian market with high price
- High Price for BEV (Battery Electric Vehicle) due to above factors.
- The recent malfunctions with electronic vehicles may carry concerns.
- Consumer perception, Coupled with above factors a negative perception on EV in India is haunting.
Advantages of EV's
- Low cost of ownership; where the ownership for EV is 27% less than a conventional vehicle
- Easy maintenance, The moving parts of EV are low compared to ICE which usually contain 2000 moving parts where as an EV has 20 in number which makes more easier maintenance.
- EV policies of states, most of states in India are ready for promoting EV either on supply side or Demand side through various policies and schemes.
- Cleaner Environment is an indispensable part of EV, which help India in achieving its target for “Reduce carbon emissions by 2030 to 33-35% of 2005 levels”.
Related Articles


