

22th August 2025 (18 Topics)
Context:
The Group of Ministers (GoM) has recommended the Centre’s proposal to move towards a two-rate GST structure, replacing the existing 12% and 28% slabs.
GST Background:
Goods and Services Tax (GST) is a destination-based indirect tax levied on the supply of goods and services. It was introduced in 2017 through the 101st Constitutional Amendment Act, subsuming multiple indirect taxes.
Current Structure:
At present, GST has four main tax slabs — 5%, 12%, 18%, and 28%, besides certain exempted items. Additionally, a compensation cess is levied on select items like tobacco, cigarettes, aerated drinks, coal, and automobiles.
Centre’s Proposal: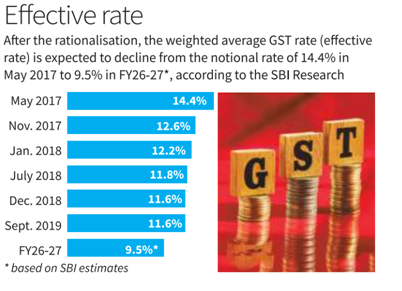
Retain only 5% and 18% slabs.
Abolish 12% and 28% slabs.
Nearly 99% of items in 12% slab to be moved to 5%.
Nearly 90% of items in 28% slab to be moved to 18%.
Remaining items in 28% slab (sin goods such as tobacco, cigarettes, online real-money gaming) to be shifted to a 40% slab.
Compensation cess on 28% slab items would no longer apply.
Significance:
Part of “next-generation GST reforms” announced by the Prime Minister.
Aims at reducing the tax burden on consumers, simplifying compliance, and ensuring better tax buoyancy.
Brings GST closer to the two-rate structure model, which is considered more efficient globally
More Articles


