Instruction:
- There will be 2 questions carrying 10 marks each. Write your answers in 150 words
- Any page left blank in the answer-book must be crossed out clearly.
- Evaluated Copy will be re-uploaded on the same thread after 2 days of uploading the copy.
- Discussion of the question and one to one answer improvement session of evaluated copies will be conducted through Google Meet with concerned faculty. You will be informed via mail or SMS for the discussion.
Question #1. What is palaeomagnetism? How is it associated to sea floor spreading?
Question #2. What is landslide? Discuss the causes and impacts of landslide with recent examples?
(Examiner will pay special attention to the candidate's grasp of his/her material, its relevance to the subject chosen, and to his/ her ability to think constructively and to present his/her ideas concisely, logically and effectively).
STEPS & INSTRUCTIONS for uploading the answers
Step 1 - The Question for the day is provided below these instructions. It will be available at 7:00 AM.
Step 2 - Uploading of Answers : Write the answer in A4 Sheet leaving proper margins for comments and feedback and upload the PDF in MY ACCOUNT section. Click on the option of SUBMIT COPY to upload the PDF.
Step 3 - Deadline for Uploading Answers: The students shall upload their answers by 7:00 PM in the evening same day. The first 50 copies will be evaluated.
Step 4 - Feedback : Mentors will give their feedback for the answers uploaded. For more personalised feedback, join our telegram channel by clicking on the link https://t.me/mains_answer_writing_cse . A one-to-one session will be conducted with the faculty after copy evaluation in 72 Hrs.
Model Answer
Question #1. What is palaeomagnetism? How is it associated to sea floor spreading?
Ans
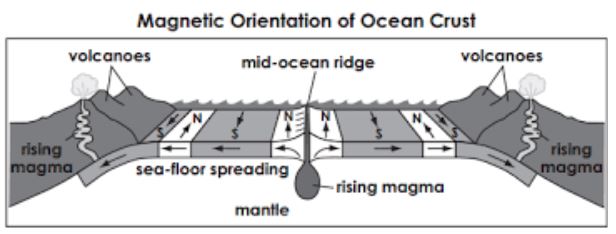
Palaeomagnetism is the study of the earth’s magnetic field preserved in the rocks. It is stored in minerals at time of their formation which have been magnetized.
Palaeomagnetism has opened way to findings of several unsolved geological mysteries about drifting of continents and wandering of poles. It has been explained in association of sea floor spreading.
Concept of sea floor spreading was first propounded by Prof. Hary Hess in 1960. He proposed that below oceanic ridges the rising limbs of convection currents are located and magma pushes outward tearing oceanic crust into two part horizontally.
Fig. 1. Palaeomagnetism and Sea Floor Spreading
Hence, ridges are formed by the cooling and solidification of lava over ocean floors over divergent margins of plates. It results in rate of displacement is equal to rate of solidification of magma. Thus, oceanic crust has been renewed along the ridges. Such solidification takes place in form of strip along oceanic ridge and rocks attain their magnetic properties i.e. known as palaeomagnetism.
Case Study: W.G.Vine and Mattheus have studied this phenomena over Indian Ocean while conducting a manetic survey along Carlsberg Ridge in 1963. They found alternate bands of normal and reverse mangnetism in sparate stripes of 20 km width on either side of ridge.
They have also advocated the concept of sea – floor spreading as propounded by Deitz and Hess that when molten hot lavas come up with the rising thermal convection current along the mid-oceanic ridges and get cooled and solidified, these also get magnetized at same time.
Thus, study of rocks at ocean floor reveals that earth’s crust is always in stage of formation along divergent margins which proves sea floor spreading.
Question #2. What is landslide? Discuss the causes and impacts of landslide with recent examples?
Ans
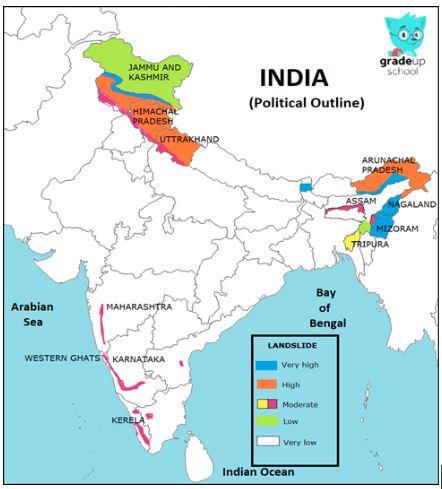
All types of mass movements of rocks wastes including soils and ice are called as landslides. Landslides have been classified as fall, slide, flows and creep. According to a new report on landslide vulnerable regions in 17 states and 2 union territories released by ISRO, Rudraprayag and Tehri Garhwal in Uttarakhand are the most landslide-prone districts in the country (fig. 2).
Fig. 2 Landslides in India
Natural Causes
- Frequent earthquakes in Himalayan zone has been observed a key factor for frequent landslides.
- Due to climate change, cloud burst and heavy rainfall have become a common seasonal phenomena in Himalayan and in states of western ghats. It makes soils over saturated of water and leads to mud flow.
Anthropogenic Causes
- Infrastructure development like construction of roads, trains, and dams in hilly areas cause landslides. Construction of roads in Himachal Pradesh and Uttarakhand in order to increase connectivity to border areas and construction of Konkan Railways in the Western Ghats have been major cause of frequent landslides.
- Deforestation is order to meet demand of land for agriculture and infrastructure development is responsible to loosen soil particles and open flow of surface water over mountain slopes. In recent time deforestation has been observed a major cause for landslides in Himachal Pradesh and Uttarakhand.
- In recent time, tourism has increased during summer season i.e. hill tourism. Hence, it is observed that hill areas have been over exhausted due to excessive arrival of tourists which increases pressure on resources and land. It demands development of infrastructure and hotels. Consequently, such demands have been met by deforestation and change in land use pattern. It resulted in rise in cases of landslides in last decade. Such case has been particularly observed in Joshimath which is on the way to Badrinath. So it is at the verge of collapse due to worst landslide.
Consequences
- The loss of irreplaceable human and animal life is the most traumatic effect of a landslide.
- Movement is restricted because the mud, boulders, and debris sliding down the hill create a barrier on vital transportation routes such as highways and railway lines.
- Damage to Infrastructure: When a landslide happens, several residences, buildings, roads, and other infrastructure are affected.
- Economic Losses: A considerable amount of money is spent on rebuilding the destroyed infrastructure, rehabilitating the masses, and giving relief assistance to the affected individuals.
- Water availability may be jeopardised: When landslides occur on the slopes of a river valley, the sliding mass may reach the valley bottom and produce a partial or total blockage of the river channel.
- This collected mass of avalanche debris that blocks a river is frequently referred to as a landslide dam.
- It may reduce the availability of water for adjacent residents.
Conclusion
Landslide has become a mojor concern of attention as a disaster. Quick and focused action only can prevent areas from landslide. People’s awareness shall be key result oriented approach for landslide management.