Instruction:
- There will be 2 questions carrying 10 marks each. Write your answers in 150 words
- Any page left blank in the answer-book must be crossed out clearly.
- Evaluated Copy will be re-uploaded on the same thread after 2 days of uploading the copy.
- Discussion of the question and one to one answer improvement session of evaluated copies will be conducted through Google Meet with concerned faculty. You will be informed via mail or SMS for the discussion.
Question #1. Discuss the factors on the basis of which Thornthwaite classified World’s climate.
Question #2. Discuss the Koppen’s scheme of climatic classification. Explain the salient characteristics of ‘Cs’ type of climate.
(Examiner will pay special attention to the candidate's grasp of his/her material, its relevance to the subject chosen, and to his/ her ability to think constructively and to present his/her ideas concisely, logically and effectively).
STEPS & INSTRUCTIONS for uploading the answers
Step 1 - The Question for the day is provided below these instructions. It will be available at 7:00 AM.
Step 2 - Uploading of Answers : Write the answer in A4 Sheet leaving proper margins for comments and feedback and upload the PDF in MY ACCOUNT section. Click on the option of SUBMIT COPY to upload the PDF.
Step 3 - Deadline for Uploading Answers: The students shall upload their answers by 7:00 PM in the evening same day. The first 50 copies will be evaluated.
Step 4 - Feedback : Mentors will give their feedback for the answers uploaded. For more personalised feedback, join our telegram channel by clicking on the link https://t.me/mains_answer_writing_cse . A one-to-one session will be conducted with the faculty after copy evaluation in 72 Hrs.
Model Answer
Question #1. Discuss the factors on the basis of which Thornthwaite classified World’s climate.
Hints:
Thornthwaite presented his first scheme of classification of climates of North America in 1931 when he published the climatic map of North America. Later he extended his scheme of climatic classification for world climates and presented his full scheme in 1933. Like Koeppen, Thornthwaite also considered natural vegetation of a region as the indicator of climate of that region. He accepted the concept that the amount of precipitation and temperature had paramount control on vegetation but he also pleaded for inclusion of evaporation as important factor of vegetal ion and climate.
This is why Thornthwaite used two factors. e.g. precipitation effectiveness and temperature effectiveness, for the delimitation of boundaries of different climatic regions.
(i) Precipitation Effectiveness: Precipitation effectiveness or precipitation efficiency refers to only that amount of total precipitation which is available for the growth of He used precipitation efficiency ratio for the calculation of this amount of water available to vegetation. Precipitation efficiency ratio (PIE ratio) is calculated by dividing total monthly precipitation by monthly evaporation and precipitation efficiency index (PIE index) is derived by summing the precipitation efficiency ratios for 12 months of a year.
|
PIE Index and boundary values for the major vegetation zones |
||
|
Humidity Zone |
Vegetation |
PIE Index |
|
A (Wet) |
Rainforest |
127 |
|
B (Humid) |
Forest |
64-127 |
|
C (Subhumid) |
Grassland |
32-63 |
|
O (Semiarid) |
Steppe |
16-31 |
|
E (Arid) |
Desert |
<16 |
(ii) Thermal Effectiveness He believed that temperature had important contribution in the growth of vegetation. He, thus, devised an index of thermal efficiency or temperature effectiveness, expressed by positive departure of monthly mean temperatures from freezing point.
On the basis of T·E index Thornthwaite divided the world into 6 temperature provinces:
|
Temperature Province |
T·E Index |
|
A’ – Tropical |
127 |
|
B’ – Mesothermal |
64-127 |
|
C’ - Microthermal |
32-63 |
|
D’ - Taiga |
16-31 |
|
E’ - Tundra |
1-15 |
|
F’ – Frost |
0 |
Thus, on the basis of precipitation effectiveness, thermal efficiency, and seasonal distribution of rainfall there may be 120 probable combinations and hence climatic types on theoretical ground but he depicted only 32 climatic types on the world map.
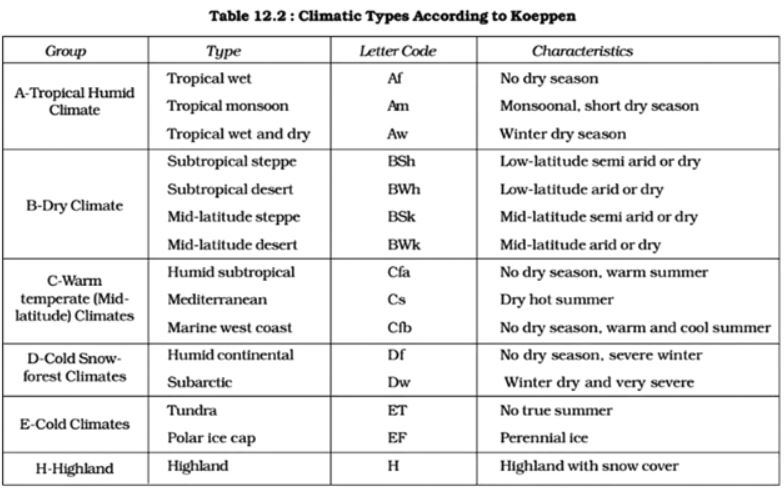
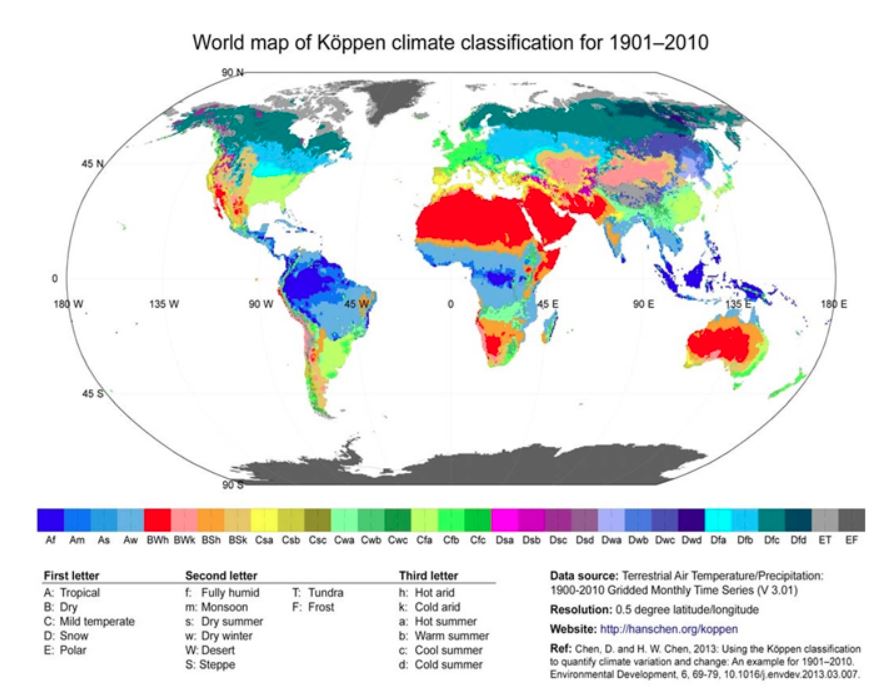
Question #2. Discuss the Koppen’s scheme of climatic classification. Explain the salient characteristics of ‘Cs’ type of climate.
Hints:
Climate is an average weather condition at a specific place over a long period of time (30-35 years and more), including absolute extremes of temperature, precipitation etc. Factors such as latitude, altitude, prevailing winds, ocean currents, maritime and continental situations exercise direct influence in determining the climate.
Wladimir Koppen (1846-1940), a Russian born German climatologist and botanist attempted he classification of world climates. Climate classification was first published as ‘thermal zones of the earth’ in 1884 in Russian language. Scholars E. Volken and S. Bronnimann translated the work in German. With several modifications, Koppen improved his classification later on, in 1918 and 1936.
Basis of climatic classification of koppen:
Koppen assumed that the vegetation is the most representative feature of precipitation and temperature. For example tropical evergreen vegetation represents high precipitation and high temperature. Similarly, alpine vegetation represents high precipitation and low to very low temperature. It is commonly found both in higher latitudes as well as in higher altitudes close to snowline. Deciduous vegetation represents high temperature and moderate precipitation in one season followed by a dry season with moderate to low temperature and hence koppen used temperature and precipitation as an indicator.
Delineation of climatic regions, For the delineation of climatic regions, Koppen considered the following:
- Mean monthly temperature,
- Mean annual temperature,
- Mean monthly precipitation,
- Mean annual precipitation
He classified climatic regions on by using various alphabets
An expression of first five capital letters that denote vegetation zones is given below. A - Mega - thermal, B - Xerophytes, C - Meso - thermal D - Micro -thermal, E - Heckiso – thermal,
Next five capital alphabets denote distinct regional characteristics. They are as follows: F - Permanently Frozen; M - Marine; S - Semi Arid/steppe; T - Tundra; W - Waste (desert)
Further he used small letters
Characteristics of seasonal precipitation:
(i) Precipitation round the year = f (ii) Hot = h (iii) Cold = k (iv)Monsoon = m (v) Summer dry = s (vi) Winter dry = w
Salient features of Cs type of climate:
C – Type of climates: This type of climate is characterized by Meso - thermal conditions in which average temperature of the coldest month averaging between 0 degree C and 18 degree C and at least one month averaging above 10 degree C.
Csa: This type of climate is found in the interior areas of Mediterranean Sea. Summer season is hot and dry but winter season is normal and wet. Madrid (Spain), Dushanbe (Tajikistan), Perth (Australia) and Beirut (Lebanon) are the representative stations of the climate.
Csb: This type of climate is found in the coastal areas of Mediterranean Sea. It has a short summer season which is dry and hot. The winter season is usually favorable as it receives rainfall. The average temperature of the hottest month is less than 220C. Santiago (Chile), Cape Town (South Africa) and San Francisco (USA) are representative stations of the climate.
Primary Characteristics Of The Mediterranean Climate
The Mediterranean climate is characterized by dry and hot summer and cold and rainy winter. The regions are located in the western parts of the continent between 30 and 45 degrees north and south of the equator. The climate zone is linked to the five large subtropical high-pressure belts of the oceans. These pressure belts include Azore, South Atlantic, Noth Pacific, South Pacific, and Indian Ocean High. The pressure belts are also called anticyclone and rotate clockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and anticlockwise in the Southern Hemisphere. The anticyclones cause the surrounding air to diverge and descend leading to a clear sky. Climatic changes are profound in the Mediterranean climatic region with rains alternating with warm sunny days during the winter seasons. Rainfall varies from year to year and does not fall evenly. The rains do not arrive yearly at the same time or within the same interval. Temperatures also vary from year to year with winter temperatures falling to as low as zero and may rise to as high as over 50 degree C in arid areas.
Cs Climatic patterns:
The climate is characterized by strong diurnal character to daily temperature during the warm months as a result of the subtropical high pressure. During winter, the Mediterranean climate zone comes into contact with the westerlies and associated sporadic storm which can extend to the Mediterranean climate zone. Since the high subtropical pressure is not there to deflect the storm away, the climatic zone will experience thunderstorm and heavy rainfall. Thus, the Mediterranean Climate zone experiences all its precipitation during winter, autumn, and spring and may last for about 3 to six months.
The Cs Biome:
The Mediterranean Climate zone is closely associated with the Mediterranean forests, woodland, and scrub biomes. Sclerophyll shrublands known as maquis is a distinctive of the climate zone, especially around the Mediterranean Basin. The aquatic communities of the climate zone are adapted to the yearly cycle of the environmental control by floods and biotic components. The vegetation of the Mediterranean climate zone must adapt to survive the hot summer and the prolonged wet winter. Some of the vegetation includes evergreen trees, deciduous trees, fruit trees, grasses, and herbs.