18th July 2024 (13 Topics)
Context
The Global Biofuels Alliance (GBA), launched by key G20 members including India, the US and Brazil in September 2023, is all set to get its diplomatic status, with New Delhi likely to sign a headquarters agreement with the agency soon.
About:
- GBA is an India-led Initiativeto develop an alliance of Governments, International organizations and Industry to facilitate adoption of biofuels.
- Objective:Bringing together the biggest consumers and producers of biofuels to drive biofuels development and deployment, the initiative aims to position biofuels as a key to energy transition and contribute to jobs and economic growth.
- Joining Members: 19 countries and 12 international organisations have already agreed to join.
- G20 countries (07) supporting GBA: Argentina, Brazil, Canada, India, Italy, South Africa, USA
- G20 Invitee Countries (04) supporting GBA: Bangladesh, Singapore, Mauritius, UAE
- Non G20 (08) supporting GBA:Iceland, Kenya, Guyana, Paraguay, Seychelles, Sri Lanka, and Uganda have agreed to be initiating members of GBA, and Finland.
- International organizations: World Bank, Asian Development Bank, World Economic Forum, World LPG Organization, UN Energy for All, UNIDO, Biofutures Platform, International Civil Aviation Organization, International Energy Agency, International Energy Forum, International Renewable Energy Agency, World Biogas Association.
Fact boxNational Biofuel Policy
|
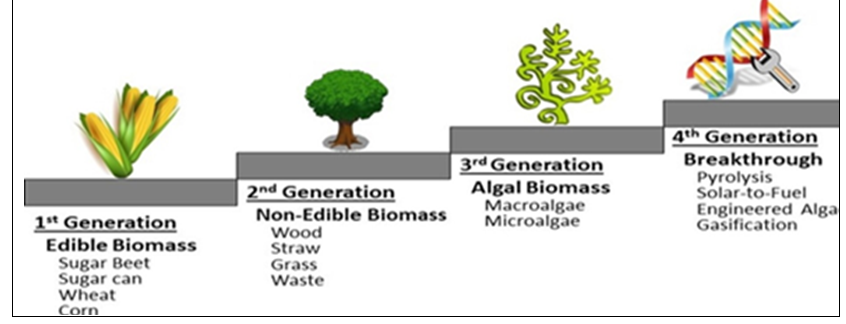
Fact BoxBiofuels
Advantages of Biofuels
Disadvantages of Biofuels
|
More Articles