21st February 2024 (11 Topics)
Context
Four of the 20 relics of Lord Buddha preserved at the National Museum are being taken to Thailand for a month-long exposition.
About
About (Kapilvastu Relics)
- The relics at the National Museum are known as the ‘Kapilvastu Relics’ as they were recovered in 1898 from a site in Bihar believed to be the ancient city of Kapilvastu.
- It was an inscribed casket found at the stupa site in Piprahwa (near Siddharthnagar in Uttar Pradesh) that helped identify Kapilavastu.
- The casket contained the relics of Buddha and Sakya, his community.
- The relics fall under the ‘AA’ (rare) category of antiquities and art treasures.
Can they be lent for exhibitions?
- They are not meant to be lent for exhibitions, within India or in foreign nations.
- But the exposition in Thailand was being held upon a “special request” by the Thai Government
What are Buddha relics?
- Simply put, they are the Buddha's cremated remains.
- As per the Buddhist belief, at the age of 80 (486-483 BC), lord Buddha obtained salvation in Kushinagar (Uttar Pradesh).
- Lord Buddha was cremated as a universal king by the Mallas of Kushinagar.
- His funeral relicswere collected and divided into eight shares to be distributed among them
- Ajathsatrus of Magadha
- Vaishali's Licchavis
- the Sakyas of Kapilavastu
- Housing in Kushinagar
- Alakappa Bullies
- Mallas of Pava
- the Colossians of Ramagrama once
- Brahmana of Vethadipa
- The purpose was to place stupas on sacred relics.
- Other stupas appeared, one on top of the pipe where the remains were collected and the other on the coals.
- The remains were later excavated by Ashoka - ruler of the Maurya Dynasty, who ruled almost the entire Indian subcontinent from c. 268 to 232 B.C.
- He dispersed the remains and built stupas over them throughout his district.
- According to Ashokavadana, Ashoka had relics of Buddha placed on 84,000 stupas made up of Yakshas (usually gentle natural spirits).
Buddhism in India:
- Siddhartha Gautam, born in 563 BC, was part of the Sakya royal family that ruled from Kapilvastu, Lumbini. At the age of 29, Gautama left home and led a life of self-denial.
- After 49 days of meditation, Gautama received enlightenment under a pipal tree at Bodhgaya in Bihar.
- Buddha made his first sermon in the village of Sarnath, near the town of Benares in the UP. The event is known as the Dharma-Chakra-Pravartana (legal wheel revolution).
- He died at the age of 80 in Kushinagara, a city in the UP. The event is known as Mahaparinibban.
The rules of Buddhism:
- Middle Path:Avoid both extremes of worldly pleasure and the practice of extreme self-The Buddha instead called the 'Madhyam Marg' or the intermediate method to be followed.
- Four good truths:Suffering (dukkha) is the backbone of the world, All suffering has a reason - Samudya, Suffering can end - Nirodha, Can be gained by following AtthangaMagga
- Eight-Way Ways:Positive Views, Proper Objective, Proper Speech, Proper Action, Proper Health, Positive Thinking, Positive Effort, Positive Concentration
- Five Principles or Pancasil- Violence, theft, sexual misconduct, lying or gossip, drunkenness
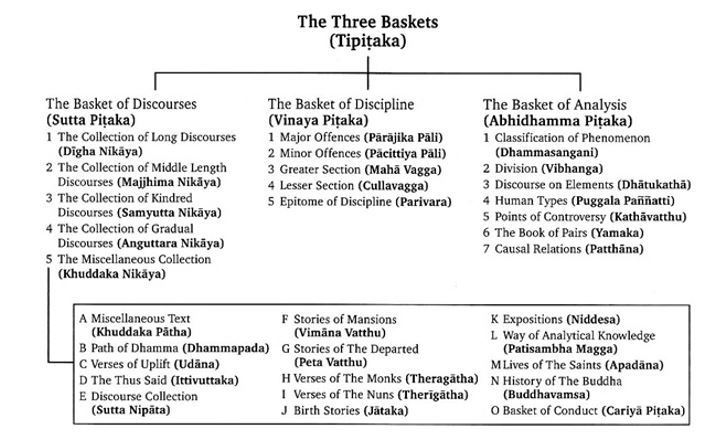
Major Buddhist texts:
- Three pitakas: VinayaPitaka (moral code), SuttaPitaka (Dhamma Buddha): Divided into five Nicayas: Digha, Majjhima, Samyutta, Anguttara, AnguttaraKhuddaka, AbhidammaPitaka (philosophical analysis)
- Other important Buddhist texts include Divyavadana, Dipavamsa, Mahavamsa, Milind Panha etc.
Buddhist Schools:
- Mahayana:literally means "Great Car". It believes in the heaven of the Buddha and the idolatrous worship of the Buddha and the Bodhisattvas including the Buddha Nature.
- Hinayana:A small car literally. It believes in the original teachings of the Buddha or the Doctrine of the Elders. He does not believe in idolatry and seeks to gain personal salvation through self-discipline and meditation.
- Theravada:is a Hinayana sect, founded in Sri Lanka and later spread throughout Southeast Asia.
- Vajrayana:means "Car of Thunder", also known as tantric Buddhism.
- Zen: It is a school of Mahayana Buddhism founded in China.
More Articles