22th August 2025 (18 Topics)
Mains Issues
Context:
The Promotion and Regulation of Online Gaming Bill, 2025, passed by the Parliament marks a landmark move to shield citizens from the menace of online money games while promoting and regulating other kinds of online games
Introduction
- Passed on 21st August 2025 to regulate online gaming.
- Aims to ban harmful money games while promoting e-sports and social/educational games.
- Protects families from addiction, fraud, and financial ruin.
- Balances digital innovation with social safeguards.
Online Gaming Sector – Three Segments

- E-sports: Competitive, skill-based digital sports, tournaments.
- Online Social Games: Casual, safe, learning/recreation based.
- Online Money Games: Involving money stakes; linked to addiction, fraud, money laundering, even suicides.
Why the Bill Was Needed
- Addiction & Financial Ruin – Losses of over ?20,000 crore; 45 crore affected.
- Mental Health Issues – Depression, suicides due to money losses.
- Fraud & Money Laundering – Used for illegal activities.
- National Security Threat – Some platforms linked to terror financing.
- Legal Loopholes – Offline gambling banned but online unregulated.
- Healthy Alternatives – To promote e-sports and safe online games.
Key Provisions of the Bill
- Applicability – Across India, including offshore operators targeting India.
- E-sports Recognition – Declared as competitive sport; guidelines by Ministry of Youth Affairs & Sports.
- Social/Educational Games – Govt to register/recognise safe games, launch awareness programmes.
- Ban on Online Money Games – Complete ban on chance/skill/combined money games; banks barred from transactions; IT Act powers for blocking sites.
- Online Gaming Authority – To regulate, categorise games, issue guidelines, handle grievances.
- Penalties – Jail up to 3 years + ?1 crore fine; harsher for repeat offenders.
- Corporate Liability – Companies & officers accountable; exemptions for non-executive directors with due diligence.
- Investigations – Govt officers empowered to search, seize, and arrest under BNSS, 2023.
- Rule-Making Powers – Central Govt to frame rules for promotion, recognition, and regulation.
Related Legal & Policy Measures
- IT Act, 2000 & Rules: Blocking illegal sites, regulating intermediaries.
- Bharatiya Nyaya Sanhita, 2023: Sections 111 & 112: punish cybercrime, illegal betting.
- IGST Act, 2017: Offshore gaming platforms under taxation rules.
- Consumer Protection Act, 2019: Bans misleading ads; penalises celebrities endorsing betting.
- Advisories: From MIB, Education Ministry on safe gaming and misleading ads.
- Cybercrime Reporting: National Cybercrime Portal (cybercrime.gov.in) and helpline 1930.
Conclusion
- Bill bans exploitative money games but encourages e-sports and educational games.
- Ensures technology serves society, not harms it.
- Strengthens India’s role as a global leader in safe and responsible digital policy.


Prelims Articles
Context:
The Government has identified and uploaded details of 4.84 lakh villages on the MGMD portal under its Cultural Mapping and Rural Heritage programme.
Cultural Mapping of Rural India
- The MGMD (Mera Gaon Meri Dharohar) portal functions under the Ministry of Culture and aims at documenting and digitally mapping the intangible cultural heritage of India’s villages.
- Till date, 84 lakh villages out of approximately 6.5 lakh villages have been mapped.
- Intangible cultural heritage elements documented include:
- Linguistic diversity – dialects, scripts, language usage.
- Oral traditions – folk tales, epics, community knowledge systems.
- Folklore and performing arts – music, dance, theatre, ritual practices.
- Local festivals and fairs – seasonal, religious, and community-specific celebrations.
- The initiative supports cultural preservation, rural development, tourism, and academic research.
- It aligns with UNESCO’s Convention for the Safeguarding of Intangible Cultural Heritage (2003), to which India is a signatory.


Prelims Articles
Context:
The Government of India has launched the Gyan Bharatam Mission to identify, conserve, digitize, and monetize India’s vast repository of manuscripts through a National Digital Repository.
Gyan Bharatam Manuscript Mission
- The Gyan Bharatam Mission is a national-level initiative aimed at the identification, conservation, and digitization of Indian manuscripts.
- It seeks to create a National Digital Repository (NDR) for all identified manuscripts, ensuring scientific preservation standards.
- The Mission envisages the use of AI, cloud platforms, and mobile applications to digitize and provide controlled access for research, translation, and publication.
- It introduces a monetization framework to benefit custodians of manuscripts while promoting knowledge dissemination.
- The Mission will also establish physical archival storage facilities using long-term archival materials such as wafer-fiche and archival-grade paper.
- The broader aim is to preserve India’s civilizational knowledge heritage and ensure its accessibility to researchers and the public through digital tools like virtual museums and online archives.
- This initiative aligns with India’s ongoing efforts in digital governance, cultural heritage preservation, and knowledge economy expansion.


Prelims Articles
Context:
India’s Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES) holds two seabed mineral exploration contracts with the International Seabed Authority (ISA) in the Indian Ocean.
Deep-Sea Mineral Exploration India
- Nodal Agency: Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES).
- Exploration Contracts with ISA:
- Polymetallic Nodules (PMN) – Contract signed in 2002; allocated area of 75,000 sq. km in the Central Indian Ocean Basin.
- Estimated reserve: 366 million metric tons (MMT).
- Average grade: Copper (1.09%), Nickel (1.14%), Cobalt (0.14%).
- Polymetallic Sulphides (PMS) – Contract signed in 2016; allocated area of 10,000 sq. km in the South-West Indian Ocean Ridge.
- Contains Copper, Zinc, Lead, Iron, Silver, Gold, etc.
- Active and inactive hydrothermal vents identified.
- Polymetallic Nodules (PMN) – Contract signed in 2002; allocated area of 75,000 sq. km in the Central Indian Ocean Basin.
- Stage of Activity:
- Currently limited to exploration only.
- Deep-sea mining not yet permitted as ISA regulations for exploitation are pending.
|
International Seabed Authority (ISA):
|


Prelims Articles
Context:
The Government has launched the web-based C-Flood platform to provide village-level inundation forecasts for Godavari, Tapi, and Mahanadi river basins.
C-Flood Unified Forecasting System
- The C-Flood Unified Inundation Forecasting System is a web-based platform designed for real-time flood management.
- It integrates outputs of 2D hydrodynamic models with flood extent and depth information, thereby enhancing the accuracy of predictions.
- Currently, it provides two-day advance inundation forecasts up to the village level in the Godavari, Tapi, and Mahanadi basins.
- The platform operates in Hindi, English, and Odia in its initial phase.
- It introduces a standardized flood alert categorization system:
- Yellow Alert: inundation < 0.5m
- Orange Alert: inundation < 1.5m
- Red Alert: inundation > 1.5m
- Data sources include satellite-based datasets and ground-based hydrological observations, making it a robust multi-source integrated system.
- From a disaster management perspective, the system reflects India’s effort to strengthen early warning and mitigation measures, aligning with the Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction (2015–30).


Prelims Articles
Context:
Kerala has become the first fully digitally literate State in India after successful completion of the first phase of the Digi Kerala project.
Digi Kerala Project:
- It is a grassroots-level initiative implemented across all local bodies in Kerala to bridge the digital divide and ensure universal digital literacy.
Survey Coverage:
- The project surveyed 5 crore people from 83.46 lakh families across the State to identify digitally illiterate individuals.
Training Achievement:
- Of the 88 lakh digitally illiterate persons identified, 21.87 lakh (99.98%) completed digital literacy training and evaluation successfully.
Inclusivity Highlight:
- Notable participation included 104-year-old M.A. Abdullah MoulaviBaqavi, symbolising inter-generational inclusiveness in digital empowerment.
National Significance:
- Kerala has set a replicable model for digital literacy campaigns in other States, showcasing a practical approach to digital governance and citizen empowerment.
Governance Implication:
- Digital literacy enhances access to e-governance services, financial inclusion schemes, and digital education, thereby strengthening participatory governance.


Prelims Articles
Context:
The Ministry of Development of North Eastern Region (MDoNER) has launched the Poorvottar Vikas Setu (PVS) Portal to streamline project approval, monitoring, and fund release processes in the North Eastern Region.
Poorvottar Vikas Setu Portal
- Objective: The PVS Portal aims to ensure efficiency, transparency, and timely clearance of development projects in the North Eastern Region.
- Earlier System: Project proposals (Concept Note/DPR) and fund requests were submitted via physical copies or email, and comments from line Ministries were also obtained through email. This led to delays in project approval and monitoring.
- New Mechanism:
- State Governments can now upload proposals directly on the portal.
- Line Ministry comments are integrated into the portal, creating a digital repository of all communications.
- Enables submission of demand requests for fund release, with provisions for uploading Utilization Certificates (UCs) and Completion Certificates.
- Significance:
- Promotes accountability and faster project clearance for the North Eastern states.
- Provides a centralized communication and monitoring system between MDoNER, NEC (North Eastern Council), States, and Central agencies.
- Aligns with Digital India and e-governance initiatives to reduce bureaucratic delays.


Prelims Articles
Context:
Confusion has arisen between Mission Mausam of the Ministry of Earth Sciences and Project Mausam of the Ministry of Culture, with both initiatives having distinct objectives.
Mission Mausam (Ministry of Earth Sciences – MoES):
- Objective: To make India a “weather-ready and climate-smart”
- Focus Areas:
- Strengthening in-situ and remote sensing
- Developing advanced Earth System Models, AI/ML-driven forecasts.
- Better numerical weather prediction and data assimilation using HPC.
- Training manpower in Earth System Science.
- Effective forecast dissemination and early warning systems.
Project Mausam (Ministry of Culture – MoC):
- Launched:2014 at the 38th Session of the UNESCO World Heritage Committee in Doha, Qatar.
- Objective: To revive maritime cultural linkages across the Indian Ocean Rim.
- Key Aims:
- Reviving lost linkages with nations.
- Redefining cultural landscapes.
- Creating links with existing World Heritage Sites.
- Preparing transnational World Heritage nominations.
- Activities:
- Draft Tentative List (TL) proposals on maritime trade and Buddhism.
- International conferences (e.g., Jaladhipurayatra, 2022).
- Digital exhibitions and panel discussions during UNESCO WHC meetings


Prelims Articles
Context:
The Group of Ministers (GoM) has recommended the Centre’s proposal to move towards a two-rate GST structure, replacing the existing 12% and 28% slabs.
GST Background:
Goods and Services Tax (GST) is a destination-based indirect tax levied on the supply of goods and services. It was introduced in 2017 through the 101st Constitutional Amendment Act, subsuming multiple indirect taxes.
Current Structure:
At present, GST has four main tax slabs — 5%, 12%, 18%, and 28%, besides certain exempted items. Additionally, a compensation cess is levied on select items like tobacco, cigarettes, aerated drinks, coal, and automobiles.
Centre’s Proposal: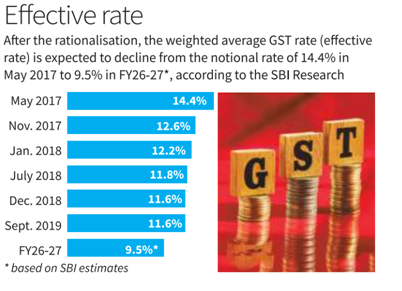
Retain only 5% and 18% slabs.
Abolish 12% and 28% slabs.
Nearly 99% of items in 12% slab to be moved to 5%.
Nearly 90% of items in 28% slab to be moved to 18%.
Remaining items in 28% slab (sin goods such as tobacco, cigarettes, online real-money gaming) to be shifted to a 40% slab.
Compensation cess on 28% slab items would no longer apply.
Significance:
Part of “next-generation GST reforms” announced by the Prime Minister.
Aims at reducing the tax burden on consumers, simplifying compliance, and ensuring better tax buoyancy.
Brings GST closer to the two-rate structure model, which is considered more efficient globally


Prelims Articles
Context:
The Government announced the Nuclear Energy Mission for Viksit Bharat, targeting 100 GW nuclear capacity by 2047, with private sector participation through amendments to the Atomic Energy Act, 1962 and the CLND Act, 2010.
Current Regulatory Framework
- Nuclear safety in India is regulated by the Atomic Energy Regulatory Board (AERB).
- AERB issues licenses to civilian nuclear facilities, subject to compliance with safety codes, guides, and standards.
- It conducts inspections and can suspend/revoke licenses in cases of extreme non-compliance.
- AERB was constituted by the Atomic Energy Commission (AEC) in 1983 and derives its powers from the Atomic Energy Act, 1962.
Proposed Changes under New Law
- Enabling private sector participation in nuclear power generation.
- Strengthening safety, security, safeguards, fuel procurement, waste management, and decommissioning.
- Establishing a new statutory regulatory framework for uniform standards and accountability.
- Task Force constituted to study ownership and operational models (Build–Own–Operate).
India’s International Commitments
- Member of International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA), committed to global safety standards.
- Follows the Convention on Nuclear Safety (CNS, 1994).
- Civil liability governed by the Civil Liability for Nuclear Damage (CLND) Act, 2010, which incorporates the Convention on Supplementary Compensation (CSC), 1997.
|
Atomic Energy Regulatory Board (AERB) Establishment & Legal Backing
Mission & Role
Functions & Jurisdiction
Regional & Research Bodies
|


Prelims Articles
Context:
The Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEF&CC) has implemented the Battery Waste Management Rules, 2022 to promote recycling, refurbishment, and circular economy in the battery sector.
Battery Waste Management Rules, 2022 (MoEF&CC):
- Covers all categories: Electric Vehicle (EV) batteries, portable, automotive, and industrial batteries.
- Introduced Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR): Producers/importers must meet annual collection, recycling, or refurbishment targets for waste batteries.
- Mandates use of minimum percentage of domestically recycled materials in new batteries starting FY 2027–28.
- Ensures formalisation of informal sector through registration, EPR certificate trading, and upgrading recycling clusters.
EPR Online Portal:
- Facilitates producer and recycler registration, certificate exchange, and compliance reporting.
- So far: 3,664 producers and 442 recyclers registered.
- Producers procured EPR certificates for 7.29 lakh MT of key battery metals against target of 10.96 lakh MT.
Technology & Industry Initiatives:
- MeitY’s role: Promoting informal sector upgradation via MSE-CDP scheme.
- C-MET technology transfer: Indigenous Li-ion battery recycling tech shared with start-ups and industries under Mission LiFE.
- PLI-ACC Scheme (2021): Outlay ?18,100 crore for 50 GWh ACC capacity. Over 10 companies announced 100+ GWh additional capacity.
- MoUs (2024): CSIR labs signed with recyclers for technology transfer, advanced recycling infrastructure, and securing critical mineral supplies.
|
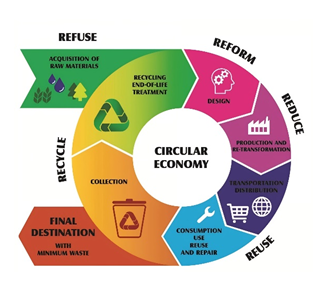
Circular Economy Concept & Principles
Need in India
Global Experience
India’s Policy Push
Benefits of CE
|


Prelims Articles
Context:
BHAVINI is commissioning the 500 MWe Prototype Fast Breeder Reactor (PFBR), expected to attain criticality by March 2026 and full power generation by December 2026.
Institution & Location:
- The PFBR is being commissioned by BHAVINI (BharatiyaNabhikiya Vidyut Nigam Limited), a PSU under the Department of Atomic Energy, at Kalpakkam, Tamil Nadu.
Capacity:
- The reactor will add 500 MWe nuclear capacity to the National Grid upon full operation.
Technology:
- It is a Fast Breeder Reactor (FBR), which uses fast neutrons (without moderators) to convert fertile material into fissile material, thereby "breeding" fuel.
Fuel Cycle:
- Operates on a closed fuel cycle regime, involving recovery and recycling of fissile (Pu-239, U-233) and fertile (U-238, Th-232) materials from spent nuclear fuel. This enhances utilization of limited uranium resources and enables long-term use of thorium.
Strategic Significance:
- Optimizes India’s scarce uranium
- Provides a pathway to utilize large thorium reserves, aligning with India’s three-stage nuclear power programme.
- Reduces high-level radioactive waste
Indigenous Development:
- PFBR is fully indigenously developed, without foreign collaboration or international technology transfer.
Timeline:
- Criticality expected by March 2026; full power generation by December 2026.


Prelims Articles
Context:
Government of India is aligning with ITU-R recommendation M.2160 and has initiated measures to position India as a global leader in 6G technology by 2030.
Global Framework:
- ITU-R recommendation 2160 (IMT-2030) provides the global roadmap for 6G rollout by 2030.
- 6G envisages enhanced data speeds, ultra-low latency, AI-native networks, communication-sensing integration, and coverage via terrestrial + non-terrestrial networks.
India’s Vision:
- Bharat 6G Vision Document (released March 2023) sets the objective to design, develop, and deploy indigenous 6G technology.
- Goal:ubiquitous, intelligent, and secure connectivity for quality living and to establish India as a global 6G leader by 2030.
Government Initiatives:
- 5G Labs: 100 labs set up across academic institutions for 6G-ready ecosystem.
- Telecom Technology Development Fund (TTDF): Launched October 2022; 104 projects worth ?275.88 crore sanctioned for 6G R&D.
- Bharat 6G Alliance: Network of industry, academia, research institutes, and standards bodies; signed MoUs with global 6G alliances.
- Technology Innovation Hub at IIIT Bangalore (Comet Foundation): Works on Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces (RIS) and O-RAN Massive MIMO to enhance future 6G coverage and sensing.


Prelims Articles
Context:
The first-ever Khelo India Water Sports Festival was inaugurated on Dal Lake, Srinagar, featuring rowing, kayaking, and canoeing events.
Strategic Importance of the Event
- Marks the first-ever Khelo India Water Sports Festival (KIWSF), positioning Dal Lake as a national sporting venue.
- Complements Gulmarg’s success as India’s winter sports hub, showcasing Jammu & Kashmir as a year-round sports destination.
- Part of the Khelo Bharat initiative, aimed at promoting grassroots sports, livelihood generation, and infrastructure revival.
Sporting Significance
- Participation: 400+ athletes from 36 States and UTs.
- Medal Events: Rowing, Canoeing, Kayaking (all Olympic events).
- Demonstration Events: Water skiing, Dragon boat race, Shikara sprint (blend of modern and cultural sports).
- Provides exposure for athletes with Olympic aspirations (16 medals in water sports at the Olympics).
- Builds a structured pipeline for water sports athletes through qualification from national championships.
Socio-Economic & Cultural Impact
- Economic Spin-offs:
- Benefits for shikara owners, houseboat operators, tourism, and hospitality sectors.
- Generates local employment in training, guiding, and logistics.
- Cultural Showcasing:
- Festival mascot: Himalayan Kingfisher.
- Logo featuring a shikara, symbolising Kashmir’s identity.
- Demonstration events highlight local culture (e.g., shikara race).
- Ecological Measures: Cleaning drives and weed removal to preserve Dal Lake’s beauty and ecosystem.
Symbolism of Dal Lake
- Known as “Lake of Flowers”, covering 18 sq. km in Srinagar.
- Integral to Kashmir’s tourism, commerce, and ecology:
- Supports fishing, floating gardens, aquatic plant harvesting.
- Surrounded by Mughal-era gardens (e.g., Shalimar Bagh, Nishat Bagh).
- A living heritage site where culture meets competition—now repurposed as a national sports arena.


Prelims Articles
Context:
The 12th edition of the bilateral naval exercise SLINEX-2025 between India and Sri Lanka concluded at Colombo on 18 August 2025, strengthening maritime security cooperation.
SLINEX Background:
- SLINEX (Sri Lanka–India Naval Exercise) is a bilateral naval exercise held since 2005, enhancing interoperability and maritime cooperation.
- Conducted annually/bi-annually in both harbour and sea phases.
SLINEX-2025 Features:
- Participants: Indian Navy – INS Jyoti (fleet tanker), INS Rana (destroyer); Sri Lankan Navy – SLNS Gajabahu and SLNS Vijayabahu (Offshore Patrol Vessels).
- Activities: Professional exchanges, HADR drills, firefighting, seamanship, VBSS (Visit, Board, Search and Seizure), gunnery firing, and joint operations.
- Focus: Enhancing tactical capabilities, maritime security, and interoperability.
Strategic Significance:
- Reinforces India’s Neighbourhood First Policy and Security and Growth for All in the Region (SAGAR) vision.
- Strengthens maritime diplomacy and people-to-people ties through port calls, ship visits, and cultural outreach.
- Adds to broader Indo-Pacific security architecture and regional stability.


Editorials
Context:
The Chhattisgarh High Court, in a recent custodial death case, reduced murder convictions of police officers to culpable homicide and remarked that the victim was assaulted “to teach a lesson,” raising concerns about judicial reasoning and constitutional morality.
Judicial Language and State Violence
- Problematic Framing: By suggesting that police acted “to teach a lesson,” the High Court reinforced vigilante logic that normalises custodial brutality rather than condemning it as unconstitutional.
- Impact of Judicial Language: Language shapes legal reasoning, which in turn influences policy and enforcement. Acceptance of “disciplinary violence” risks legitimising future custodial abuse.
- Constitutional Role of Police: Police officers are constitutional functionaries bound by law, not instruments of coercive correction. Any judicial validation of extra-legal punishment undermines due process and the rule of law.
Caste and Custodial Violence
- Caste-Coded Enforcement: The victim, a Dalit man, was killed by upper-caste police officers, reflecting entrenched patterns of caste-based violence in custodial settings.
- Narrow Jurisprudence under SC/ST Act: Courts often demand explicit caste slurs or intent as proof, overlooking structural power dynamics that enable caste-motivated violence.
- Denial of Justice: By refusing to apply the SC/ST Act in such cases, the judiciary undermines the law’s very purpose and perpetuates systemic caste oppression in policing.
Way Forward for Accountability
- Judicial Integrity: Courts must avoid framing custodial violence as discipline and reinforce that it is a criminal act, irrespective of the victim’s conduct.
- Robust Safeguards: Independent accountability mechanisms, strict adherence to K. Basu guidelines, and enforceable procedural checks are essential to prevent custodial abuse.
- Strengthening Equality and Dignity: The judiciary must affirm that violence in custody, especially against marginalised groups, violates constitutional guarantees of dignity, proportionality, and equality before the law.
Practice Question
“Custodial violence continues to undermine the constitutional guarantee of dignity and equality. Critically examine the role of judicial reasoning and the SC/ST Act in addressing this challenge, and suggest institutional reforms for ensuring accountability.” (250 words)


Editorials
Context:
Recent irregularities in voter lists, such as duplication and ineligible entries, have raised questions on the credibility of the Election Commission of India (ECI) and the role of political parties.
Declining Institutional Trust
- Erosion of Credibility: The Election Commission of India, once hailed under T.N. Seshan’s tenure for enforcing electoral integrity, now faces declining trust due to opacity and weak accountability.
- Shift in Campaigning: Political parties increasingly depend on digital tools, social media, and AI-driven campaigns, weakening traditional grassroots networks.
- Role of Consultants: Reliance on professional consultants for campaign strategies has centralized decision-making and marginalized local party workers.
Weakening Local Party Structures
- Neglect of Local Linkages: Technological and consultant-driven campaigns have eroded the role of local party organisations, which are crucial for monitoring voter rolls.
- Booth Level Agents (BLA): The ECI created BLAs as a link between parties, voters, and local officers to scrutinize draft rolls and ensure corrections during revision periods.
- Safeguards in System: Mechanisms like restricting bulk applications and limiting BLA submissions theoretically ensure transparency and minimize voter fraud.
Opportunity for Democratic Renewal
- Lessons from Karnataka Case: Irregularities in Mahadevapura constituency highlight lapses by BLAs, weak local vigilance, and potential institutional bias.
- Revival of Local Units: Parties can use this controversy to rebuild dormant local structures and strengthen electoral oversight beyond election cycles.
- Warning from History: As seen in post-Independence land reform failures, weak local organisations risk undermining democracy itself and creating unfair electoral arenas.
Practice Question
“Discuss how the decline of local party organisations and institutional opacity in the Election Commission of India have together contributed to the weakening of electoral integrity in India. Suggest reforms to restore public trust.” (250 words)


Editorials
Context:
The Prime Minister’s August 15 address proposed education reforms, highlighting the need to strengthen vocational education and training (VET) for boosting employability in India.
Challenges in India’s VET System
- Low Enrolment and Utilisation: Despite over 14,000 Industrial Training Institutes (ITIs) and 25 lakh sanctioned seats, actual enrolment in 2022 was only 12 lakh, with just 48% seat utilisation.
- Weak Employment Outcomes: Employment rates for VET graduates in India remain low at 38.5%, compared to 80–90% in countries like Germany, Singapore, and Canada.
- Academic Bias and Skill Gap: India’s education system emphasises academic degrees, neglecting vocational pathways, leading to limited employability skills and inadequate industry orientation.
International Best Practices
- Germany’s Dual System: Germany integrates vocational training with high school education, offering paid apprenticeships and strong industry linkages that ensure smooth labour market absorption.
- Singapore’s Quality Assurance: Singapore ensures high standards in VET through regular audits, feedback mechanisms, and structured pathways from technical to university education.
- Public-Private Collaboration: Advanced economies invest heavily in VET by linking government funding with industry participation, ensuring financial viability and market relevance.
Way Forward
- Strengthening ITIs and NSDC: India must improve ITIs’ financial autonomy, upgrade outdated curricula, and align training with local industry needs through the National Skill Development Corporation (NSDC).
- Increasing Public Investment: India allocates only 3% of its education expenditure to VET, compared to 10–13% in advanced economies, requiring higher investment to match global standards.
- Integrated Policy Reforms: Employment-linked schemes like PM Internship Scheme, ELI, and ELPTA must be linked with quality vocational training, providing clear career progression and improved employability.
Practice Question
“India’s vocational education and training (VET) system faces challenges of low enrolment, poor industry linkage, and weak employability outcomes. Critically examine the gaps in India’s VET framework and suggest reforms by drawing lessons from global best practices.” (250 words)