Chief Election Commissioner and Other Election Commissioners (Appointment, Conditions of Service and Term of Office) Bill, 2023 passed in LokSabha
Context
The LokSabha has passed the bill to regulate the appointment of the chief election commissioner and other election commissioners.
About
About the Bill:
- Background: The Bill replaces the Election Commission (Conditions of Service of Election Commissioners and Transaction of Business) Act, 1991.
- Aim: The bill provides details related to the appointment, qualifications, search committee, selection committee, term of office, salary, resignation and removal, leave, and pension of the chief election commissioner and other election commissioners.
- Provisions of the Bill:
- As per the provisions of the bill, the CEC and ECs will be appointed by the President of India on the recommendation of a selection committee.
- However, the panel will consist of three members – the prime minister, the Union cabinet minister, and the leader of the opposition.
- Recommendations of the Selection Committee will be valid even when there is a vacancy in this Committee.
- A Search Committee headed by the Cabinet Secretary will propose a panel of names to the Selection Committee.
- Eligibility for the posts includes holding (or having held) a post equivalent to the Secretary to the central government.
- The salary and conditions of service of the CEC and ECs will be equivalent to that of Cabinet Secretary. Under the 1991 Act, it was equivalent to the salary of a Supreme Court Judge.
- Eligibility criteria: The CEC and ECs must:
- be persons of integrity,
- have knowledge and experience in the management and conduct of elections, and
- be or have been Secretary (or equivalent) to the government.
- Term and reappointment: Members of the Election Commission will hold office for six years, or until they attain the age of 65 years, whichever is earlier.
- Members of the Commission cannot be re-appointed. If an EC is appointed as a CEC, the overall period of the term may not be more than six years.
Key Issues and Analysis
- The selection process of the Election Commission may be dominated by the government, which has implications for its independence.
- Accepting the Selection Committee’s recommendations in spite of a vacancy in its constitution may effectively lead to a monopoly of government members in selecting candidates.
- Making the CEC and EC’s salary equivalent to the Cabinet Secretary may lead to government influence as it is fixed by the government. This is unlike the salary of a Supreme Court judge which is fixed through an Act of Parliament.
- CECs and ECs also perform quasi-judicial functions. Limiting these posts to senior bureaucrats may exclude other suitable candidates.
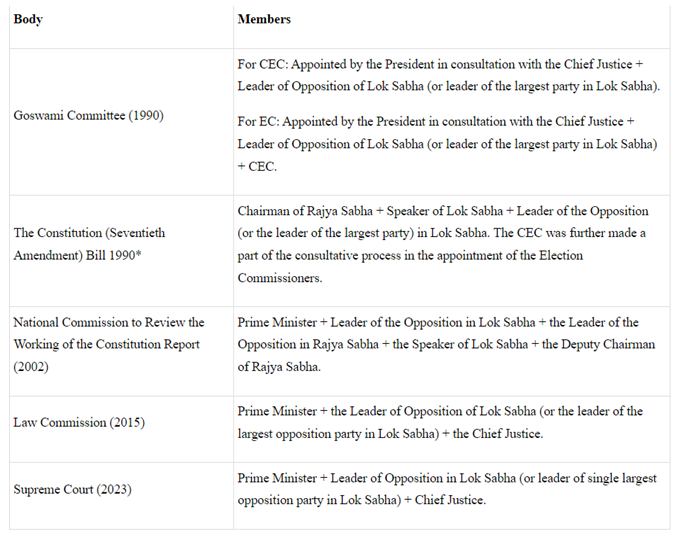
- Table: Suggestions made by various Commissions/Courts for composition of the Selection Committee: