

19th October 2024 (11 Topics)
Context
Atmospheric rivers are shifting toward higher latitudes, and that’s changing weather patterns around the world.
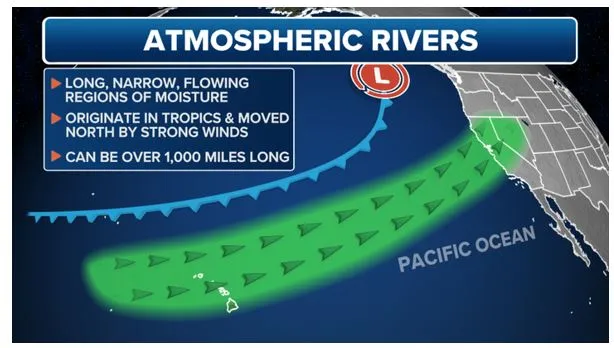
What are Atmospheric Rivers?
- Atmospheric riversare large, narrow sections of the Earth’s atmosphere that carry moisture from the Earth’s tropics near the equator to the poles.
- Similar to terrestrial rivers, atmospheric rivers can vary in strength and size. They carry massive amounts of moisture.
- On average, the Earth has four to five active atmospheric rivers at any time.
- Occurrence: They can occur both in the:
- Northern hemisphere – typically between December and February
- Southern hemisphere – typically between June and August, when extratropical cyclones are prevalent
- Each moves the equivalent of the liquid water that flows through the mouth of the Amazon River. When they reach land, atmospheric rivers release this moisture, producing heavy snow and rain.
- Role of atmospheric rivers:
- Atmospheric rivers are responsible for 90 percent of the movement of moisture from the tropics toward the poles.
- They are a major factor in the formation of cloudsand therefore have a significant influence on air temperatures, sea ice, and other components of the climate.
More Articles


