Instruction:
- There will be 2 questions carrying the First Question is-10 marks Write your answers in 150 words and the Second Question is-15 marks Write your answers in 250 words.
- Any page left blank in the answer-book must be crossed out clearly.
- Evaluated Copy will be re-uploaded on the same thread after 2 days of uploading the copy.
- Discussion of the question and one to one answer improvement session of evaluated copies will be conducted through Google Meet with concerned faculty. You will be informed via mail or SMS for the discussion.
Question #1. Biological and cultural factors in Human Evolution 10 marks (150 words)
Question #2. Give a critical account of the processes of organic evolution and explain how they contribute to speciation. 15 marks (250 words)
(Examiner will pay special attention to the candidate's grasp of his/her material, its relevance to the subject chosen, and to his/ her ability to think constructively and to present his/her ideas concisely, logically and effectively).
STEPS & INSTRUCTIONS for uploading the answers
Step 1 - The Question for the day is provided below these instructions. It will be available at 7:00 AM.
Step 2 - Uploading of Answers : Write the answer in A4 Sheet leaving proper margins for comments and feedback and upload the PDF in MY ACCOUNT section. Click on the option of SUBMIT COPY to upload the PDF.
Step 3 - Deadline for Uploading Answers: The students shall upload their answers by 7:00 PM in the evening same day. The first 50 copies will be evaluated.
Step 4 - Feedback : Mentors will give their feedback for the answers uploaded. For more personalised feedback, join our telegram channel by clicking on the link https://t.me/mains_answer_writing_cse . A one-to-one session will be conducted with the faculty after copy evaluation in 72 Hrs.
Model Answer
Question #1. Biological and cultural factors in Human Evolution 10 marks (150 words)
Approach
- Introduce the emergence of human beings as confluence of environment and heredity
- Discuss biological and cultural factors responsible for human evolution
- Conclusion
Hints:
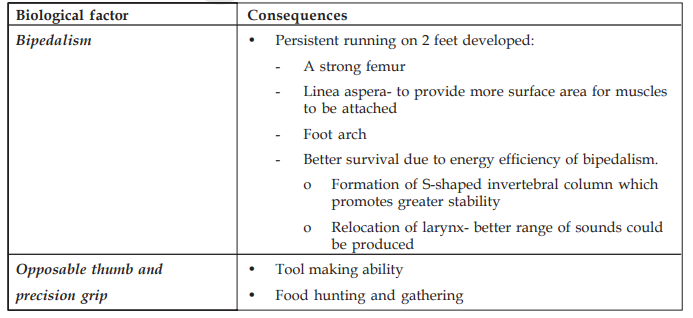
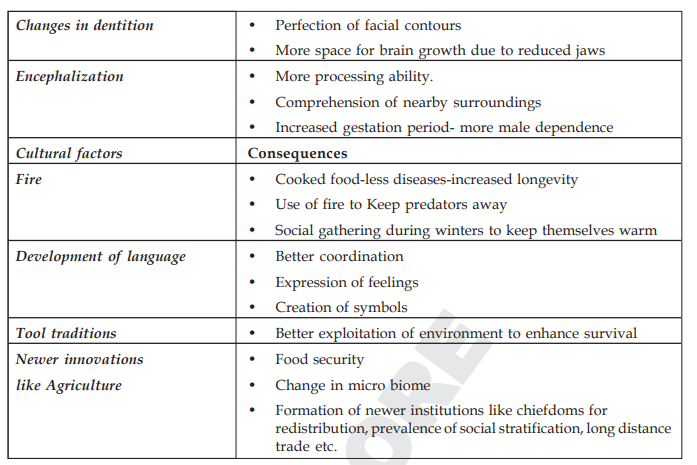
The emergence of modern humans has been a result of the interplay between biological and cultural factors. The Hominization process is the evolutionary transformation of hominoids into Hominids. It is a process that has occurred in the hominoid-line since its divergence from the last common hominoid ancestor shared with any living ape.
Conclusion:
Palaeo-anthropological evidence increasingly suggests that culture appears early in the evolutionary history of our genus. Homo sapiens' brain, genes, and biology have long been shaped by the interaction between cultural and genetic evolution. Culture appears to have opened up entirely new evolutionary vistas not available to less developed species.
Question #2. Give a critical account of the processes of organic evolution and explain how they contribute to speciation. 15 marks (250 words)
Approach
- Introduction- definition and explanation of the term
- Theories of organic evolution
- Different patterns of organic evolution
- Causes and the consequent speciation
- Conclusion
Hints:
“Changes in the genetic makeup of species in a population as a result of responding to environmental changes is organic evolution”
Living entities possess the basic characteristic of reproducing. Entities being reproduced can sustain life only if there is proper coordination and adaptation with the changing environment. To maintain harmony in the ecosystem, changes must be endured and suitably adapted. Structural changes in living entities can be permanently integrated through changes in the genetic composition.
Evolution is a gradual and continuous process.
Theories of Organic Evolution
Evolution corresponds to change in the form and behaviour of organisms between generations. It refers to change within a lineage of populations between generations.
A number of theories were put forward to substantiate and describe the evolutionary process. Some of these theories are listed below:
Darwin’s theory of evolution
Organic evolution by Charles Darwin is emphasized as “Descent with modification” stating that the present complexities in animals and plants are as a result of evolution from simpler forms that existed earlier through eventual changes.
Darwin’s book on “Origin of Species” in 1859, was the earliest one to put forward the theory of evolution through natural selection which stated that the entities, as a result of alterations in the inherited behavioural and physical characteristics, undergo changes over a period of time. These changes allow species to better adapt to changing environments, helping in the survival of offspring.
One of the best-sustained theories has been the evolution of natural selection backed by evidence from a range of scientific disciplines such as genetics, geology, palaeontology, developmental biology, etc.
The theory highlighted the main points as per Brian Richmond, which are – “All life on earth is connected and related to each other” and diversity of life is as a result of modifications of populations through natural selection wherein few characteristics were selected in an environment over others. Many times the theory is referred to as “survival of fittest” which can be misled more often.
Lamarckian Theory of Evolution
The first theory of evolution was Lamarckism proposed by Jean Baptiste de Lamarck, the outline of this theory came into the picture in 1801 only. He is responsible for coining terms “Annelida” and “invertebrates”.
Lamarck’s Propositions
4 main factors are:
- Internal vital force – this force causes all living things and their component parts to be continually increased
- Effect of environment and new needs – environmental changes have an impact on living entities causing them to change leading to new needs. These needs generate new structure altering habits of entities
- Use and disuse of entities – more usage of organs causes it to develop better, disuse of organs leads to degeneration
- Inheritance of acquired traits – characteristics adapted as a result of all these above factors passing on to the next generations. It is a continuous process. These variations are accumulated over generations leading to the formation of a new species.
Examples In Support of Lamarckism:
- Webbed toes of aquatic birds
- Evolution of giraffe
- The disappearance of limbs in snakes
- Flightless birds
- Flat fishes
- Cave dwellers
Mechanism of Organic Evolution
The phenomenon of genetic variation is basic for organic evolution. It is upon this that selective forces act for evolution to take place. The mechanism of evolution emphasizes on:
- Descent and genetic differences which can be inherited to the next generation. Genetic drift, migration, mutation, natural selection as mechanisms of change
- Significance of genetic variation
- Consequences of a reduction in genetic variation and random nature of genetic drift
- Impact of various species on each other’s evolution process via co-evolution
- Role of differential reproduction, variation, heredity in evolution by natural selection
Evolution is observed in a population as it contains genes in the gene pool, changes in this pool cause evolution.
- Mutation: It is a driving force for evolution. It can be a random change in the genetic composition having an impact on the gene pool of a population. This alteration in the nature of DNA in 1 or more chromosomes produces new alleles, hence a cause for genetic variation. Natural selection is decisive in mutation to eliminate the less-fit, allowing survival of fittest.
- Natural selection: It occurs when entities are left up to an environment where survival of fittest is observed. These characteristics when inherited in offspring reproduce a population better suited to the changing environment. Traits from less-fit entities are less likely to be passed to the upcoming generation. In natural selection, the significant selective force is the role of the environment. For instance, the ability to attract and mate can also be seen as a measure of fitness. Those who
are better adapted, produce comparatively more offspring, passing on their genes at a higher success rate compared to the entities that are less adapted.
- Gene flow: Migration of entities may cause a cluster of them to move to a new geographical location. When the migratory entities interbreed with the newly introduced population, they result in the addition of new genes to the already existing gene pool as a result of the local population, thereby contributing to the gene flow.
- For instance, when pollens are blown by wind beyond the reach of the parent plant population, gene flow takes place. Some animals can be shifted away from a herd compelling them to move to a new location, interbreed and introduce new genes to the pool.
- Genetic drift: It can take place when a small population moves to a new geographical location, establishing in a completely isolated area. For instance, when a few fishes are introduced in a lake, the population evolves over time into a different one from the parent ones. This process does not take place in densely populated areas.
Development of Species
A particular group of entities sharing a number of traits with the ability to interbreed with each other, leading to the production of fertile offspring are species. These usually share the same gene pool.
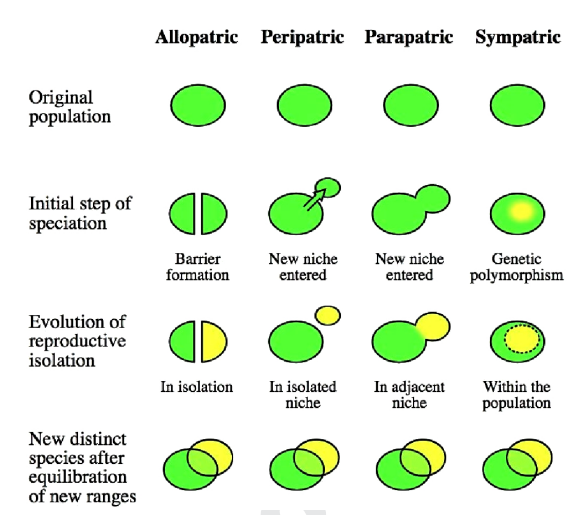
Types of speciation:
- Parapatric speciation:
– The suffix -patric still means "place" and when the prefix para-, or "beside", is attached, it implies that this time the populations are not isolated by a physical barrier and are instead "beside" each other.
– Even though there is nothing stopping the individuals in the entire population from mixing and mating, it still does not happen in parapatric speciation. For some reason, individuals within the population only mate with individuals in their immediate area.
– Some factors that could influence parapatric speciation include pollution or an inability to spread seeds for plants. However, in order for it to be classified as parapatric speciation, the population must be continuous with no physical barriers. If there are any physical barriers present, it needs to be classified as either peripatric or allopatric isolation.
- Sympatric speciation:
– The final type is called sympatric speciation. The prefix sym-, meaning "same" with the suffix -patric, which means "place" provides a clue to the meaning of this type of speciation: The individuals in the population are not separated at all and all live in the "same place." So how do the populations diverge if they live in the same space?
– The most common cause of sympatric speciation is reproductive isolation. Reproductive isolation may be due to individuals coming into their mating seasons at different times or preference of where to find a mate. In many species, choice of mates may be based on their upbringing. Many species return to where they were born to mate. Therefore, they would only be able to mate with others who were born in the same place, no matter where they move and live as adults.