Instruction:
- There will be 2 questions carrying the First Question is-10 marks Write your answers in 150 words and the Second Question is-15 marks Write your answers in 250 words.
- Any page left blank in the answer-book must be crossed out clearly.
- Evaluated Copy will be re-uploaded on the same thread after 2 days of uploading the copy.
- Discussion of the question and one to one answer improvement session of evaluated copies will be conducted through Google Meet with concerned faculty. You will be informed via mail or SMS for the discussion.
Question #1. Systems theory is an ambitious attempt to construct a theoretical framework from within political science but it is conservative and status quoist. Comment. 10 marks (150 words)
Question #2. Hegemonic stability theory is losing its relevance. Substantiate your views with examples from global politics of the 21st century. 15 marks (250 words)
(Examiner will pay special attention to the candidate's grasp of his/her material, its relevance to the subject chosen, and to his/ her ability to think constructively and to present his/her ideas concisely, logically and effectively).
STEPS & INSTRUCTIONS for uploading the answers
Step 1 - The Question for the day is provided below these instructions. It will be available at 7:00 AM.
Step 2 - Uploading of Answers : Write the answer in A4 Sheet leaving proper margins for comments and feedback and upload the PDF in MY ACCOUNT section. Click on the option of SUBMIT COPY to upload the PDF.
Step 3 - Deadline for Uploading Answers: The students shall upload their answers by 7:00 PM in the evening same day. The first 50 copies will be evaluated.
Step 4 - Feedback : Mentors will give their feedback for the answers uploaded. For more personalised feedback, join our telegram channel by clicking on the link https://t.me/mains_answer_writing_cse . A one-to-one session will be conducted with the faculty after copy evaluation in 72 Hrs.
Model Answer
Question #1. Systems theory is an ambitious attempt to construct a theoretical framework from within political science but it is conservative and status quoist. Comment. 10 marks (150 words)
Approach:
- Introduction: Proposed to address the limitations of the traditional approach; Easton main proponent.
- Body: The features of the approach, strengths and limitations.
- Conclusion: Limited in scope but has induced new elements to the field of comparative politics.
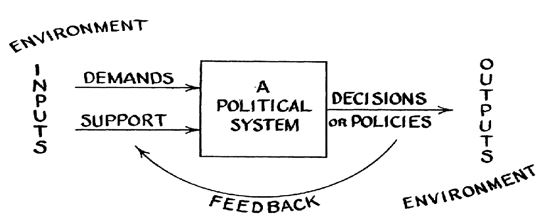
The introduction of the systems analysis in comparative politics by Easton, Almond, Kaplan was a reaction against the traditional tendency of uni-dimensionalisation which impedes the patterns of scientific analysis which make possible the unification of all knowledge. It is influenced by natural and social sciences.
The systems approach is one of the modern approaches that helps to understand political activity and political behaviour more clearly than before. It looks out the social phenomenon as a set of interactive relationships. According to Prof SN Ray the application of the systems' approach to politics, out, allows one to see the subject in such a way that 'each part of the political canvas does not stand alone but is related to each other part and the operation of one part cannot be fully understood without reference to the way in which the whole itself operates.
The features of Systems Approach:
- A social phenomenon is not what exists in isolation; it is not just numerous parts joined together to make a whole. It is a unit, a living unit with an existence and goal of its own.
- Its parts may not be and in fact, are not organically related together, but they do make a whole in the sense that they interact and are inter-related. Specific behavioural relationships pattern them into a living system.
- It operates through a mechanism of inputs and outputs and under within an environment which influences it and which, in turn, provides feedback to the environment.
- Its main concern is as to how best it can maintain itself and face the challenges of decay and decline.
- It implies patterned relationships among its numerous parts, explaining their relative behaviour and role they are expected to perform.
Limitations of Systems Approach:
- All the systems theorists have committed themselves to building and maintaining the system.
- Their concern has been only to explain the system as it exists.
- What they have, additionally, done is to state the causes which endanger its existence and factors which can strengthen it.
- They are, at best, the status-quoits who have little knowledge about past and perhaps no concern for the future.
- All the concepts that systems theorists have developed do not go beyond the explanation and understanding of the present. The entire approach is rooted in conservation and reaction.
- What the systems analysists have done is that they have condemned the traditionalists for having made the political analysis descriptive, static and noncomparative. What they have, instead, done is that they have Introductionduced the numerous concepts in both natural and other social sciences in Political Science or Comparative Politics so as to make the discipline more inter-disciplinary. The claim that the systems theorists have evolved a scientific and empirical discipline is too tall.
Strengths of Systems theory:
The system theory gives us an excellent opportunity for fusing microanalytical studies with macro-analytical ones. The concepts developed by this theory open up new questions and create new dimensions for investigation into the political processes. It often facilitates the communication of insights and ways of looking at things from other disciplines. It may be regarded as one of the most ambitious attempts to construct a theoretical framework from within political Sciences."
Conclusion:
The systems approach, though claims to provide a dynamic analysis of the system, remains confined to its maintenance. It claims to have undertaken an ' empirical research, but has failed to provide enough conceptual tools for investigation. It has not been able to project system, particularly political system more than the state. The approach is, more or less, conservative in so far as it is status-quoist. Yet the systems approach is unique in many respects. It has provided a wider scope in understanding and analysing social behaviour and social interactions. It has drawn a lot from natural sciences and has very successfully used their concepts in social sciences. It has been able to provide a degree of methodological sophistication to comparative politics.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Supplementary information:
Derivatives of Systems Analysis:
Political system or the input-output approach by David Easton
- The political system is seen as a conversion process performing work, producing output and altering its environment, with a continuous exchange between a political system and its environment based on the steady operation of the dynamic processes.
- At the same time, this approach provides numerous concepts for dealing both with political dynamics in the form of systematic adaptation processes and even with purposive redirection in the form of goal changing feedback.
Easton's political system approach has been severely attacked. Eugene Meehan says that Easton does less to explain the theory and more to create the conceptual framework. His analysis, it may be pointed out, is confined to the question of locating and distributing power in the political system. Nevertheless, this approach has provided an excellent technique for comparative analysis. It has also provided a set of concepts and categories which have made comparative analysis more interesting and instructive
The structural functional analysis is another derivative of the systems approach adopted in comparative politics by Gabriel Almond. It is basically concerned with the phenomenon of system maintenance and regulation. The basic theoretical proposition of this approach is that all systems exist to perform functions through their structures. The central question of this approach is: 'What structures fulfil what basic functions and under what conditions in any given society"? All political systems have a structure, i.e., legitimate patterns of human interactions by which order is maintained; all political structures perform their respective functions, with different degrees in different political systems;
While Easton lays emphasis on interaction and interrelationship aspects of the parts of the political system, Almond is more concerned with the political structures and the functions performed by them. And this is perhaps the first weakness of the structural-functional analysis which talks about the functions of the structures and ignores the interactions which are characteristics of the numerous structures as parts of the political system. Almond's model suffers from being an analysis at the micro-level, for it explains the western political system, or to be more specific, the American political system. There is undue importance on the input aspect, and much less on the output aspect in his explanation of the political system, giving, in the process, the feedback mechanism only a passing reference. Like Easton, almond too has emerged as status-quoist, for he too emphasised on the maintenance of the system.
Cybernetics or communication approach is another derivative of the system analysis by Karl Deutsch (The Nerves of Government, 1966) Its focus is "the systematic study of communication and control in organisations of all kinds. The viewpoint of Cybernetics suggests that all organisations are alike in certain fundamental characteristics and that every organisation is held together by communication." Drawing largely from the science of neuro-physiology, psychology and electrical engineering, Deutsch is able to perceive similarities in processes and functioning requirements, between living things, electronic machines and social organisations. "The brain, the computer, the society, .... all have characteristics which make them organisations: they have the capacity to transmit and react to information"
Question #2. Hegemonic stability theory is losing its relevance. Substantiate your views with examples from global politics of the 21st century. 15 marks (250 words)
Approach:
- Introduction: HST: Stability through a hegemon will result in prosperity. Kindleberger’s views.
- Body: The components of the theory and its current day application.
- Conclusion: Criticism of Keohane; multipolarity and its importance.
Hegemonic stability theory is the theory, accepted by realists and many neoliberals, that a dominant military and economic power is necessary to ensure the stability and prosperity in a liberal world economy. Charles Kindleberger is the theory's most influential proponent. In the 1973 book The World in Depression: 1929-1939, he argued that the economic chaos between World War I and World War II that led to the Great Depression was partly attributable to the lack of a world leader with a dominant economy.
The theory has two main components.
- First, it recognizes that a liberal world economy is in constant danger of being subverted by rising nationalism and the spread of protectionism. This was clearly demonstrated by the so-called ‘beggar-thy-neighbour’ policies that helped to create the Great Depression of the 1930s.
- A set of ground rules for economic competition are therefore needed, particularly focused on upholding free trade, in order for such an economy to be successful.
- Second, a dominant or hegemonic power is likely to be both willing and able to establish and enforce such rules. Its willingness derives from the fact that, being a hegemon, its interests coincide significantly with those of the system itself. It has a crucial stake in the system: in ensuring the stability of the world economy, the hegemon is attending to its own long-term interests.
- By contrast, smaller, less powerful states are forced to act more narrowly in line with national self-interest.
- To be a hegemon, a state must therefore (1) have sufficient power to enforce the rules of the system, (2) possess the will to use this power, and (3) be committed to a system that brings benefit to the mass of states.
Criticism of this theory:
- Keohane's 1984 book After Hegemonyused insights from the new institutional economics to argue that the international system could remain stable in the absence of a hegemon, thus rebutting hegemonic stability theory.
- John Ruggie's work on embedded liberalismalso challenged hegemonic stability theory. He argued that the post-WWII international order was not just held together by material power but through "legitimate social purpose" whereby governments created support for the international order through social policies that alleviated the adverse effects of globalization.
- Robert Gilpin's contends that the system naturally goes toward equilibrium with or without a hegemon. And a hegemon will create the system of the world with their own set of preferences, not necessarily in the interest of others.
Examples from 21st century:
- The decline in hegemony of US is marked with rise of China both economically and militarily. China not only seeks to influence its neighbourhood but also in Africa, Latin America and beyond.
- The rise of EU, ASEAN, India as dominant players in the global politics has not created any instability but has made the world multipolar and less influenced by one or two major powers.
- The GCC and African Union too wield influence in their region and have led to stability in the region.
Conclusion:
It is argued that the Hegemon (USA) was seen to be causing instability in the regions in pursuit of its own interests. The invasion of Iraq and Afghanistan by US has resulted in disorder and instability in the region. It is said that the push by NATO under the pressure of US led to Russian invasion of Ukraine. The contemporary world politics with its multipolarity will not only make the world more co-operative but also protect the interest of developing and small nations states from the unilateral sanctions of the hegemon.