18th July 2024 (13 Topics)
Context
The International Committee of the Red Cross (ICRC) has highlighted the compounded impact of armed conflict and climate risks, which significantly weakens people’s ability to cope with disasters.
Key Highlights of the Report
- Report Title: ‘When Rain Turns to Dust’
- Study Focus: The report is based on research conducted in 2019 and 2020, focusing on the Central African Republic (CAR), southern Iraq, and northern Mali.
- Double Threat: Countries affected by conflict are disproportionately impacted by climate change, exacerbating issues such as displacement, food production disruption, and weakened healthcare services.
Reasons Behind the Situation
- Geographical Vulnerability: The geographical location of CAR, Iraq, and Mali makes them particularly susceptible to climate change.
- Impact of Conflicts: The lasting consequences of conflicts in these regions exacerbate their vulnerability, disrupting communities, systems, and institutions.
- Human Movement Patterns: In CAR, changing human movement patterns due to conflict have increased tensions between farmers and herders.
- Resource Scarcity: In Mali, the fear of attacks forces pastoralists to congregate near water sources, increasing tensions with farmers and fishermen over scarce resources.
- Historical Impact: In Iraq, the destruction of date palms for military purposes during the Iran-Iraq war has had long-term effects on water and farming.
Impact on Societies
- Displacement and Migration: Armed conflicts and climate change force people out of their homes, leading to temporary settlements and further displacement due to natural disasters.
- Health and Livelihoods: Conflicts disrupt food production and healthcare services, leading to amplified diseases and weakened health systems.
- Tensions Over Resources: Increased competition for limited resources like water exacerbates tensions and conflicts within communities.
Required Measures
- Institutional Support: There is a need for strong institutional support to help communities adapt to the consequences of climate and environmental crises.
- Diversification of Livelihoods: Communities need to adapt by changing or diversifying their livelihoods to cope with changing environmental conditions.
- Mobilization for Climate Action: The ICRC calls for mobilization from both within and beyond the humanitarian sector to ensure climate action and finance reach conflict zones.
- Support for Hardest-Hit Communities: It is crucial to ensure that communities most affected by the combined impacts of conflict and climate change receive the necessary support to adapt.
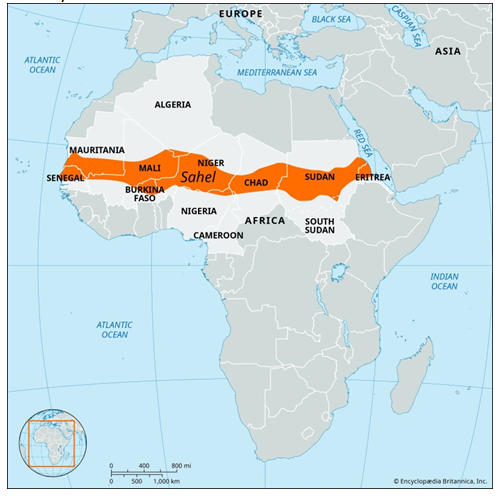
Sahel
|
UPSC Mains Question
Q: "Discuss the compounded effects of armed conflict and climate risks on vulnerable societies