Instruction:
- There will be 2 questions carrying 10 marks each. Write your answers in 150 words
- Any page left blank in the answer-book must be crossed out clearly.
- Evaluated Copy will be re-uploaded on the same thread after 2 days of uploading the copy.
- Discussion of the question and one to one answer improvement session of evaluated copies will be conducted through Google Meet with concerned faculty. You will be informed via mail or SMS for the discussion.
Question #1. How does a river develop its valley and what are the factors influencing this development
Question #2. Analyse the cause and consequences of interruption in a normal cycle of erosion
(Examiner will pay special attention to the candidate's grasp of his/her material, its relevance to the subject chosen, and to his/ her ability to think constructively and to present his/her ideas concisely, logically and effectively).
STEPS & INSTRUCTIONS for uploading the answers
Step 1 - The Question for the day is provided below these instructions. It will be available at 7:00 AM.
Step 2 - Uploading of Answers : Write the answer in A4 Sheet leaving proper margins for comments and feedback and upload the PDF in MY ACCOUNT section. Click on the option of SUBMIT COPY to upload the PDF.
Step 3 - Deadline for Uploading Answers: The students shall upload their answers by 7:00 PM in the evening same day. The first 50 copies will be evaluated.
Step 4 - Feedback : Mentors will give their feedback for the answers uploaded. For more personalised feedback, join our telegram channel by clicking on the link https://t.me/mains_answer_writing_cse . A one-to-one session will be conducted with the faculty after copy evaluation in 72 Hrs.
Model Answer
Question #1. How does a river develop its valley and what are the factors influencing this development.
Hints:
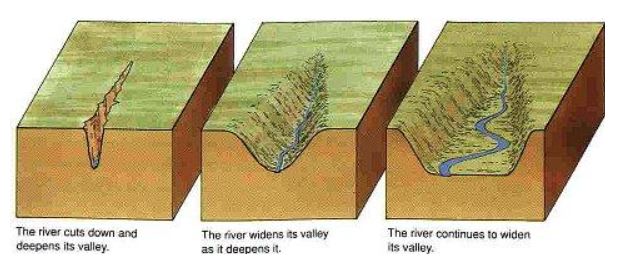
“A river valley is an elongated depression formed by a river, sloping towards the sea or an inland drainage basin”. The shaping of valleys and their utmost continuous modifications through time produce a changing balance between valleys and interfluves and consequently ongoing dynamism in the configuration of most parts of the continental surfaces.
Development of river valley occurs through the following process:
- Valley Deepening: It is the result of vertical erosion as well as weathering phenomena. In the upper reaches valley deepening rate is greater than valley widening.
- Valley Widening: The valley widening occurs due to various processes like
-
- Lateral erosion – It results in the undercutting of valley wall slopes.
- Weathering and mass wasting – It results in the breaking down of the valley slopes and their movement along the valley slopes.
- Overland flow – It results in the flow of weathered materials in the form of sheet-wash and rain-wash.
- Rill erosion – It helps in the widening of the gullies and ravines on between the valley.
- Valley Lengthening: The valley lengthening results in the erosion of the valley in three ways.
-
- Headward erosion: It is prominent in the upper course of the river and occurs due to the presence of step gradient, weathering of rocks and presence of weak structures of rocks and sometimes differential layers of rock structures. Here it also occurs due to river capturing which is very common in the upper course of a river.
- Meanders: The meanders are generally formed in the middle and lower course of the river but also form in the upper river course responsible for the valley lengthening.
- Delta: The deltas are formed at the mouth of the river and its extension towards the mean sea level also results in the valley lengthening.
The types of valleys formed are:
- Gulley: It is the smallest form of valley which is small and narrow but relatively deep incised. It involves a steep cut in harder or weaker rocks with steep sides and steep headwall.
- Ravines: The larger valleys cut into bedrocks or even in unconsolidated sediments such as glacial deposits. They are generally seen in the degradation of land.
- V-shaped valley: It is generally formed in an upper course of the river due to vertical erosion or incision which is greater than lateral cutting.
Factors affecting the river valley formation can be seen as:
- Lithology: The rocks can be harder like igneous rocks or softer like sedimentary rocks which have different rate of erosion, which affect the process of valley formation by enhancing or slowing the rate of valley erosion.
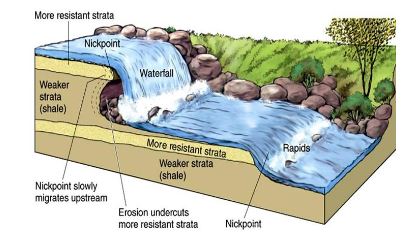
- Changes in river gradient: Abrupt changes in river and valley bottom gradients like knickpoints, waterfalls, etc. influences the course and rate of river valley formation.
- Climate: The climate plays an important role in the formation of valleys like semi-arid and arid region lacking vegetation results in the formation of canyons.
- River Capture: River capture is basically the seizure of a river by neighboring river or a predator stream. The phenomena usually occur due to the change in base levels increasing or decreasing the rate of rate of erosion and valley forming process.
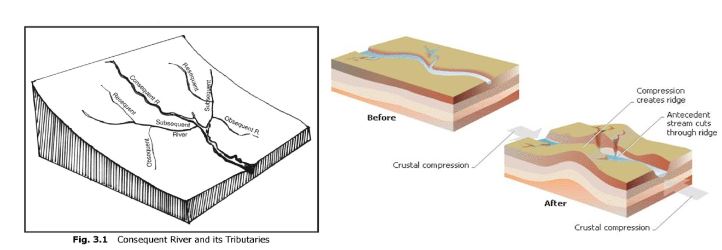
- Type of river stream: The river stream can be sequent or insequent which determines the formation of river valley of a region.
- Sequent rivers: Sequent rivers generally adjust itself according to the underlying rock present in the river course. The types of sequent rivers are consequent, subsequent, obsequent and resequent stream.
- Insequent rivers: The rivers which do not adjust its flow according to the underlying rocks or regional structure are called as insequent streams. The two type of insequent strams are antecedent rivers and super-imposed river.
The rivers plays an important role in the formation of valleys through vertical and horizontal incision and which also determines the human settlement, infrastructure projects, industries, etc. and the socio-economic development of the region.
Question #2. Analyse the cause and consequences of interruption in a normal cycle of erosion.
Hints:
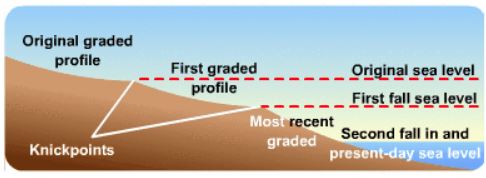
Usually the cycle of erosion based on Davisian concept is not able to run its full course and remains incomplete on account of various kinds of interruptions that it may have face in the course of its progress. Such interruption cause several incomplete cycle to run one after the other in the same region. Such cycles are called polycyclic or multicyclic and landscapes as multi-cyclic or poly-cyclic landscape. These multicyclic landscape are more common than monocyclic.
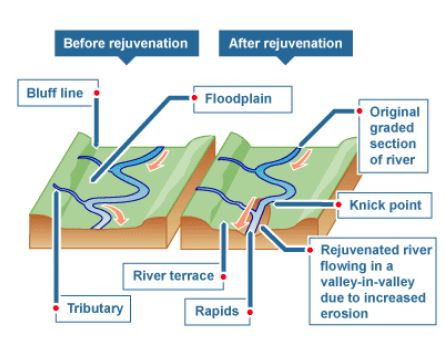
Main cause of interruption in the orderly sequence of the erosion cycle is rejuvenation. As a result of uplift and rejuvenation the rivers which have reached their base level of erosion , again become capable of deepening their valleys.
Causes and consequences of interruption in normal cycle of erosion
- Tectonic factor: Tectonic activity are one of the reason for the subsidence or upliftment of land causing changes in sea level and river course, resulting in the interruption in cycle of erosion.
a.Interruptions due to base level changes: The changes in the base level i.e. sea level occurs due to the tectonic activities results in the change in cycle of erosion.
- Positive change: Positive change of base level (or rise in base level) shortens the cyclic time and it also results in the accelerated deposition or alluviation process.
- Negative Changes: Negative change in base level (or fall in sea level) increases the cyclic time and also results in the accelerated erosion or rejuvenation process.
The rejuvenation or upliftment of land becomes one of the major interruption in the cycle of erosion in the fluvial cycle of erosion causing increase in rate of erosion, which was previously dominated by the deposition of sediments. It will also result in the formation of new knick points and waterfalls due to the upliftment of land. E.g. Chotanagpur plateau.
- Volcanic activity: A wide scale flow of volcanic lavas results in the rejuvenation of land due to immense pouring of volcanic lavas from fissures results in the obliteration of all existing streams. Later various new set of streams will appear after the surface is cooled and solidified resulting in the start of new cycle of erosion.
- Climatic factor: Climatic interruptions occur due to major changes in the climate of the concerned region of the world, for example, if the fluvial cycle of erosion in a humid region is passing through mature stage, and there is sudden climatic change leading to onset of either extreme dry conditions or extreme cold conditions, then the cycle of erosion is interrupted to such an extent that the current erosion cycle is abruptly stopped and another set of cycle either arid cycle or glacial or periglacial cycle sets in.
The interruption in the cycle of erosion occurring due to various factors help in understanding the multi-cyclic process through which the landform has been developed and thus, helps in the planning and development of the region accordingly.
Geomorphic cycles are based on the dictum of Hutton “the present is the key to the past”, later on modified as uniformitarianism. Based on the concepts of Hutton and Darwin, WM Davis presented the cycle of development which was concerned with the evolution of landforms in humid temperate areas but later on the cyclic concept is applied to all Geomorphic process which includes arid, glacial, karst and periglacial. As per the syllabus, we are expected to study Davis, Penck and LC King. This concept is equally applied to other topics of the syllabus like Erosion surfaces, and slope development.