Instruction:
- There will be 2 questions carrying the First Question is-10 marks Write your answers in 150 words and the Second Question is-15 marks Write your answers in 250 words.
- Any page left blank in the answer-book must be crossed out clearly.
- Evaluated Copy will be re-uploaded on the same thread after 2 days of uploading the copy.
- Discussion of the question and one to one answer improvement session of evaluated copies will be conducted through Google Meet with concerned faculty. You will be informed via mail or SMS for the discussion.
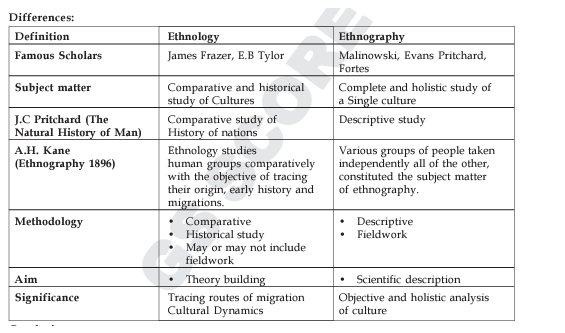
Question #1. Compare and contrast between Ethnology and Ethnography 10 marks (150 words)
Question #2. Discuss the characteristics and phylogenetic significance of Narmada man. 15 marks (250 words)
(Examiner will pay special attention to the candidate's grasp of his/her material, its relevance to the subject chosen, and to his/ her ability to think constructively and to present his/her ideas concisely, logically and effectively).
STEPS & INSTRUCTIONS for uploading the answers
Step 1 - The Question for the day is provided below these instructions. It will be available at 7:00 AM.
Step 2 - Uploading of Answers : Write the answer in A4 Sheet leaving proper margins for comments and feedback and upload the PDF in MY ACCOUNT section. Click on the option of SUBMIT COPY to upload the PDF.
Step 3 - Deadline for Uploading Answers: The students shall upload their answers by 7:00 PM in the evening same day. The first 50 copies will be evaluated.
Step 4 - Feedback : Mentors will give their feedback for the answers uploaded. For more personalised feedback, join our telegram channel by clicking on the link https://t.me/mains_answer_writing_cse . A one-to-one session will be conducted with the faculty after copy evaluation in 72 Hrs.
Model Answer
Question #1. Compare and contrast between Ethnology and Ethnography 10 marks (150 words)
Approach
- Definition
- Subject Matter
- Development
- Methods: Comparative analysis vs description
- Relationship between the two
- Conclusion
Hints:
Ethnography and ethnology are two inter-related methodologies to study and enquire into human cultural development. The main difference between ethnography and ethnology lies in their content and the context of study. Ethnography is a natural science that studies different procedures practiced by different societies, while ethnology is a natural science that studies the demographics of the societies in a detailed and descriptive manner.
Ethnography
Ethnography refers to data-gathering in a single society, usually in a spatially and temporally bounded situation, such as when the fieldworker spends considerable time as a participant observer in a local community and later writes up the findings in a stand-alone, case study-type monograph (also called ethnography).
- Ethnography is literally writing about people.
- More broadly speaking, it is any study of a group of people for the purpose of describing their sociocultural activities and patterns.
- Its central aim is to understand another way of life from the point of view of the person experiencing that way of life and as such, always implies a theory of culture.
- Ethnography takes a step away from the sort of research that describes subjects and behaviors and focuses on actors and actions.
- Case study- Malinowski- Argonauts of Western Pacific
Ethnology Ethnology is a comparative study of human cultures with an added element of historical perspective. It studies human groups comparatively with the objectives of tracing origin and patterns of migration.
- It included speculative theories on assumed interrelations between cultural and biological group differences.
- It studies the dynamism of culture and the changes induced in it due to certain exogenous and endogenous factors.
- It is concerned with man’s cultural history.
- Via a Cross-Cultural Frame of Reference, Ethnological research makes use of previously collected information to understand other cultures and environments and to gear up the study to achieve more effective and realistic goals.
Conclusion:
The main difference between ethnography and ethnology is that ethnography is an area of study in natural science where ethnographers conduct their studies on different procedures practiced by different societies, while ethnology is another area of study in natural science where ethnologists study demographics of the societies in a more detailed and descriptive manner.
Question #2. Discuss the characteristics and phylogenetic significance of Narmada man. 15 marks (250 words)
Approach
- Introduce Narmada man and site where it was found.
- Author associated with its study.
- Features of Narmada man.
- Phylogenetic significance.
- Conclusion
Hints:
The discovery in 1982 of a fossilized skull in the central Narmada valley in Madhya Pradesh, India, provides the first scientifically recorded evidence of human skeletal remains from the Indian subcontinent dating to the late Middle Pleistocene of 300,000 to 150,000 years ago.
Dr.ArunSonakia of the Geological Survey of India found the fossil exposed on the ground surface of a thick Quaternary sediment of fluvial origin and embedded in a fossiliferous gravel conglomerate on the north bank of the Narmada River. This is near the village of Hathnora and some 40 km northeast of Hoshangabad town.
- Preserved parts of the specimen are the left side of the cranial vault, most of the base of the skull, and the left half of the brow ridges and orbit.
- Hence, it is a calvaria, not a complete skull with a full face including upper and lower jaws. Teeth are absent.
- In 1997, an announcement was made of the finding of a hominid right clavicle from Middle Pleistocene deposits in the Hathnora region during field explorations between 1983 and 1992, a bone that Dr. A. A. Sankhyan of the Anthropological Survey of India, Calcutta, associates with the Narmada Man calvaria and describes as having belonged to a female the size of a modern adult pygmy of "stocky" build.
Narmada Man, rather men, is known by the cranial and postcranial fossil remains representing two types of archaic hominins or human populations. Cranial Remains
A partial right portion of the skullcap (calvaria) Narmada Man was discovered from Hathnora in Central Narmada valley during 1982 by ArunSonakia of the Geological Survey of India, who reported the finding in 1984 in the Records of the Geological Survey of India. Detailed studies on it were conducted by M.A. de Lumley in France during 1985, and in USA during 1991 by Kenneth A.R. Kennedy
Phylogenetic status:
In Sonakia’s description, published in 1984 in the Records of the Geological Survey of India, he assigned “Narmada Man” to the hominid taxon Homo erectus narmadensis.
- Its antiquity is based upon the direct association of the calvaria with stone tools, mainly handaxes and cleavers, typical of the prehistoric Acheulian technological tradition that was dominant in Middle Pleistocene times in India.
- The fossilized animal remains in the deposit—cattle, buffalo, elephant—include some species that are now extinct, but they are reliable “index fossils” of the late Middle Pleistocene.
- Radiometric dating methods are not feasible, so the age of the specimen is a relative dating estimate based upon its lithic and faunal associations.
- By 1988, reexaminations of the calvariahad been undertaken independently by biological anthropologists from the Laboratory of Human Paleontology and Prehistory at Marseille in France and from the Human Biology Laboratory at Cornell University at Ithaca in the United States.
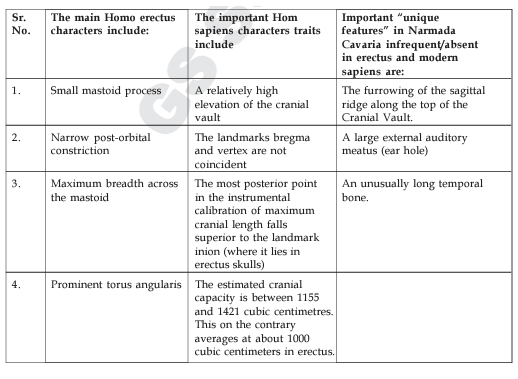
- The French investigator, Dr. Marie-Antoinette de Lumley, recognized that some physical features of the calvaria were not typically those found in Homo erectus fossils from Southeast Asia, China, and Africa.
- For example, the cranial capacity of these Early and Middle Pleistocene specimens averages 1,000 cm3, but estimates for the Narmada cranial vault fell between 1,155 and 1,421 cm3, values within the range of anatomically archaic Homo sapiens.
- Dr. de Lumley christened Narmada Man as an “evolved Homo erectus.” This label is acceptable to those biological anthropologists who profess that anatomically modern humans have a lineage that includes Homo erectus as an ancestral species, the anatomically archaic hominids of the Middle and Late Pleistocene (called Homo heidelbergensis) having an intermediate status in this evolutionary progression.
- Aside from learned debates over this matter, the American investigator, Dr. Kenneth A. R. Kennedy, broadened de Lumley’s observations by an extensive examination of the calvaria using measurements, morphological analyses, and statistical procedures that support the thesis that Narmada Man (actually a young adult female) merited reassignment as an early Homo sapiens.
- The specimen was compared with crania of other hominid fossils of the Middle Pleistocene (Bodo, Kabwe, Petralona, Dali, Ngandong, Saldanha, Sambungmachen, and those from other sites in Africa, Asia, and Europe), with which it exhibited a significant number of anatomical similarities.
- The archaeological data do not rule out the possibility that Homo erectus had inhabited the Indian subcontinent, but fossil remains of this species have not been recovered.
- The importance of the Narmada calvaria is that it demonstrates that the Acheulian tool tradition was practiced by early sapiens in a part of the world that lies between the richer hominid fossil sites in Africa and in Southeast Asia and the Far East. It is the most ancient hominid fossil recovered in India at the time of this writing.
But, scholars remained divided on the status of Narmada calvaria as either “evolved” H. erectus or “archaic” H. sapiens, but, recently many favour it as H. heidlebergensis.