

21st July 2023 (7 Topics)
Context
The Directorate General of Foreign Trade under the Union Commerce Ministry has announced the ban on export of white rice other than Basmati, which would come into effect immediately and exemptions would be given only if the loading of non-basmati rice on the ship had commenced form ports before the notification.
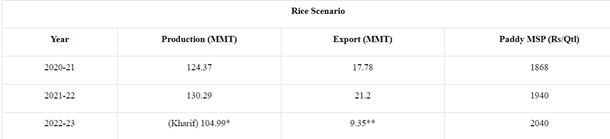
- India is the world's second-largest producer and the largest exporter of rice.
|
The Indian rice varieties cultivated widely are Basmati, Joha, Jyothi, Navara, Ponni, Pusa, Sona Masuri, Jaya, Kalajiri (aromatic), Boli, Palakkad Matta, etc. |
India’s Rice exports:
- Polished Rice and Basmati Rice constitute around 55% of total rice export from India.
- India commands 40% share in the global rice trade.
- Due to the current geo-political situation, the international price of rice was lucrative, leading to high export of rice as compared to previous year.
Need of such a step:
- As the domestic prices of rice are on an increasing trend.
- The retail prices have increased by 5% over a year and 3% over the past month.
- Due to sharp increase in exports ascribed to high international prices due to geo-political scenario, has led to such a move by the government.
- So, after this the farmers will continue to get good remunerative prices and dependent/vulnerable countries will have adequate availability of par-boiled rice as India has significant share in the global rice export.
|
Non-basmati rice was exported under the category ‘Free with export duty of 20%’, which was imposed last year to lower the price and to ensure availability in the domestic market. |
Rice as a Crop:
- Rice (Oryza sativa) has a major role in diet, economy, employment, culture and history, and this staple food (of eastern and southern India) plays a pivotal role in the food and livelihood security of people.
- Rice is a nutritional staple food which provides instant energy as its most important component is carbohydrate (starch).
- On the other hand, it is poor in nitrogenous substances and fat content or lipids.
- It is fundamentally a kharif crop in India and demands a temperature of around 25 degrees Celsius and above, and rainfall of more than 100 cm.
What will be the impacts of the move?
- The export will put up the price of export product and reduce the domestic consumption as well as the consume surplus.
- While on the other hand, export contributes to improving the export country's national revenue because consumption is increasing.
- If the price effect is bigger than the revenue effect of export, then the total domestic demand will reduce, that’s how the export crowds out the domestic demand.
- Also, the crowding-out effect of export on domestic consumer demand depends on the cost of the export transferring to the domestic demand.
- If the switching cost is too high, then the investors would not transfer these produce materials to the domestic consume produce, this also develops the export crowd out the domestic demand.
Why are exports significant for economy?
- Exports facilitate international trade and stimulate domestic economic activity by creating employment, production, and revenues.
- Exporting into foreign markets can often reduce per-unit costs by expanding operations to meet increased demand.


