

19th October 2023 (8 Topics)
Context:
Recently, the Third Belt and Road Forum for International Cooperation that was convened in Beijing, China met for celebrating Belt and Road Initiative’s (BRI) 10th anniversary.
What is China’s Belt and Road Initiative?
- Background- In 2013, Chinese President Xi Jinping, during his visits to Kazakhstan and Indonesia, expressed his vision to build a Silk Road Economic Belt and a 21st Century Maritime Silk Road, to break the “bottleneck” in Asian connectivity.
- Objective:
- The primary goal of the BRI is to boost international connectivity by enhancing infrastructure, trade, and economic cooperation.
- The initiative encompasses a wide range of projects, including railways, ports, highways, and energy infrastructure.
- Investment- The initiative envisioned a Chinese led investment of over 1 trillion dollars in partner countries by 2025.
- Partnership- More than 60 countries have now joined BRI agreements with China, with infrastructure projects under the initiative being planned or under construction in Asia, Africa, Europe, and Latin America.
|
The project was first named the ‘One Belt, One Road’ but renamed as the BRI to convey a more open and inclusive initiative as opposed to a Chinese-dominated one. |
|
Routes of BRI:
|
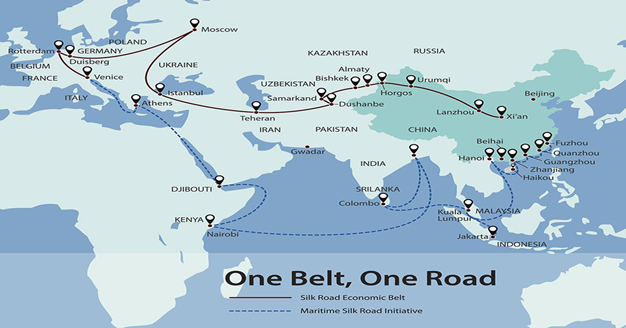
India’s stance on BRI:
- Sovereignty and Transparency Concerns: India opposes the BRI primarily due to concerns related to sovereignty and transparency.
- It believes that projects under the BRI should respect the territorial integrity and sovereignty of nations involved.
- India has boycotted BRI summits held by China and has not endorsed the joint statements issued by the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO) related to the BRI.
- Objection to China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC): India's main point of contention with the BRI lies in the inclusion of the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC).
- The CPEC passes through the Pakistan-occupied Kashmir (PoK), a territory that India asserts as its own. India views this as a violation of its territorial integrity, leading to a firm opposition to the BRI.
- Advocating for International Norms, Rule of Law, and Financial Sustainability: India asserts that BRI projects should adhere to international norms, uphold the rule of law, and ensure financial sustainability.
- It emphasizes the need to avoid creating debt traps and mitigate environmental and social risks for the host countries.
- India advocates for alternative connectivity initiatives, such as the Partnership for Global Infrastructure and Investment (PGII), a G7 initiative aimed at funding infrastructure projects in developing nations, which align more closely with these principles.
More Articles


