2nd July 2024 (9 Topics)
Mains Issues
Context
Recent heavy rainfall in Delhi has once again highlighted the chronic issue of urban flooding in the city, exacerbated by unchecked urban expansion and inadequate drainage systems.
How urbanisation is responsible?
Delhi is undergoing one of the world’s fastest urban expansions. The geographic size of Delhi almost doubled from 1991 to 2011. This urban expansion, however, has paid little heed to Delhi’s natural topography.
- Unchecked Urban Growth: Rapid and unplanned urbanization has expanded Delhi without adequate consideration for natural drainage patterns.
- Impact on Drainage: Historical areas of Delhi were built on higher ground, allowing rainwater to naturally drain. Modern construction in low-lying areas disrupts these natural drainage routes.
- Concrete Jungle: Extensive concretization reduces the land's ability to absorb rainwater, leading to increased surface runoff during heavy rains.
- Drainage Infrastructure: Existing drainage systems, including nallahs (drains), are often insufficiently maintained and become clogged easily.
- Role of Civic Authorities: Inadequate desilting of drains by civic bodies exacerbates flooding during monsoon seasons.
- Infrastructure: The introduction of infrastructure like railways and roads in flood plains has further compromised natural drainage systems.
In short, Delhi is grappling with urban flooding caused by a combination of factors: unprecedented and extreme rainfall patterns, silt buildup, and encroachment on floodplains
How Sustainable urban planning can help?
- Cities must prioritise sustainable urban planning, comprehensive infrastructure development, and the preservation and restoration of natural water bodies to effectively address urban flooding.
- Measures such as green roofs, rainwater harvesting systems, and permeable pavements can reduce surface runoff and alleviate pressure on drainage systems. These solutions are crucial in building flood-resilient communities.
Fact Box: Government Measures for Urban Flooding
|


Mains Issues
Context
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has joined Project Nexus, a multilateral international initiative to enable instant cross-border retail payments by interlinking domestic Fast Payments Systems (FPSs). India’s Unified Payments Interface (UPI) and FPSs of Malaysia, the Philippines, Singapore and Thailand will be interlinked through Nexus. Going ahead, the platform can be extended to more countries.
What is Project Nexus?
- Project Nexus is a multilateral international initiative among central banks and financial authorities to enable instant cross-border retail payments.
- Initiated by: Innovation Hub of the Bank for International Settlements (BIS)
- It is the first BIS Innovation Hub project in the payments area to move towards live implementation
- It focuses on linking domestic instant payment systems (IPS) globally, enabling near-instantaneous transactions between countries.
- Founding members of Project: Central banks of India, Malaysia, Philippines, Singapore, and Thailand.
- The platform standardizes the connection process, making it easier for countries to join and allowing for rapid expansion of cross-border payment capabilities.
- Key Objectives
- Standardization of IPS Connections: Instead of creating custom connections for each country, Nexus provides a unified platform where a single connection enables access to all member countries.
- Facilitation of Instant Cross-Border Payments: By interlinking FPSs, Project Nexus aims to reduce the time and cost associated with cross-border transactions, aiming for transaction times within 60 seconds in most cases.
- The platform is expected to go live by 2026.
Benefits of Project Nexus
- Enhanced Efficiency: Standardized connections streamline the process of linking domestic FPSs, reducing the complexities involved in establishing cross-border payment networks.
- Reduced Costs: Near-zero costs to both senders and recipients are expected due to the efficiency gains and elimination of intermediary fees associated with traditional cross-border transactions.
- Improved Accessibility: Enables broader access to instant cross-border payments, promoting financial inclusion and facilitating smoother international transactions for individuals and businesses alike.


Mains Issues
Context
The National Human Rights Commission (NHRC) has taken note of reports alleging discrimination against married women at Foxconn's iPhone assembly plant in Sriperumbudur, Tamil Nadu. It issued notices to the Union Labour Ministry and the Tamil Nadu government, citing potential violations of gender equality norms under Indian and international law.
Ethical Issues
The case revolves around ethical principles of equality and non-discrimination in employment, particularly concerning marital status. It raises questions about corporate ethics, gender inclusivity, and compliance with labor laws.
- Gender Equality: Discrimination based on marital status violates principles of equality and fairness. All individuals should have equal access to employment opportunities irrespective of their marital status.
- Corporate Responsibility: Companies have an ethical obligation to ensure non-discriminatory practices and create inclusive work environments. Excluding married women from employment opportunities contradicts these principles.
- Transparency and Accountability: Job seekers should have clear and transparent information about eligibility criteria. Misinformation or lack of clarity in hiring processes can lead to unfair practices and distrust.
- Compliance with Laws and Regulations: Companies must adhere to national and international laws that prohibit discrimination based on gender or marital status. Failure to comply reflects ethical lapses in governance and corporate culture.
- Impact on Individuals and Society: Discriminatory practices not only harm individual job seekers but also perpetuate gender inequalities in society. Upholding ethical standards in employment contributes to social justice and equal opportunities for all.
- Role of Regulatory Bodies: Regulatory bodies play a crucial role in safeguarding rights and enforcing ethical standards. Prompt action and investigation are essential to address grievances and uphold ethical norms in corporate practices.


Prelims Articles
Context
Despite having elevated inflationary pressures, India's manufacturing activity in June witnessed a rebound, thanks to strong demand leading to the fastest rate of hiring in more than 19 years. The seasonally adjusted HSBC India Manufacturing Purchasing Managers’ Index or PMI increased from 57.5 in May to 58.3 in June, indicating a sharper improvement in business conditions. In PMI parlance,
- print above 50 means expansion
- while, a score below 50 denotes contraction
What is manufacturing PMI?
- Manufacturing PMI, or Purchasing Managers’ Index, is an economic gauge derived from monthly surveys of companies.
- It assesses business conditions in manufacturing and services sectors.
- Types of PMI:
- Manufacturing PMI
- Services PMI
- PMI helps determine if conditions are expanding, contracting, or stable, offering insights into current and future economic health.
- Variables: For manufacturing PMI, surveys are sent to manufacturing firms with factual questions about key areas: new orders (30%), output (25%), employment (20%), suppliers’ delivery times (15%), and stock levels (10%).
- A PMI number above 50 indicates growth, below 50 signals contraction.
- Started in 1948 by the Institute for Supply Management, PMI is produced globally.
- It's a leading indicator, often released before GDP data, providing early signals about economic trends. Investors and businesses use PMI to gauge economic conditions and make informed decisions.


Prelims Articles
Context
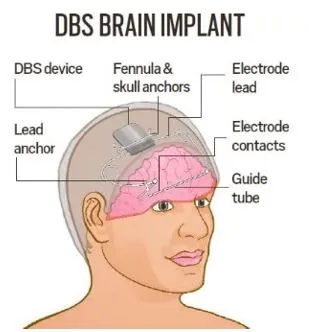
Oran Knowlson, a teenager from the UK, recently made headlines for becoming the first person worldwide to receive a brain implant aimed at reducing epileptic seizures. This deep brain stimulation (DBS) device, surgically implanted into his skull and connected to electrodes targeting the brain's thalamus, has successfully reduced his daytime seizures by an impressive 80%.
About DBS device
- The DBS device delivers constant electrical impulses to disrupt seizure-causing brain signals.
- It offers a promising alternative for patients resistant to traditional anti-seizure medications or those for whom surgery is not viable.
- It is surgically placed in the skull, electrodes inserted into the thalamus (brain's relay station).
- Effectiveness: Reduced Knowlson’s seizures by 80%.
- Comparison with Existing Treatments:
- Medication: Many patients are resistant (30%) to available anti-seizure drugs.
- Surgery: Effective but invasive; removes seizure-originating brain areas.
- Ketogenic Diet: High-fat, low-carb diet also used to control seizures.
Fact Box:
|


Prelims Articles
The Cheetah Project has made headlines due to plans to relocate surplus cheetahs from Kuno National Park to Gandhi Sagar Wildlife Sanctuary. This decision follows concerns over a decline in the chital population, the primary prey for cheetahs, and challenges posed by leopard predation.
Key Findings:
- Kuno National Park currently hosts 26 cheetahs, including 13 cubs.
- Concerns arose as Kuno's chital population, the main prey for cheetahs, decreased by over 25% since 2022.
- Leopard predation on chital is a significant issue, despite efforts to control it.
- Introducing Larger Cats: To address the issue of leopard predation and balance the predator-prey dynamics, the project is considering introducing larger cats like tigers into Kuno. Tigers are viewed as natural competitors to leopards and could potentially reduce their impact on the chital population.
- Project Challenges and Efforts: Efforts are ongoing to bolster the chital numbers in Kuno, including plans to bring in 1,500 more from other areas. Meanwhile, Gandhi Sagar Wildlife Sanctuary faces hurdles in removing leopards from prey enclosures to facilitate the introduction of cheetahs.
Fact Box:About Cheetal (Axis axis)
Kuno National Park (Madhya Pradesh):
Gandhi Sagar Wildlife Sanctuary (Madhya Pradesh)
|


Editorials
Context
Recent satellite images showing Chinese J20 stealth fighters deployed at the Shigatse air base in Tibet have sparked speculation and raised concerns about regional military dynamics, particularly concerning India's air power capabilities.
Strategic Significance of J20 Deployment
- PLAAF Capability Display: Deployment showcases PLAAF’s capability to operate high-end platforms at high-altitude air bases. It ndicates a shift from territorial disputes to sovereign airspace issues, impacting regional security dynamics.
- Strategic Intent: Potential impact of buffer and aerial buffer zones on IAF operations near disputed areas. Deployment underscores China's strategic efforts to neutralize India's air power advantage through enhanced operational presence.
Strategic Challenges and Future Preparedness
- IAF's Current Fleet: Current fleet of fourth-generation fighters supplemented by limited Rafale squadrons provides an asymmetric advantage.
- Urgent MRFA Requirement: Urgent need to fulfill the Multi-Role Fighter Aircraft (MRFA) gap to maintain air superiority. Delayed development of indigenous fifth-generation fighters risks eroding India's combat air power.
- Reducing Dependence: Importance of reducing dependence on single-source suppliers like Russia and volatile markets like the US. Strategic acquisitions and indigenous production crucial for bolstering defense capabilities amidst evolving threats.
Maintaining Deterrence and Capability
- Impact on Deterrence: Challenges posed by China's efforts to offset India's air power advantage.
- Strategic Imperatives: Leveraging partnerships, accelerating indigenous defense production, and prioritizing acquisition programs.
- National Security Safeguarding: Ensuring robust defense preparedness critical in safeguarding India's national interests.
Mains Question
Q. Critically analyze the strategic implications of China's deployment of J20 fighters in Tibet on India's national security. Discuss the challenges in maintaining air superiority and the strategic measures required to counterbalance evolving military capabilities in the region.


Editorials
Context
The Union government has recently introduced three new criminal laws in India, replacing longstanding statutes such as the Indian Penal Code, Code of Criminal Procedure, and the Indian Evidence Act. This legislative overhaul has sparked significant debate and raised concerns about the readiness of the policing and judicial systems for the implementation of these new legal frameworks.
Challenges in Preparedness
- Insufficient Training and Technological Upgrades: Despite some rudimentary training sessions and technological upgrades like the Crime and Criminal Tracking Network and Systems (CCTNS), doubts persist regarding the preparedness of both upper and lower levels of the police force.
- Minimal Training for Station-House Personnel: Reports indicate that station-house personnel have received minimal training, which may hinder their ability to effectively enforce the new laws.
- Rushed Transition and Inadequate Workshops: The hurried transition to the new legal frameworks underscores the inadequacy of current workshops and training programs in equipping law enforcement and judicial officers adequately.
Concerns Regarding Implementation
- Ambiguity in Legal Framework: The introduction of new laws with Hindi names and the absence of English equivalents has caused confusion among stakeholders, impacting accessibility and comprehension of the legal provisions.
- Insufficient Legislative Debate: Critics argue that the legislative process lacked sufficient time for thorough debate within the legislature and broader civil society, raising questions about transparency and stakeholder inclusiveness.
- Concerns Over Expanded Police Powers: Concerns persist over potential loopholes and unintended consequences of certain provisions, such as expanded police powers related to custody, which could potentially infringe upon citizens' rights.
Implications and Future Outlook
- Inclusion of Terrorism Offenses: The inclusion of terrorism as a regular criminal offense alongside existing anti-terrorism laws has introduced ambiguity and operational challenges.
- Autonomy for States in Amendments: States have been granted autonomy to amend the new laws, but uncertainties remain regarding the speed and assurance of Presidential assent to these amendments.
- Mixed Reactions to Procedural Reforms: While procedural reforms like mandatory FIR registration and the use of videography in searches are seen as positive steps, doubts linger about the overall effectiveness and the potential for unintended consequences in the implementation of the new legal framework.
Mains Question
Q. Critically analyze the implications of the recent enactment of the Bharatiya Nyaya Sanhita, Bharatiya Nagarik Suraksha Sanhita, and Bharatiya Sakshya Adhiniyam on India's criminal justice system. Discuss the challenges in their implementation and evaluate their potential impact on police-citizen relations.


Editorials
Context
The launch of Jaadui Pitara by the Minister of Education highlighted India's commitment to integrating play-based learning into early education, aligning with global recognition of the International Day of Play and educational policies like the NEP 2020 and NCF-FS 2022.
Importance of Play in Early Education
- Natural Learning Tool: Play is recognized as a natural and powerful tool for holistic development encompassing physical, socio-emotional, language, cognitive, and cultural aspects.
- Safe and Curious Exploration: Encourages children to explore, experiment, and learn in a safe and non-judgmental environment, fostering curiosity and creativity.
- Community Bonding: Facilitates interaction among students, teachers, parents, and the community, creating a supportive learning ecosystem.
Policy Framework and Curriculum Integration
- NEP 2020 and NCF-FS 2022: Introduction of "learn through play" as a core principle, legitimizing play-based learning in early childhood education.
- Diverse Learning Pathways: Acknowledgement that learning encompasses various forms beyond traditional methods like writing and reading, promoting inclusivity and individualized learning paths.
- Comprehensive Approach: Incorporates conversation, storytelling, toys, songs, rhymes, music, arts, crafts, indoor and outdoor games into the curriculum to enhance engagement and learning outcomes.
Jaadui Pitara: Transformative Teaching-Learning Materials
- Content and Design: Includes toys, games, puzzles, puppets, posters, flashcards, storybooks, and playbooks tailored for the foundational stage (ages 3-8).
- Learning Outcomes: Each component mapped to specific learning outcomes to ensure educational efficacy and developmental impact.
- Customization and Adaptation: Efforts by states to customize Jaadui Pitara contents to suit local contexts and enhance relevance and effectiveness.
Mains Question
Q. Critically analyze the role of play-based learning in early childhood education as emphasized by India's Jaadui Pitara initiative. Discuss the significance of integrating play in the National Education Policy and its potential impact on holistic child development and educational outcomes.