17th May 2024 (11 Topics)
Mains Issues
Context
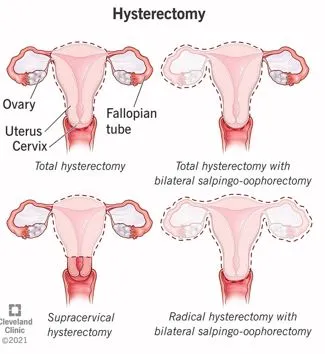
The lack of comprehensive data on women-specific health issues, including hysterectomies, impedes policymaking and awareness efforts in India. A recent study delves into the prevalence and underlying reasons for hysterectomies among women aged 45 and above in India, shedding light on this crucial aspect of women's health.
Key-findings
- The most common reasons for hysterectomies in India include heavy menstrual bleeding, fibroids, and uterine prolapse.
- It reveals regional disparities in hysterectomy prevalence, with southern and western India reporting higher rates.
- Factors associated with a higher likelihood of undergoing hysterectomy: education level, socioeconomic status, and age at marriage.
- Patriarchal norms and misconceptions contribute to the overuse of hysterectomies, with some women undergoing surgery unnecessarily.
- Women from marginalized communities and those with multiple children are particularly vulnerable.
Issues associated with Hysterectomy
- There has been found a correlation between hysterectomy and chronic diseases (cardiovascular events, cancers, depression, metabolic disorders, and dementia).
- Hysterectomies are also associated with hypertension, high cholesterol, diabetes, and bone disease.
- Women who could have been offered alternative treatments are unnecessarily subjected to hysterectomies, posing significant risks to their health. Medical professionals stress the importance of exploring non-surgical treatments and ensuring informed decision-making among patients.
Fact Box: About Hysterectomies:
|


Mains Issues
Context
China's President Xi Jinping and Russia's President Vladimir Putin have pledged a "new era" of partnership, positioning themselves against the United States, which they describe as a disruptive Cold War-era hegemon.
About the Joint Statement
- "No Limits" Partnership: In February 2022, China and Russia declared a "no limits" partnership when Putin visited Beijing, just before the invasion of Ukraine.
- Geopolitical Alignment: Both countries find common ground in their geopolitical struggles—Russia against NATO-supported Ukraine and China facing U.S. efforts to curb its military and economic rise.
- Strategic Deepening: The statement highlighted plans to enhance military ties and defense sector cooperation, claiming it would improve regional and global security.
- Shared Opposition: The statement expressed opposition to the U.S. on security issues and aligned their views on Taiwan, Ukraine, North Korea, and cooperation on peaceful nuclear technologies and finance.
- Criticism of the U.S.: The document specifically criticized the United States.
West versus Xi and Putin
- U.S. Concerns: Putin's visit to China followed U.S. Secretary of State Antony Blinken's trip to China, where he raised concerns about China's support for Russia's military. However, Blinken's visit did not weaken Xi's relationship with Putin.
- Message of Priorities: By choosing China for his first foreign trip since his recent re-election, Putin signals the importance of his ties with Xi and his geopolitical priorities.
Factors Bringing Russia and China Together
While animosity towards the West is a significant factor in the Russia-China relationship, several other important elements also contribute:
- Mutual Benefits in Trade: Russia benefits from continued trade with China, especially in the energy sector. China gains from Russia's shared interest in maintaining security and stability in Central Asia.
- Military Cooperation: China benefits from Russia's military experience and rapid advancements in defense technology.
Critical Concerns for India
For India, the growing Russia-China defense partnership raises several important questions:
- Dependence on Russian Supplies: India relies on Russia for 60-70% of its defense supplies, especially crucial during the ongoing border standoff with China.
- Russia as a "Junior Partner" to China: Western analysts warn that Russia might become subordinate to China. India is concerned about the impact of Western sanctions on Russia's defense industry, which could affect India's military capabilities.
- Russia's Stance in an India-China Conflict: Historically, the Soviet Union was not very supportive of India during the 1962 India-China war but supported India during the 1971 war. The current geopolitical scenario is different, and Putin's Russia may not act like the old Soviet Union.


Mains Issues
Context
The Election Commission of India (ECI) has raised concerns about the lack of explicit powers to deregister political parties for non-compliance with electoral norms. This issue highlights the challenges regarding the registration and recognition of political parties in India and the need for stronger regulatory mechanisms to uphold electoral integrity.
Issues and Concerns
- Many registered but unrecognised parties don't contest elections, raising concerns about potential misuse of privileges.
- The Election Commission of India (ECI) lacks explicit powers to deregister parties for failure to contest, conduct inner-party elections, or submit returns.
- The Supreme Court has limited ECI's power to deregister parties, allowing it only under exceptional circumstances like fraud or violation of constitutional allegiance.
- Parties not contesting elections may misuse tax exemptions and donations for illicit purposes.
MCC Violations
- The Model Code of Conduct (MCC) prohibits using caste and communal sentiments for votes, as well as voter bribery or intimidation.
- Recognised parties have been found guilty of MCC violations, but ECI sanctions are often limited to short campaign bans.
- Recommendations for Action
- ECI has proposed amendments to empower itself to deregister parties, supported by the Law Commission's recommendation.
- The Law Commission suggested deregistration for parties failing to contest elections for ten consecutive years.
- ECI can suspend or withdraw recognition of parties under Paragraph 16A of the Symbols Order for MCC violations, although this power is seldom used.
Fact Box
|


Mains Issues
Context
The recent announcement of new tariffs on Chinese imports (EVs, solar cells, semiconductors and advanced batteries) has raised concerns about escalating tensions between the two countries. The development is concerning for India as escalation of a trade war between the US and China may push Beijing to dump goods in the Indian markets.
What is Dumping?
- Dumping occurs when a company sells its products in a foreign market at a lower price than in its home country.
- This flooding of the foreign market with cheap goods can harm local businesses by undercutting their prices and driving them out of business.
- Dumping can take several forms:
- Predatory Dumping: Selling goods in a foreign market at a consistently lower price to eliminate competition and establish a monopoly.
- Sporadic Dumping: Exporting excess inventory to a foreign market where the products are not selling.
- Persistent Dumping: Selling products at a lower price consistently due to constant demand in the foreign market.
- Reverse Dumping: Charging higher prices for a product in the foreign market when demand is low, while selling it at a lower price domestically.
Impact on International Trade:
- Dumping can distort international trade, and can also lead to trade wars and retaliation, damaging international trade relations.
- Domestically, it can cause harm to the domestic industry of the importing country by undercutting local businesses and potentially leading to their failure.
- Protectionism: Countries often use tariffs and import duties to counter dumping practices, but these measures can also be viewed as protectionist actions aimed at blocking foreign competition. WTO members have the option to lodge formal complaints about dumping and protectionist measures with the organization.
Fact Box:Rules for Dumping
Components of India's protectionism strategy
|


Prelims Articles
Context
Eleven people were killed after being struck by lightning in various places across Malda district in West Bengal. The numbers are concerning as lightning is the biggest killer among “forces of nature”, which also include avalanches, cyclones and landslides. It accounted for 40% of 7,126 such deaths in 2021, according to the latest data from the National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB).
What is Lightning?
- Lightning is a rapid and massive discharge of electricity in the atmosphere, some of which reaches the Earth.
- It forms in large, moisture-laden clouds that are about 10-12 km tall. The cloud base is typically 1-2 km from the Earth's surface, with the top about 12-13 km high, where temperatures range from –35° to –45°C.
- Formation of Lightning:
- Cloud Formation: As water vapor moves up in the cloud, it cools and condenses into water droplets. When the droplets reach temperatures below 0°C, they turn into ice crystals.
- Movement and Collisions: Smaller ice crystals move upward, while larger ones fall downward. Their collisions release electrons, generating a chain reaction of free electrons.
- Charge Separation: This movement causes the top of the cloud to become positively charged and the middle to become negatively charged, creating a massive electrical potential difference of one to ten billion volts.
- Current Flow: A large current, between 100,000 to a million amperes, flows between the cloud layers.
- Forms of Lightning:
- Inter-cloud
- Intra-cloud
- Cloud-to-ground (this form kills humans, as well as animals and livestock, and can substantially damage property)
- The Earth, being a good conductor of electricity but electrically neutral, becomes positively charged compared to the cloud's middle layer.
- Consequently, about 15%-20% of the current is directed towards the Earth, causing damage to life and property.
- Vulnerable states: Madhya Pradesh, Chhatisgarh, Maharashtra, Odisha, West Bengal, Bihar, UP, Karnataka, Jharkhand and Tamil Nadu.
- This is to be noted that lightning is not classified as a natural disaster in India.
PYQsQ.1 During a thunderstorm, the thunder in the skies is produced by the (2013)
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
Solution: (d) |


Prelims Articles
Context
The Supreme Court stressed the importance of constitutional safeguards when the State acquires private property, ensuring fair procedures and protecting property owners' rights under the Indian Constitution.
Key Points:
- Fair Procedure Requirement: Article 300A prohibits the deprivation of property without following a fair procedure established by law. This applies when the State acquires private property for public purposes and compensates the owner.
- Procedural Justice: Procedural fairness is essential, emphasizing that acquisition must adhere to proper procedures even with compensation.
- Fundamental Procedural Rights: Property owners have seven fundamental rights during acquisition. These sub-rights, as traced in the judgment, are:
- The Right To Notice: duty of the State to inform the person that it intends to acquire his property
- The Right To Be Heard: duty of the State to hear objections to the acquisition
- The Right To A Reasoned Decision: duty of the State to inform the person of its decision to acquire
- The Duty To Acquire Only For Public Purpose: duty of the State to demonstrate that the acquisition is for public purpose
- The Right Of Restitution Or Fair Compensation: duty of the State to restitute and rehabilitate
- The Right To An Efficient And Expeditious Process: duty of the State to conduct the process of acquisition efficiently and within prescribed timelines of the proceedings
- The Right Of Conclusion: final conclusion of the proceedings leading to vesting
- State Obligations: The State must acquire property only for public purposes and conduct the process efficiently within set timelines.
Fact Box: About Article 300-A
|
PYQQ. What is the position of the right to property in India? (2021)
Solution: (b) |


Prelims Articles
Context
Amid strained relations with China following the 2020 standoff in eastern Ladakh, the Indian Army has taken significant steps to bolster its defences near the Line of Actual Control (LAC). Recently, two tank repair facilities have been established in Ladakh, marking a crucial development in India's military infrastructure.
Key-highlights
- Located near the Line of Actual Control (LAC), the Indian Army has set up two tank repair facilities in Ladakh (both at altitudes exceeding 14,500 feet),
- one in the Daulat Beg Oldi (DBO) Sector
- the other in Nyoma
- These facilities are vital for maintaining and repairing armoured vehicles deployed in the region.
Need for Repair Facilities:
- Following the 2020 Galwan Valley clash with China, India deployed numerous tanks, BMP combat vehicles, and Quick Reaction Fighting Vehicles in Ladakh.
- However, due to the challenging terrain and harsh weather conditions, transporting these vehicles for maintenance and repair posed significant logistical challenges.
- The establishment of these repair centres addresses the logistical hurdles faced by the Indian Army, enhancing the effectiveness and serviceability of armoured fighting vehicles.
- With over 500 tanks and infantry combat vehicles stationed in eastern Ladakh, having local repair facilities is crucial for maintaining operational readiness.
Fact Box: Strategic Importance of Locations:
|


Editorials
Context
The rise of populism and the mainstreaming of non-serious individuals in positions of power and influence has led to widespread intellectual stagnation and erosion of traditional intellectual authority in society.
Decline of Institutional Leadership
- Erosion of Integrity: Institutions of knowledge have seen a decline in quality leadership due to a lack of integrity and moral courage, compromising their intellectual output.
- Rigid Structures: Hierarchical and bureaucratic processes have made institutions insular and unrepresentative, unable to keep pace with societal changes.
- Loss of Credibility: These issues have led to widespread erosion of trust and credibility in institutions.
Rise of Social Media Influencers
- New Class of Influencers: Social media has enabled individuals without deep knowledge or experience to shape public opinion, prioritizing visibility over substantive engagement.
- Value-Blind Content: The value-neutral approach of social media platforms has empowered these influencers to disseminate content without accountability.
- Evangelism of Stupidity: This has led to a discourse dominated by superficial and sensational content, undermining serious intellectual engagement.
Moral Relativism and Partisanship
- Moral Decline: The erosion of shared values and the rise of moral relativism have created an environment where ends justify the means, leading to opportunistic leadership.
- Partisan Agendas: Leadership selection processes favor deal-makers and status quoists, lowering the intellectual bar and promoting illiberalism and suppression of dissent.
- Instrumental Use of Stupidity: Political and corporate powers harness the spread of stupidity for their own agendas, prioritizing engagement and partisanship over quality discourse.
Mains Question:
Discuss the impact of the decline in institutional leadership and the rise of social media influencers on intellectual stagnation in society. How do moral relativism and partisanship contribute to this phenomenon?


Editorials
Context
While public concern has focused on COVID-19 vaccines and their potential link to blood clots, hypertension, a proven and preventable risk factor for heart attacks and strokes, continues to be a major but often overlooked health issue. The WHO's 2023 report highlights the global and national burden of hypertension.
Hypertension: The Silent Killer
- Global Impact: Hypertension is the leading risk factor for early deaths, responsible for 10.8 million preventable deaths annually. It causes more deaths than tobacco use and high blood sugar.
- Prevalence: The number of adults with hypertension nearly doubled since 1990, reaching 1.3 billion. 311 million Indians have hypertension, three times the number of diabetics in the country. Indian adults consume 8-11 grams of salt daily, twice the WHO recommendation. High salt intake causes an estimated 175,000 deaths annually in India.
- Reducing Salt Intake: Excessive salt intake is a key risk factor for hypertension, contributing to two million cardiovascular deaths in 2019. Reducing salt intake can lower cardiovascular risks by 30% and mortality by 20%.
India Hypertension Control Initiative (IHCI)
- Strategies: The IHCI implements simplified drug protocols, strengthens the drug supply chain, and focuses on team-based, decentralized care.
- Recognition and Expansion: The IHCI received the 2022 UN Interagency Task Force Award and expanded to over 140 districts in 2023. Achieving 50% hypertension control by 2050 could prevent 76 million cardiovascular deaths globally and 4.6 million deaths in India by 2040.
- Recommendations for Hypertension Control: Awareness and public health interventions, address modifiable and non-modifiable risk factors, reduce salt consumption, multi-sectoral action, stronger food regulation.
Mains Question:
Discuss the public health significance of hypertension in India, highlighting the challenges in its management and control. What strategies can be implemented to address this silent killer effectively?


Editorials
Context
The Supreme Court of India's decision to invalidate the arrest and remand of NewsClick founder highlights significant procedural lapses by the Delhi police, particularly the failure to provide written grounds for his arrest, and raises questions about the misuse of the Unlawful Activities (Prevention) Act (UAPA).
Police Misconduct and Due Process Violations
- Clandestine Custody Obtaining: The Supreme Court criticized the Delhi police's surreptitious actions in obtaining Purkayastha's custody before dawn, bypassing standard legal procedures.
- Deprivation of Legal Rights: The Court noted that the police intentionally kept Purkayastha's lawyer uninformed, denying him the chance to oppose the remand and seek bail, and instead used a ‘remand advocate’.
- Circumventing Legal Requirements: The Court condemned the police's blatant attempt to circumvent due process, emphasizing that the accused was not informed of the grounds of his arrest.
Principle Extension to UAPA
- Extension of Pankaj Bansal Principle: The judgment extends the principle from Pankaj Bansal (2023) to the UAPA, mandating that grounds for arrest be given in writing, interpreting constitutional provisions to apply this universally.
- Requirement for Written Grounds: The Court asserted that providing written grounds for arrest should be a standard procedure under UAPA and other offences.
- Adherence to Constitutional Provisions: The Court underscored that adherence to procedure is crucial, particularly for serious allegations under laws like the UAPA.
Outlandish Allegations and Legal Implications
- Allegations Against Purkayastha: The police charge sheet claims Mr. Purkayastha was funded by the Chinese government and involved in a conspiracy to replace Indian democracy with a party-state system like China's.
- Support for Riots and Terrorism: The charge sheet alleges his involvement in fomenting riots and protests in India and funding terrorists, despite the far-fetched nature of these claims.
- Importance of Procedural Adherence: Given the severe allegations, the Court's insistence on procedural adherence, especially the need to provide grounds of arrest, is particularly significant for ensuring fair legal processes.
Mains Question:
Discuss the implications of the Supreme Court of India's recent judgment on procedural adherence in arrests under the UAPA. How does this judgment enhance the protection of individual rights against misuse of anti-terrorism laws?