22th August 2025 (18 Topics)
Context:
The Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEF&CC) has implemented the Battery Waste Management Rules, 2022 to promote recycling, refurbishment, and circular economy in the battery sector.
Battery Waste Management Rules, 2022 (MoEF&CC):
- Covers all categories: Electric Vehicle (EV) batteries, portable, automotive, and industrial batteries.
- Introduced Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR): Producers/importers must meet annual collection, recycling, or refurbishment targets for waste batteries.
- Mandates use of minimum percentage of domestically recycled materials in new batteries starting FY 2027–28.
- Ensures formalisation of informal sector through registration, EPR certificate trading, and upgrading recycling clusters.
EPR Online Portal:
- Facilitates producer and recycler registration, certificate exchange, and compliance reporting.
- So far: 3,664 producers and 442 recyclers registered.
- Producers procured EPR certificates for 7.29 lakh MT of key battery metals against target of 10.96 lakh MT.
Technology & Industry Initiatives:
- MeitY’s role: Promoting informal sector upgradation via MSE-CDP scheme.
- C-MET technology transfer: Indigenous Li-ion battery recycling tech shared with start-ups and industries under Mission LiFE.
- PLI-ACC Scheme (2021): Outlay ?18,100 crore for 50 GWh ACC capacity. Over 10 companies announced 100+ GWh additional capacity.
- MoUs (2024): CSIR labs signed with recyclers for technology transfer, advanced recycling infrastructure, and securing critical mineral supplies.
|
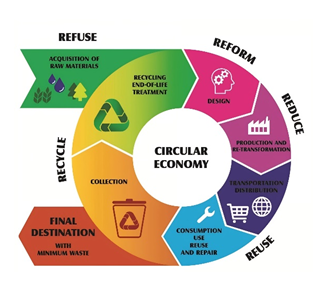
Circular Economy Concept & Principles
Need in India
Global Experience
India’s Policy Push
Benefits of CE
|
More Articles