

Past 2010 digital payments to India is unknown but now-a-days digital payments overtake the conventional method of payments, Especially due to COVID-19 pandemic and SOP to contain spread of virus digital payments were preferred than that of conventional payment method’s. Since its inception in 2016 the value of monthly UPI transactions for four years comprises of 3-lakh-crore by 2020 September. Astonishingly the payments doubled to Rs 7 Lakh- crore in a year owing the due credits to cheaper internet data, growth of smart phone usage and exponential growth of digital payments platforms.
This as a part of digital payment system said to be a revolutionary step towards digitalisation of currency in India. Unified Payments Interface (UPI) has been at the forefront of India’s digital payments revolution, making faster inroads into retail payments than any other online mode, monthly transactions value clocked by UPI vaulting from ₹1.8-lakh crore in November 2019 to ₹7.6-lakh crore by November 2021. While credit and debit card payments flat-lined at ₹13-lakh crore between FY19 and FY21 and use of IMPS grew from ₹2-lakh crore to ₹3.6-lakh crore, UPI payments have jumped from ₹8.7-lakh crore to ₹41-lakh crore.
To ensure that digital transactions are both affordable to users and remunerative to service providers, RBI plans to issue a discussion paper specifying transaction charges across digital modes. The time is opportune for RBI to redouble efforts to wean the economy away from cash to digital modes.
Digital currency is a form of currency that is available only in digital or electronic form. It is also called digital money, electronic money, electronic currency, or cybercash, has utility similar to physical currencies also be used to purchase goods and pay for services.
- Digital currencies also enable instant transactions that can be seamlessly executed across borders. Typical digital currencies do not require intermediaries and are often the cheapest method for trading currencies.
- All crypto currencies are digital currencies, but not all digital currencies are crypto currencies.
CBDC (Central Bank Digital Currency) is the digital form of fiat currency issued and regulated by central bank of a country which promotes financial inclusion and simplify implementation of fiscal and monetary policy.
CBDC’s are of 2 types:
- Wholesale CBDC, primarily used by financial institutions.
- Retail CBDC, used by consumers and businesses similar to physical form of currency.
Across the world, only 9 countries launched CBDC and 80 countries with CBDC initiatives are underway till date.
Finance minister during budget session 2022 announed; CBDC in India will be ready by 2023 and overseen by RBI.
Finance minister announced during budget session 2022-2023 that “Non Fungible Tokens”-NFT’s will be taxed at 30% on any income from their transfer. On the same stage finance minister also announced rolling out of “Digital currency” by RBI sooner in 2023 called after “The Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC)”.
Here, erupts a conflict on the weather digital currency and crypto currency are same? But the idea of digital currency is different from crypto currency as follows:
- Digital currency is a legal tender issued by RBI mostly centralised, where as crypto currencies are decentralised and run by single group or community which are not yet accepted as legal tender in India.
To put in simple words; All crypto currencies are digital currencies but not officially accepted as legal tender and Digital currencies are official, issued by government and used in exchange of any goods and services free and fairly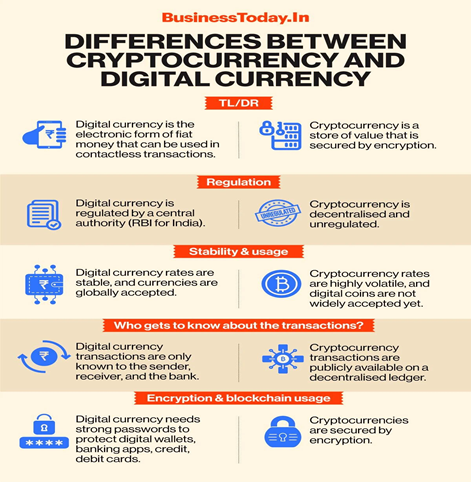
Unified Payments Interface (UPI) is a system that powers multiple bank accounts into a single mobile application (of any participating bank), merging several banking features, seamless fund routing & merchant payments into one hood. It also caters to the “Peer to Peer” collect request which can be scheduled and paid as per requirement and convenience.
- Digital Rupee/ currency in itself will be the underlying payment mode that can be used for digital payments in lieu of currency/cash. “The payment rails like UPI, IMPS etc use the underlying currency/cash to transfer the funds.
- Currently, UPI payments are made using the digital equivalent of existing currency notes. That means every rupee transferred via UPI is backed by physical currency. “The digital rupee will be legal tender in and of itself and need not necessarily be backed up by physical currency
- The digital rupee/ currency will be operated by RBI and not by bank intermediaries in the case of UPI where each bank has a different UPI handler. Digital rupee will be Settled by RBI instantly, where as UPI payments were settled by transacting bank with RBI
- Retail CBDCs can help reshaping a financial system into one that is more accessible to the unbanked and under banked. Retail CBDCs are issued by a central bank directly to people without going through traditional bank accounts. In this system, individuals have CBDC accounts directly on the central bank core ledger.
- CBDCs would replace or provide an alternative to fiat currency, potentially addressing a number of current problems facing by unbanked and under banked communities. Retail CBDCs can do this in two ways:
- By establishing a more inclusive digital payments ecosystem and
- Creating financial data identities.
- It transforms the payments ecosystem; management of physical currency is expensive and should hold a wider network/ chain of branches of banks to deal with. Whereas digital currency reduces this expenditure on maintenance, Resulting in including more people into the financial ecosystem.
- The high cost for small ticket size financial transaction in conventional financial system makes the transactions unviable. Digital currency and mobile technology can cater the needs of small transaction at affordable cost. It can also help reducing time, more accurately and make faster transactions in bulk.
- Many emerging economies like India, Brazil, and Nigeria have embarked on mobile technology to overcome financial exclusion.
- Arguments for CBDC increasing digital currency:
-
- Digitizing the value chains in the economy.
- People can access a wide range of digital financial products and services that are not easily accessible when using cash.
- Can help to enlarge the digital economy, where service provides develop API (Application Programming Interface) used to serve better for customers on real time basis.
- It allows faster payment settlements enabling more transparency.
- The advantage of a CBDC has offline features as well that helps people in remote areas where there is no internet connectivity, will be able to use retail CBDC conveniently.
Advantages of digital currency:
There are many advantages of digital currency including:
- It is Free from credit and liquidity risk as it curbs financial misuse such as; Fake currency printing, money laundering and so on.
- Cross-border payment improves; with this digital mode it creates an eco system of similar currency even at distant places.
- Financial inclusion will took place as it will be accessible to everyone in the society, expanding peer to peer transactions.
- Expands access to the general public through API.
- It is more secure compared to conventional payment as it is more discrete and confidential.
- Reliable and faster way of transaction with fewer charges.
- Helps in saving tonnes of paper in banking sector as it will completely run on digital platform.
- As it is centralised, Regulating will be easier.
Disadvantages of digital currency:
- Concerns of cyber attacks, as data are the mostly held in digital devices.
- As it requires less number of people, will result in loss of employment in financial sector.
- In rural areas implementation will be a great task, where internet connectivity is low.
- Chances of generating digital divide.
- Non-interest bearing CBDCs hinders financial inclusion.
- Digital illiteracy may act as barrier.
- Privacy concerns may turn up.
Digital currency in India is how ever yet to be launched but the digital payments and crypto currencies were regulated to secure India’s soverign digital currency by restricting the role existing crypto currencies which can form as a great threat to economy.
"The Crypto currency and Regulation of Official Digital Currency Bill, 2021". Is the only bill introduced in parliament related to crypto currency regulation in India which has major provisions such as
- Ban on crypto currencies: The draft Bill bans the use of crypto currency as legal tender or currency. It also prohibits mining, buying, holding, selling, dealing in, issuance, disposal or use of crypto currency.
- In particular, the use of crypto currency is prohibited for:
- Use as a medium of exchange, store of value or unit of account.
- Use as a payment system.
- Providing services such as registering, trading, selling or clearing of crypto currency to individuals.
- Trading it with other currencies.
- Issuing financial products related to it
- Using it as a basis of credit
- Issuing it as a means of raising funds, and
- Issuing it as a means for investment.
- Under the Bill, mining, holding, selling, issuing, transferring or using crypto currency is punishable with a fine or imprisonment of up to 10 years, or both.
- Issuing any advertisement, soliciting, assisting or inducing participation in use of crypto currency is punishable with a fine or imprisonment of up to seven years, or both
- The Bill provides for a transition period of 90 days from the commencement of the Act, during which a person may dispose of any crypto currency in their possession, as per the rules notified by the government.
The Inter-Ministerial Committee (2019) noted that the technology underlying crypto currencies i.e., DLT, could improve the efficiency and inclusiveness of the financial system. It can help lower the costs of personal identification for KYC, and improve access to credit. Global regulators (such as IMF) have also noted benefits of crypto currencies. These currencies could provide cheaper, faster and more efficient transactions.
|
Offence |
Maximum imprisonment |
|
Mining, holding, selling, issuing, transfer or use of crypto currency in the country (draft Bill) |
10 years |
|
Proceeds of crime involved in money laundering related to offences under the Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances Act, 1985 (PMLA) |
10 years |
|
Involvement in activities connected with proceeds of crime including its concealment, possession, acquisition or use or projecting it as untainted property (PMLA) |
7 years |
|
Holding of foreign exchange of aggregate value exceeding one crore rupees (FEMA) |
5 years |

The digital currency plays a major role if considered in achieving 5 trillion dollar economy by 2025 based on its advantages over conventional currency, but the digital currency not yet rolled out and will ready by 2023 can be a challenge to Indian’s goal to become 5 trillion dollar economy. Additionally, the recent pandemic pushed back the growth rate and settled down at 8.2% for FY2023 following the ongoing Russia-Ukraine war.
According to the World Bank, India needs to create 8.1 million jobs annually to achieve its growth targets. But on other hand, The NASSCOM has recently said that the Indian Crypto currency market has been growing exponentially over the last few years and is expected to reach up to $241 million by 2030 in India and $2.3 billion by 2026 globally.
A recent study on “Crypto Industry in India” by the NASSCOM and industry partner WazirX also said that the Indian investors have shown keen interest towards adopting Crypto currencies such as Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Polygon to make investments that promise them viable returns.
Former RBI Governor Raghuram Rajan, while addressing Reuters Markets Forum recently, had also endorsed the potential in Crypto currencies. The Crypto currency might find a way to become an effective means of payment, he had added.
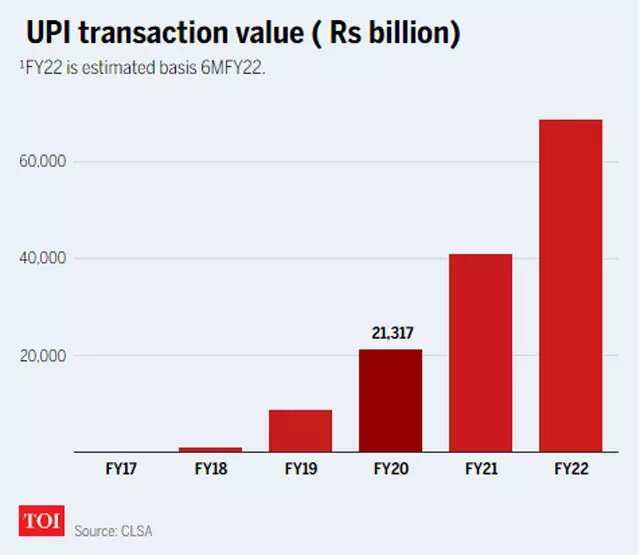
India as 3rd largest economy in the world, its ambition to join 5 trillion dollar economy club is a great challenge ahead as there are many issues within the country, across the neighbourhood and environmental concerns posing continues obstacles for growth. The growth in digital payments in India and thriving for CBDCs can enhance the efficiency of digital payments. Whether CBDC will eventually increase financial inclusion depends on the CBDC design. However the digital transactions growth in India is throwing a positive ray of hope on India’s digital currency revolution.
Related Articles


